Table of Integrals
A. Dieckmann, Physikalisches Institut der Uni Bonn
![]()
![]()
This integral table contains hundreds of expressions: indefinite and definite integrals of elliptic integrals, of square roots, arcustangents and a few more exotic functions. Most of them are not found in Gradshteyn-Ryzhik.

Sometimes m, n, k denote real parameters and are restricted mostly to 0 < {m, n, k} < 1, at times they represent natural numbers.
Results may be valid outside of the given region of parameters, but should always be checked numerically!
Definite Integrals:
Substitute ![]() and the Feynman-Hibbs Integral can be calculated with Mathematica:
and the Feynman-Hibbs Integral can be calculated with Mathematica:
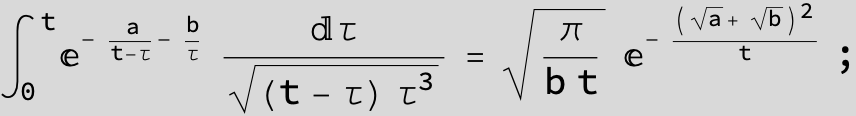

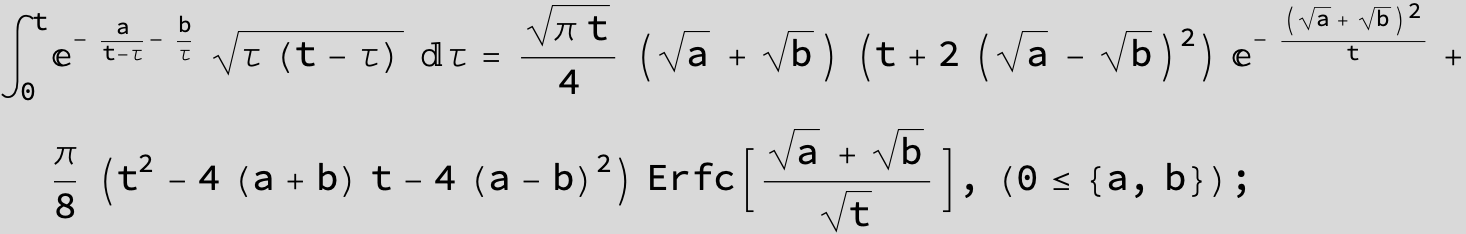
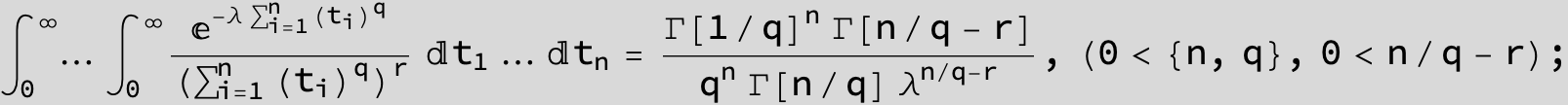
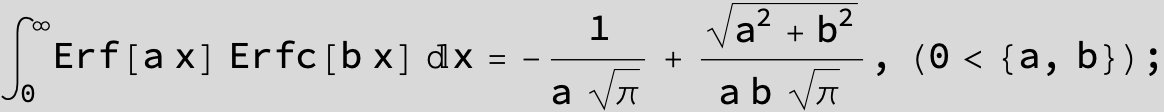
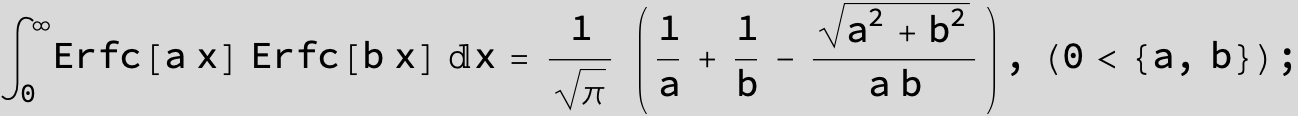
![]()
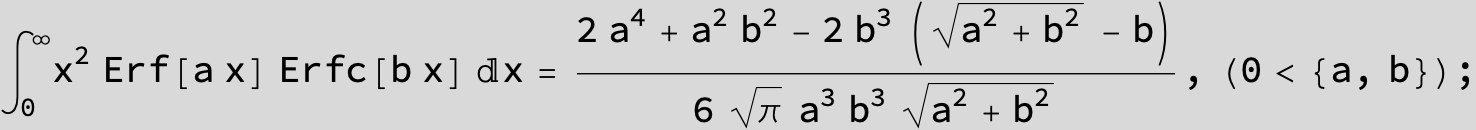
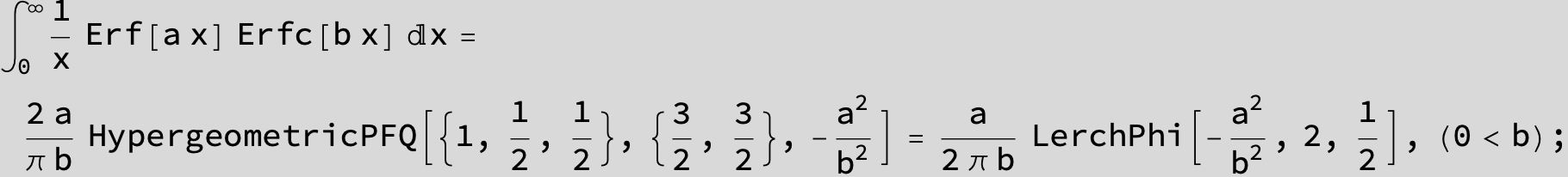

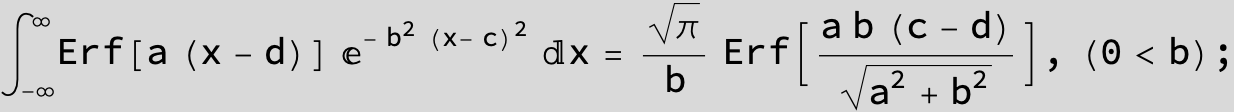
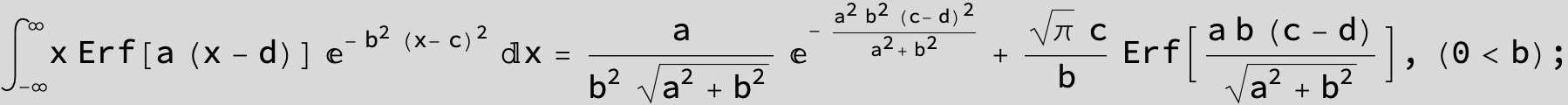
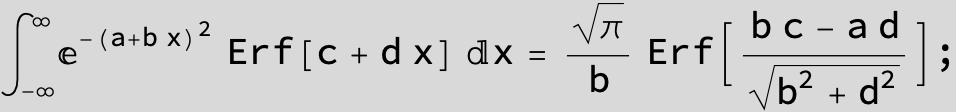
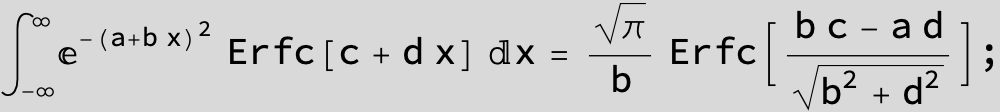

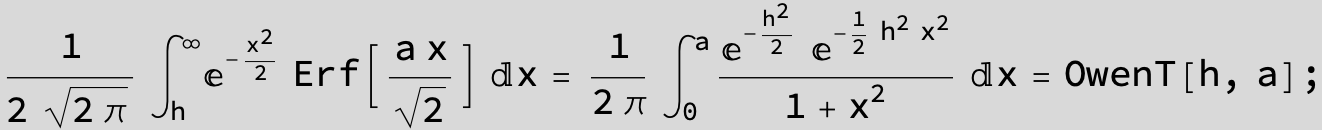
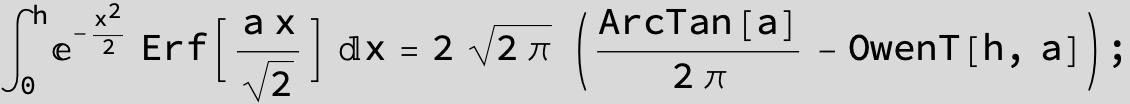

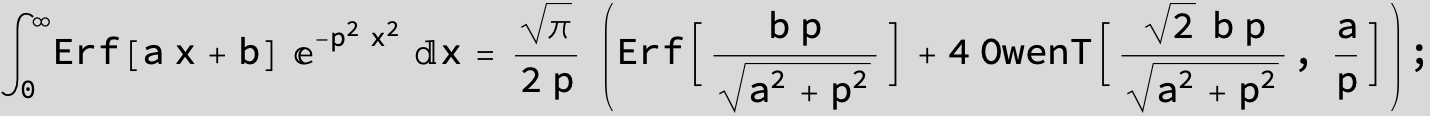
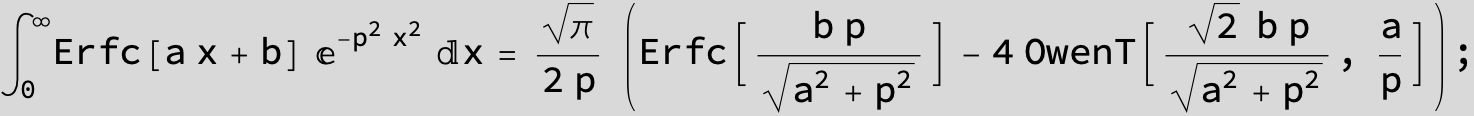
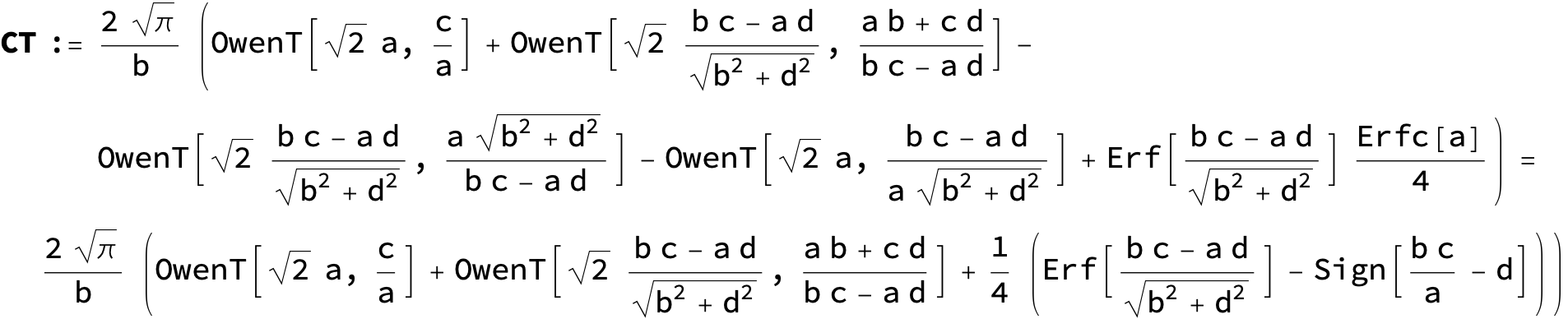
The expression below containing OwenT functions shows up as Common Term

in the next six integrals combining Gauss- and Error functions with general linear arguments and integration range from Zero to Infinity :
![]()
(The integral above got cracked on my daughter' s birthday, so I call it Charlotte' s Integral .)

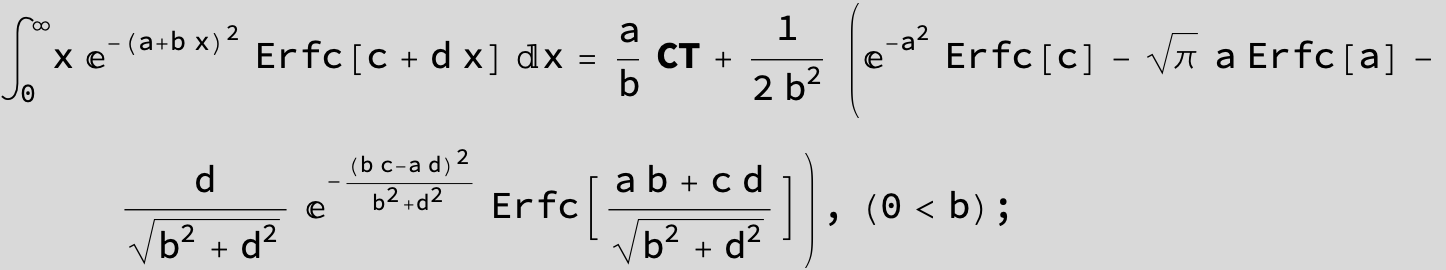
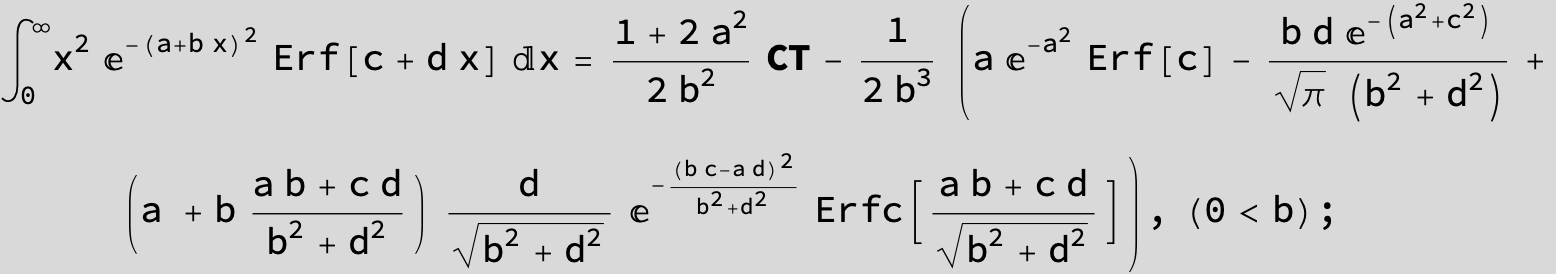
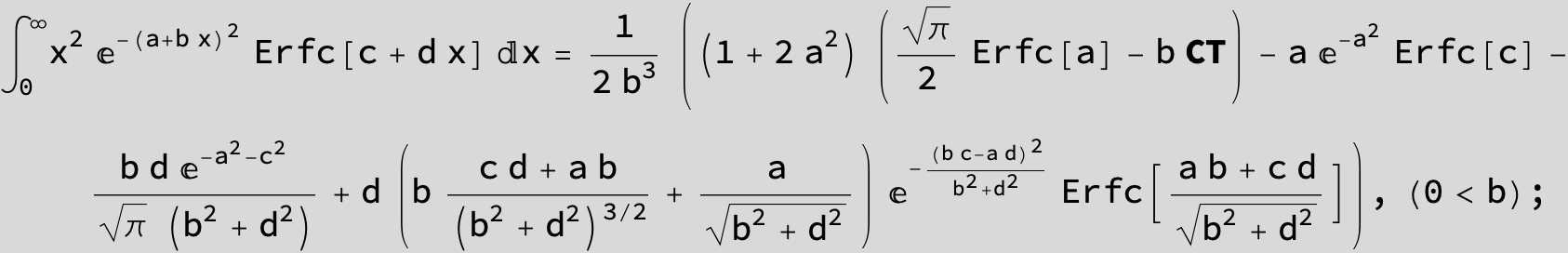
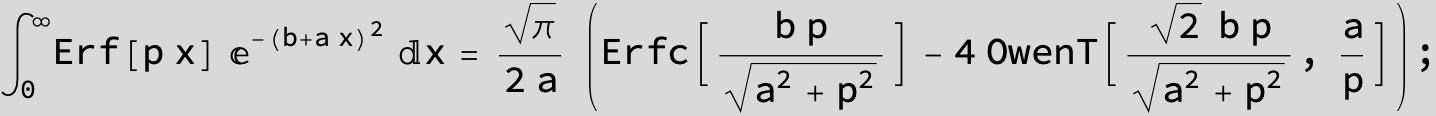
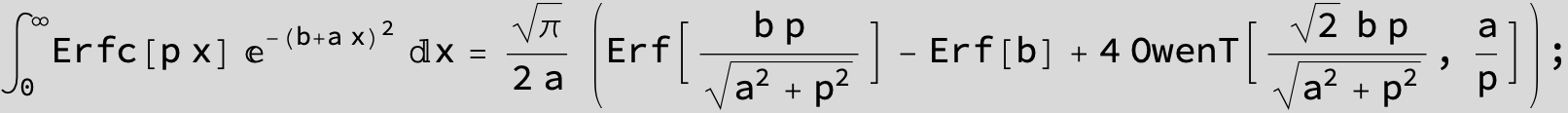
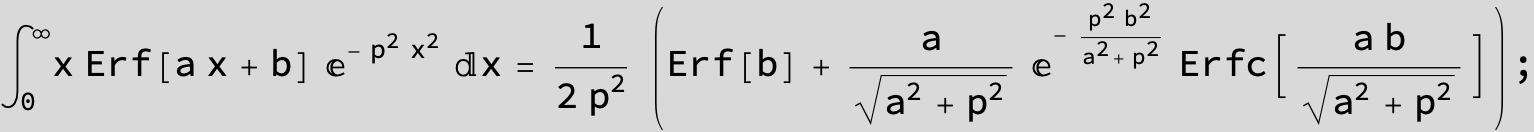
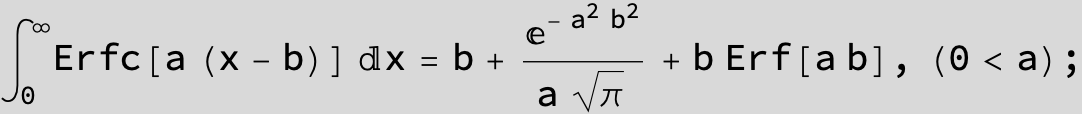
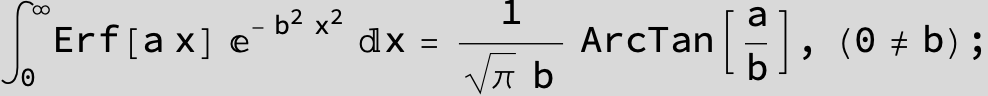
![]()
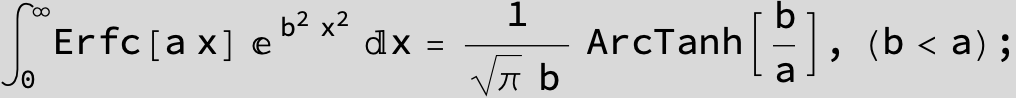
![]()
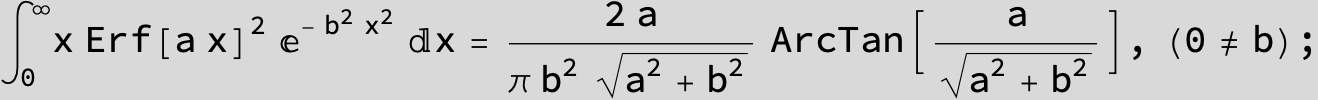

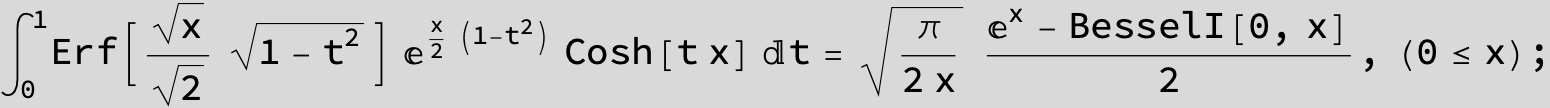


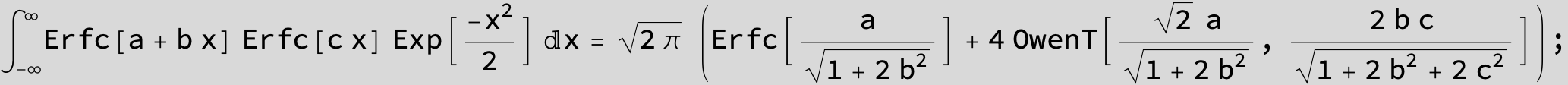
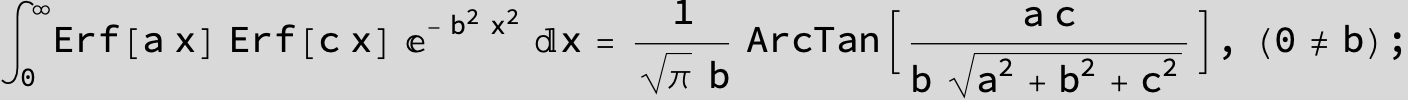

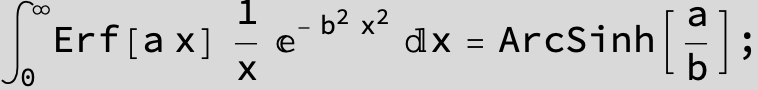
![]()
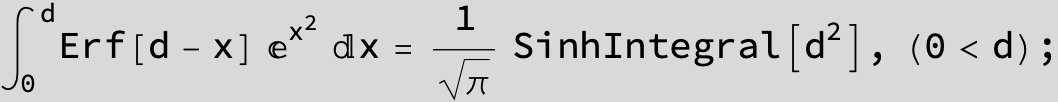
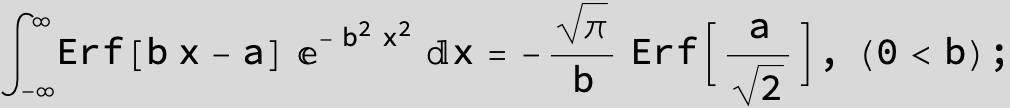



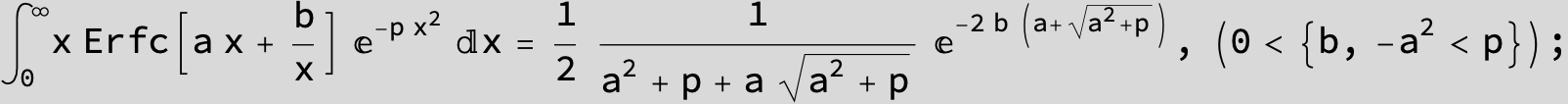
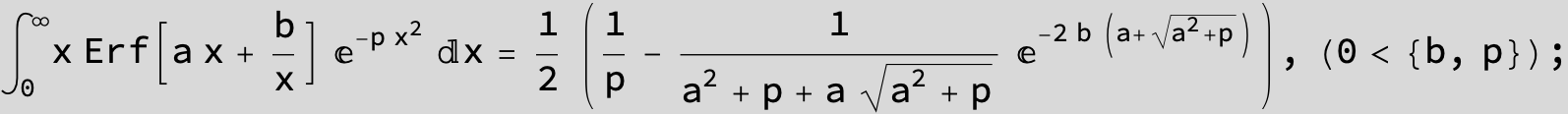
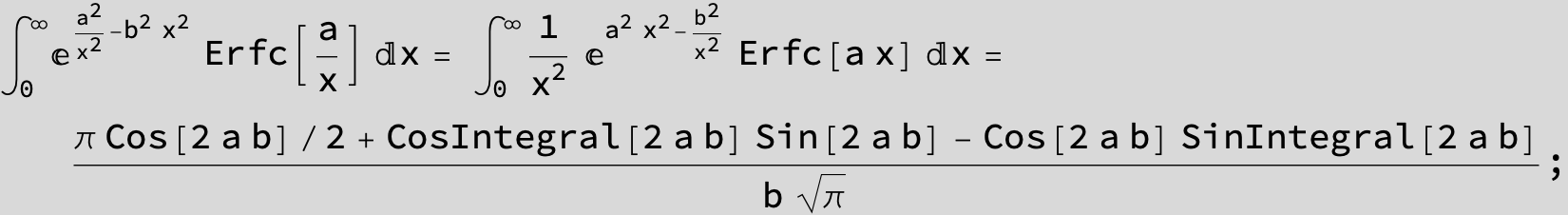

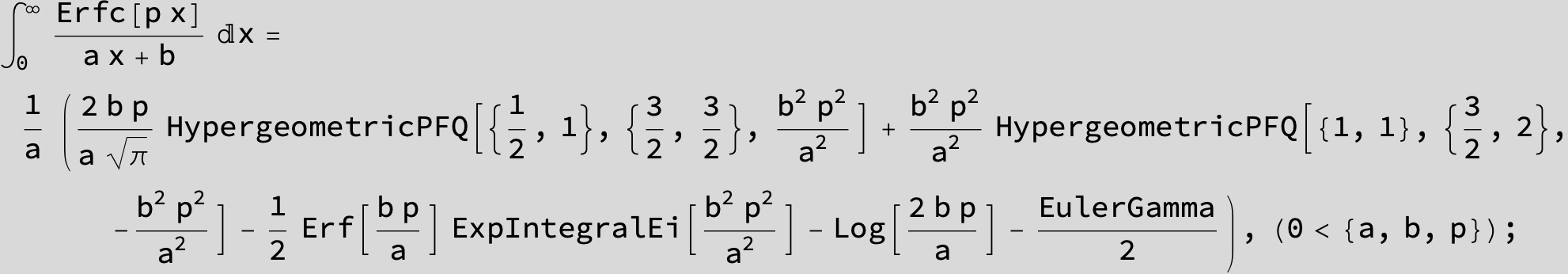
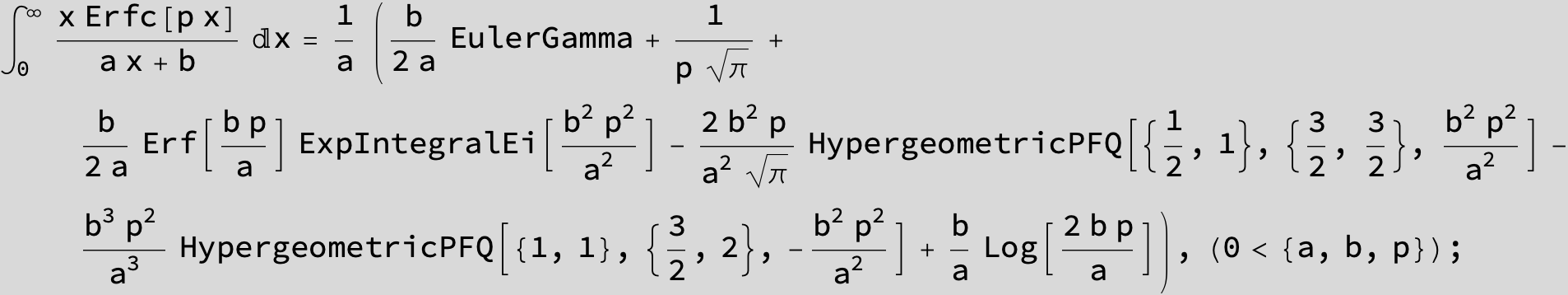

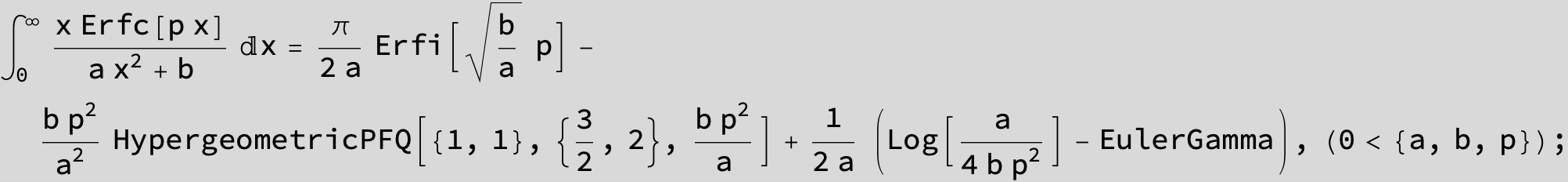


![]()
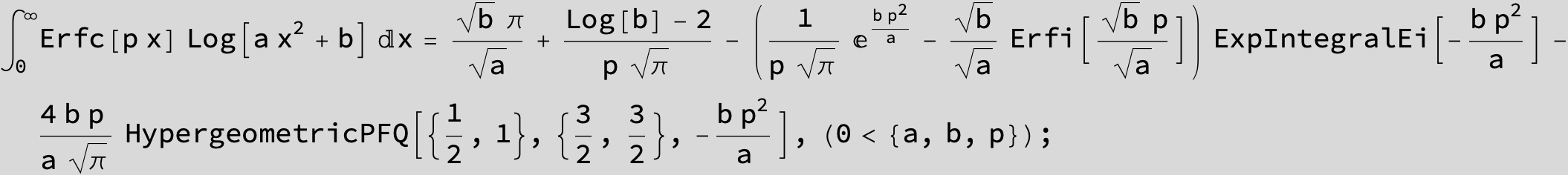

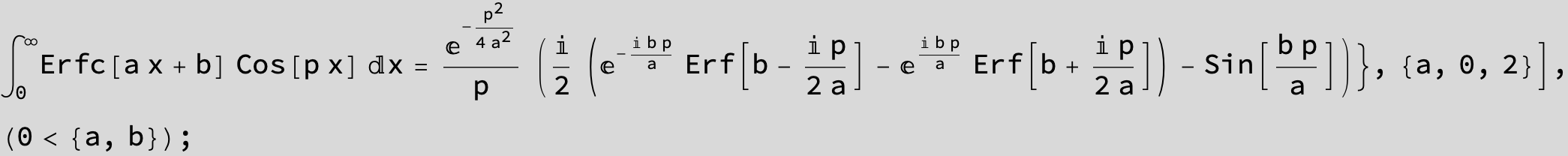
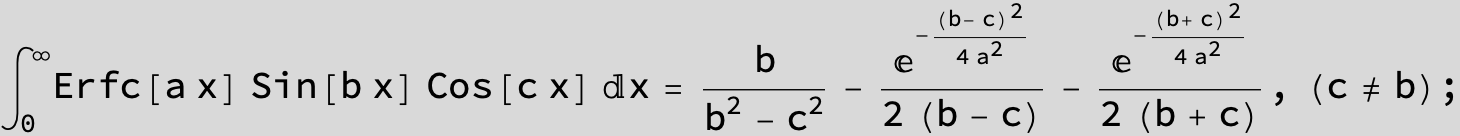
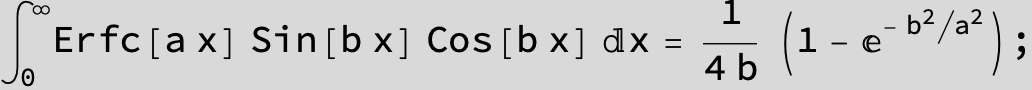
![]()
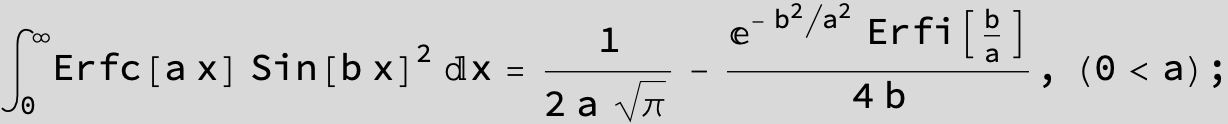
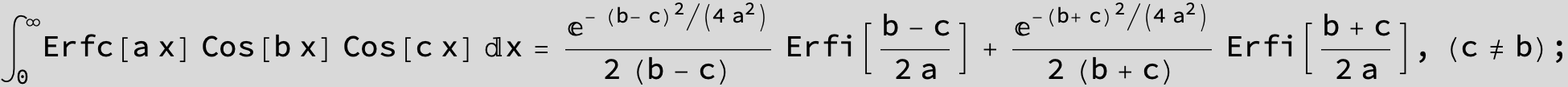
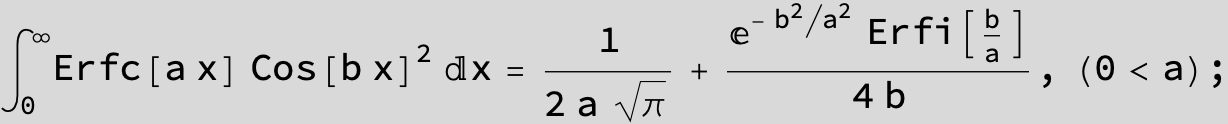
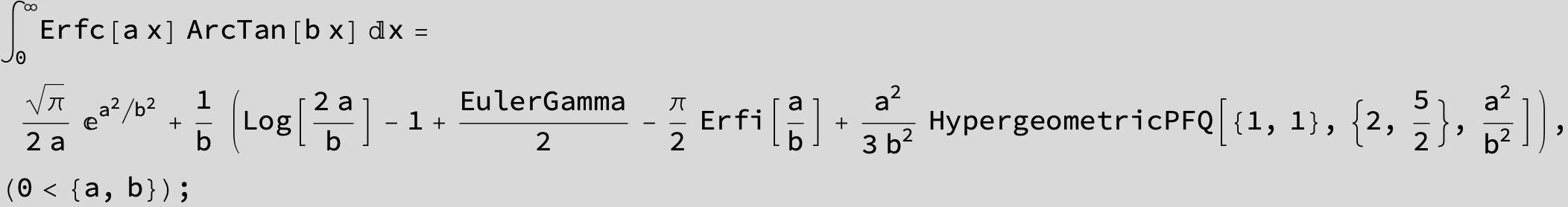
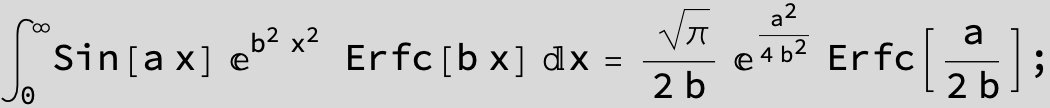
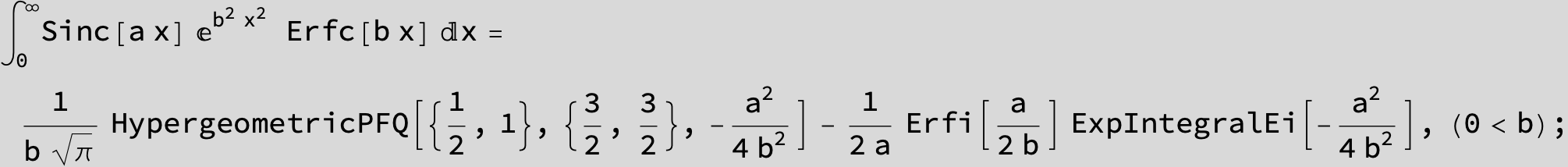
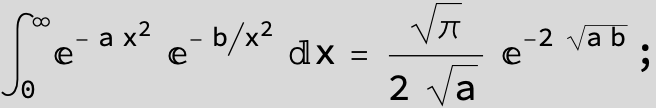
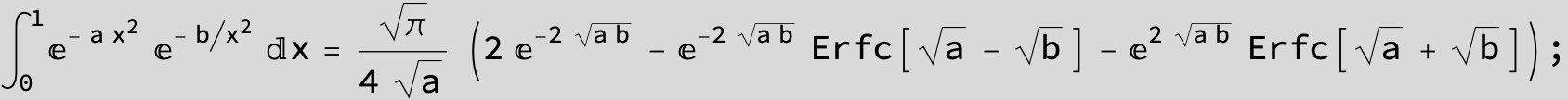
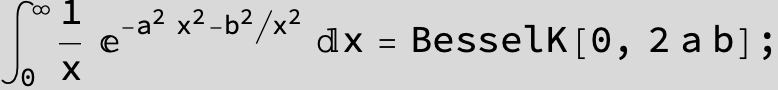
![]()

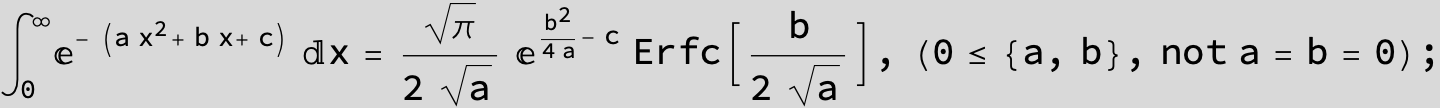
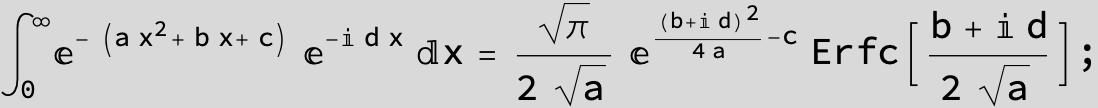
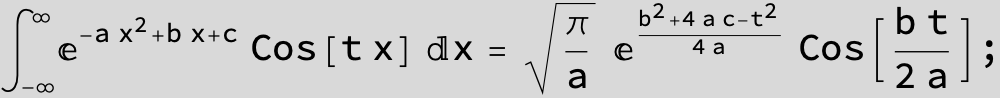
![]()
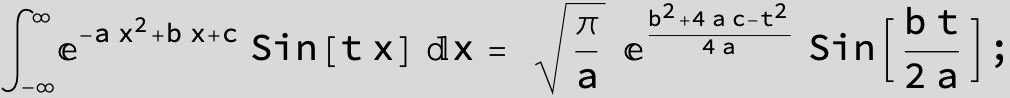
![]()

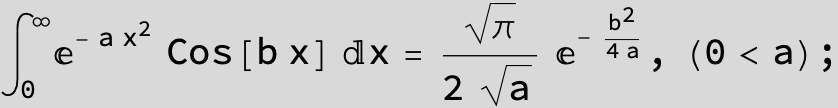
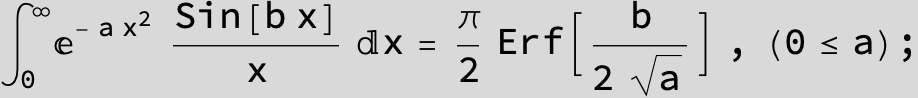
![]()
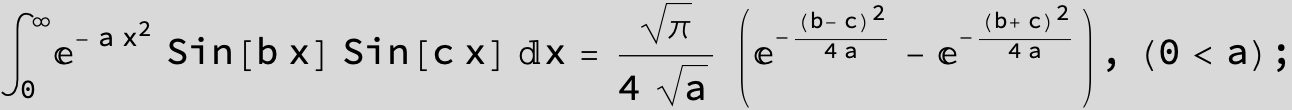
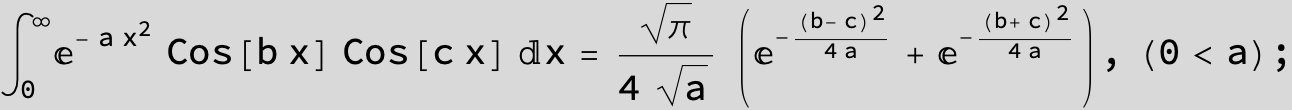
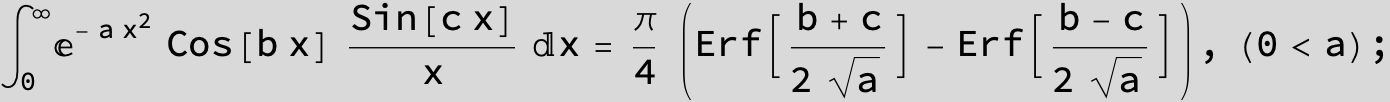
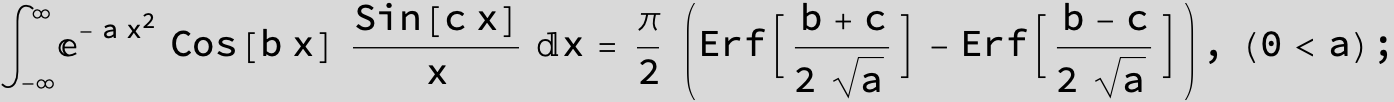
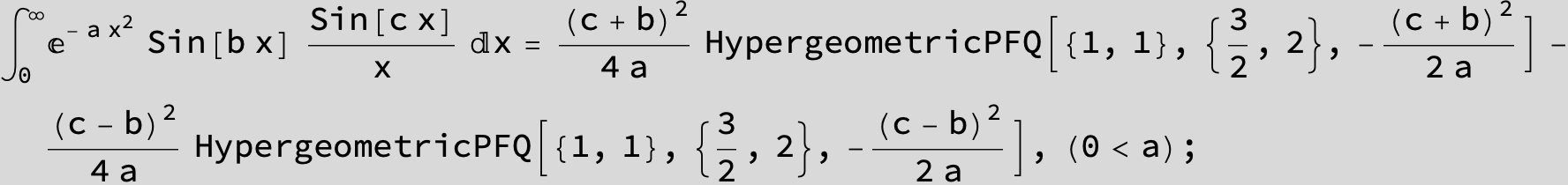

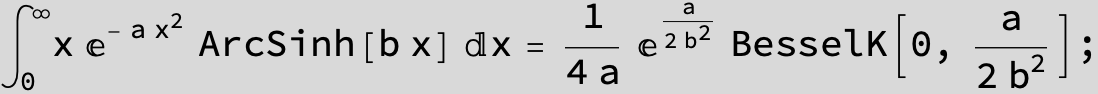
![]()

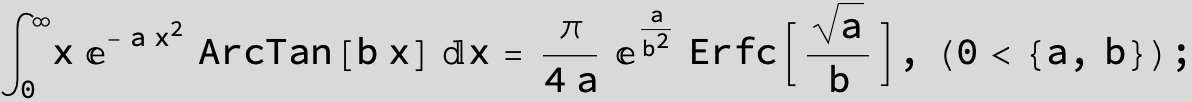

![]()
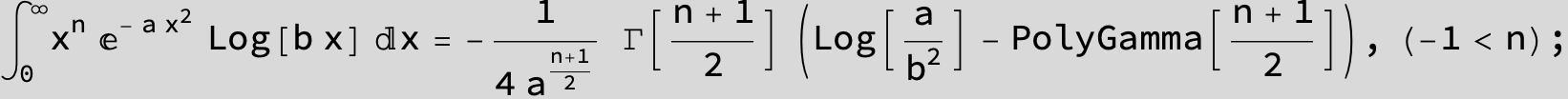

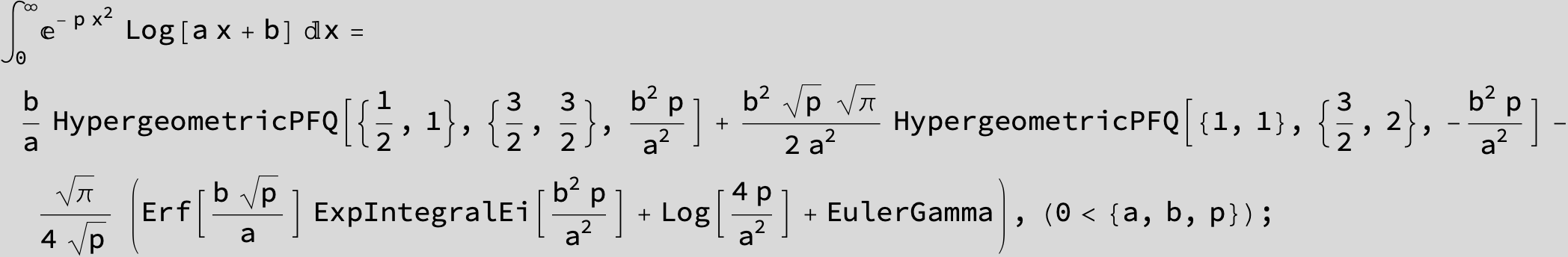
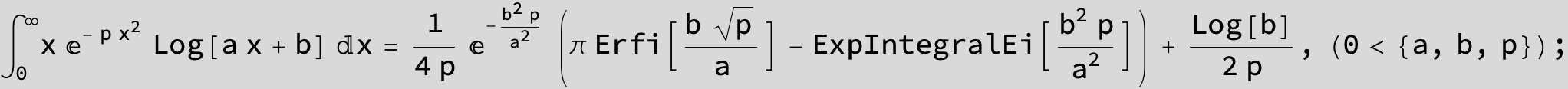

![]()

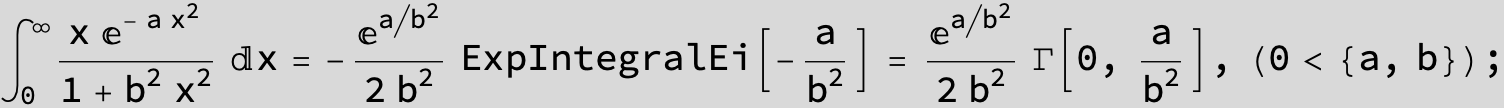
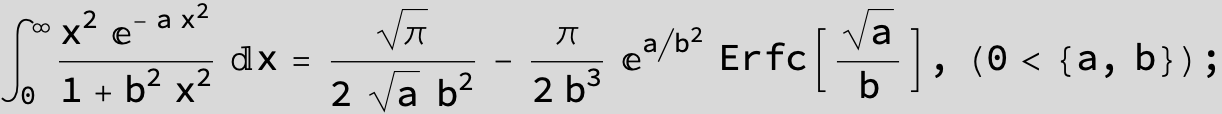
![]()

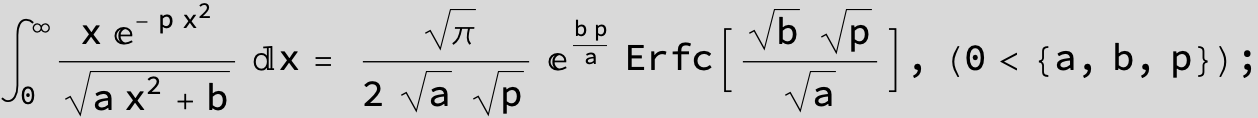
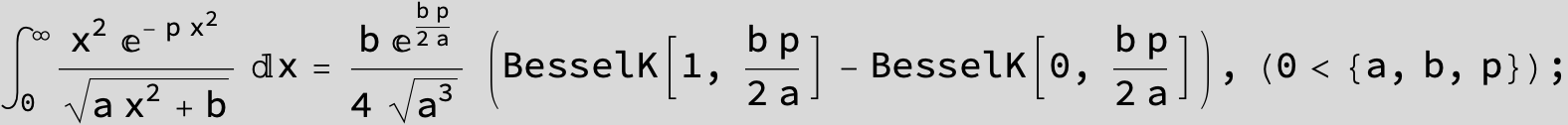

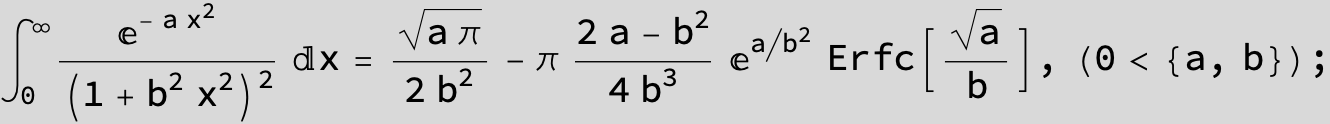
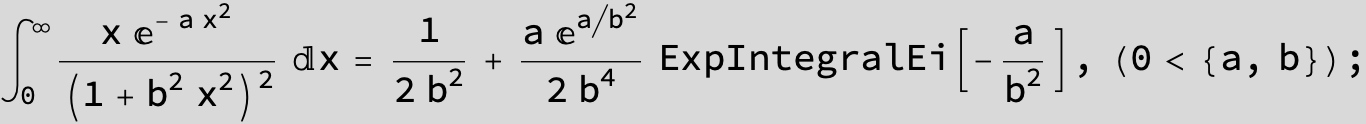
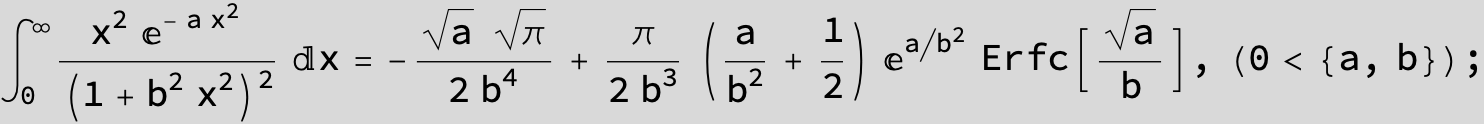
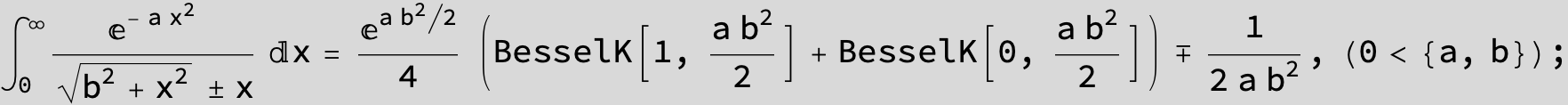
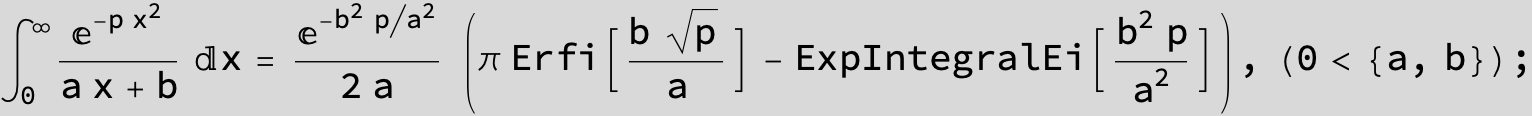
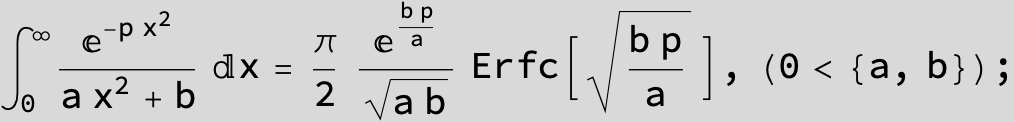

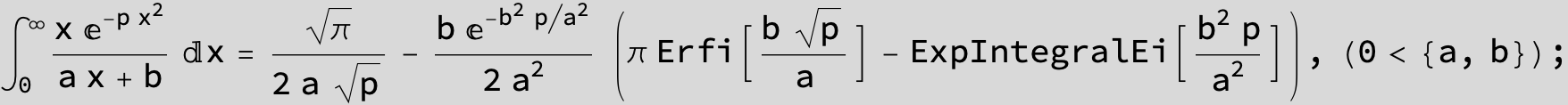
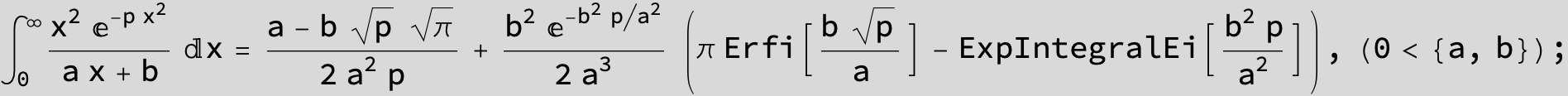
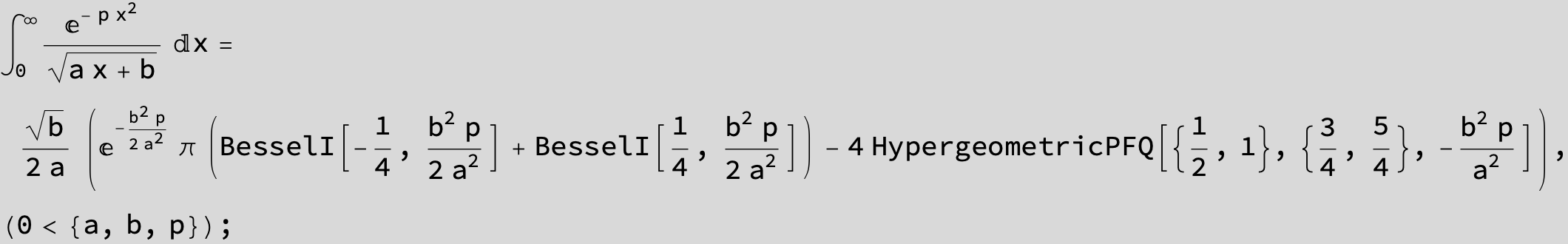

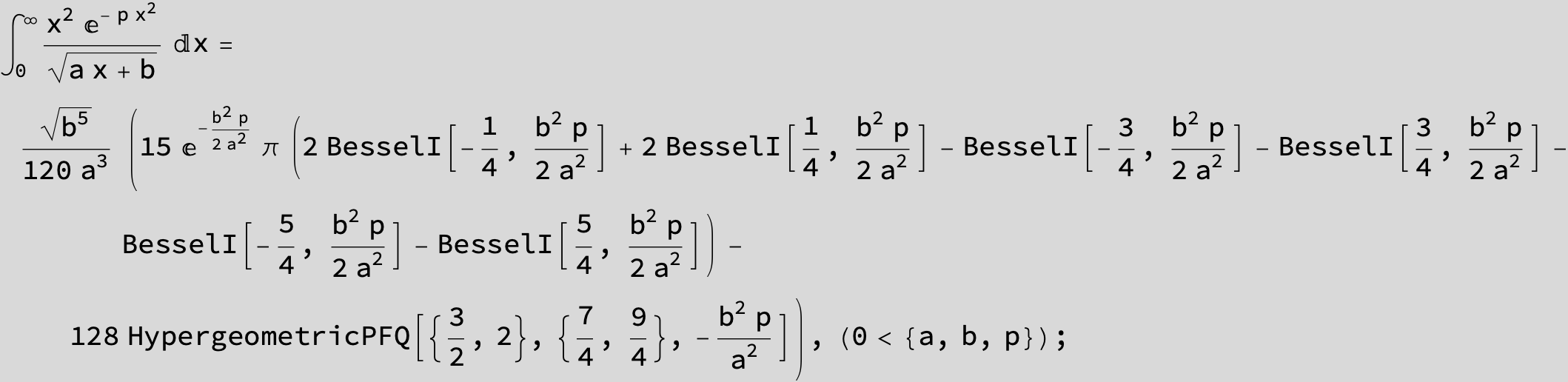

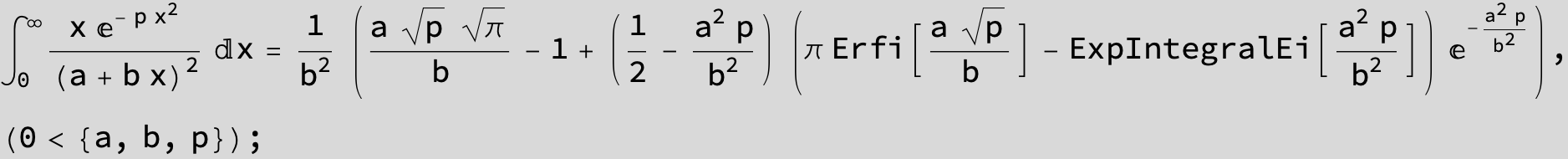
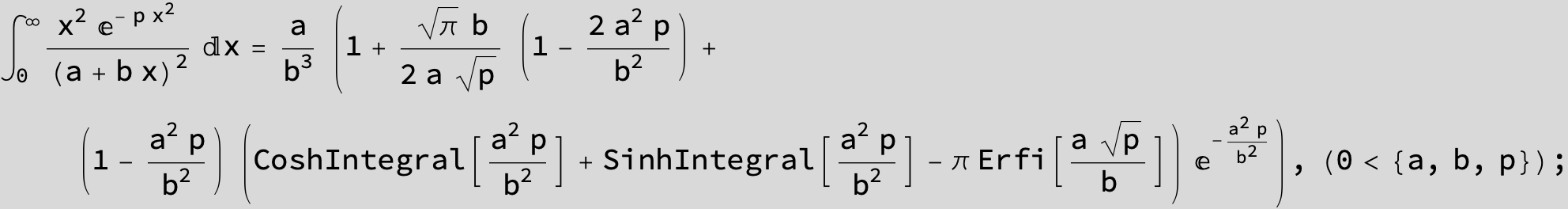
To see a nice cancellation of singularities at work plot the next expression around c = negative Integer:
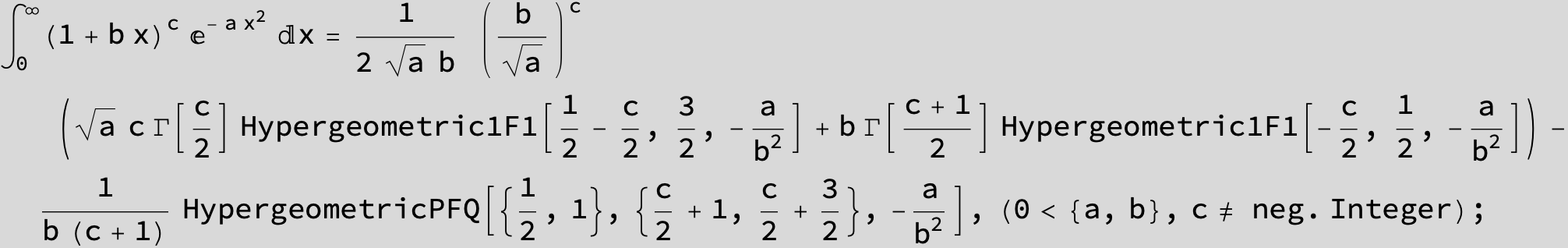
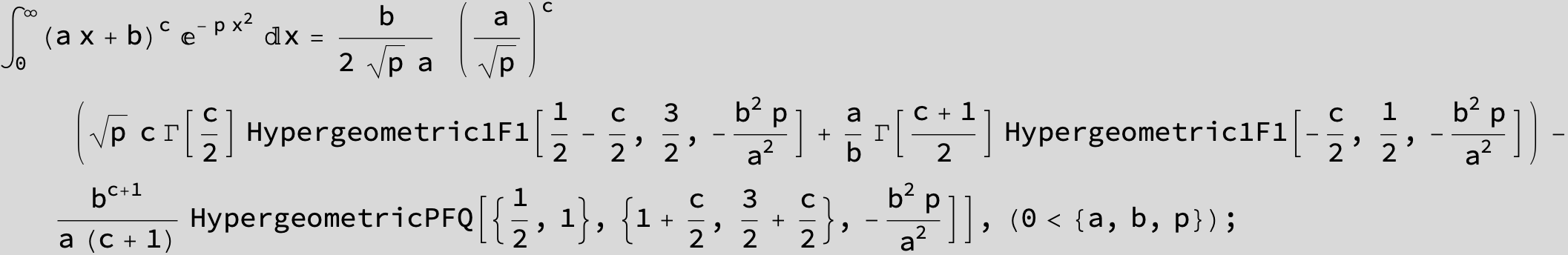
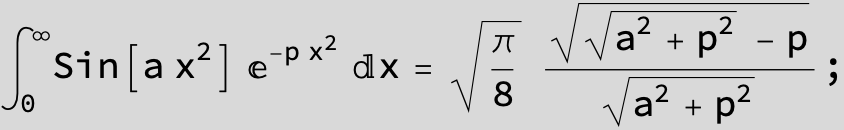
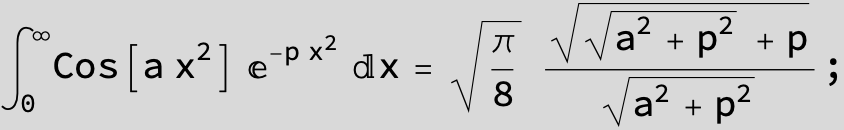

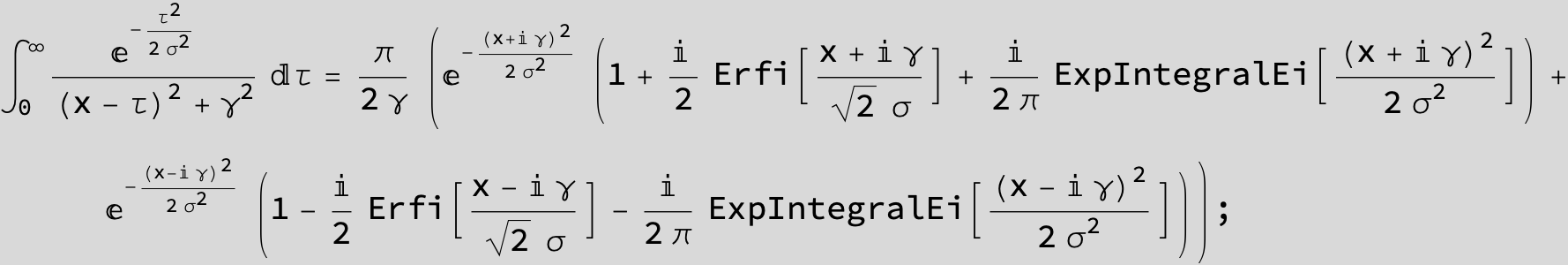
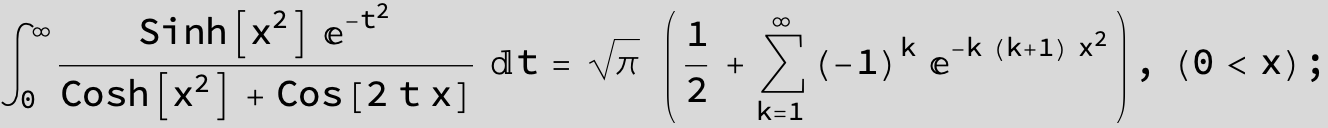
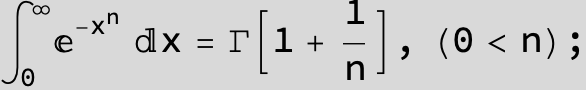
![]()
![]()
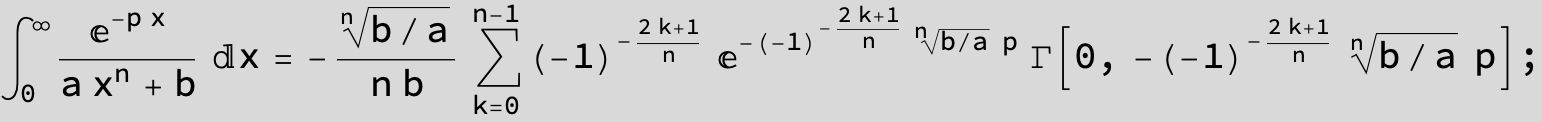
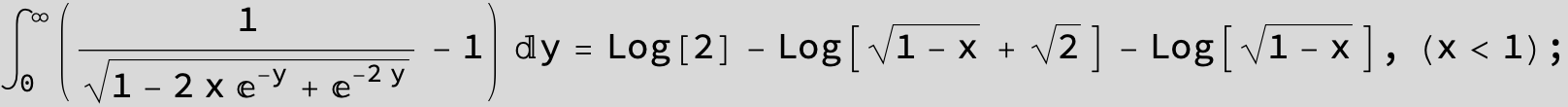
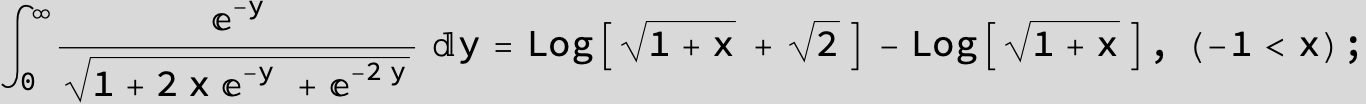
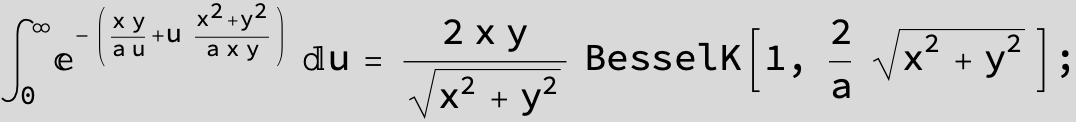

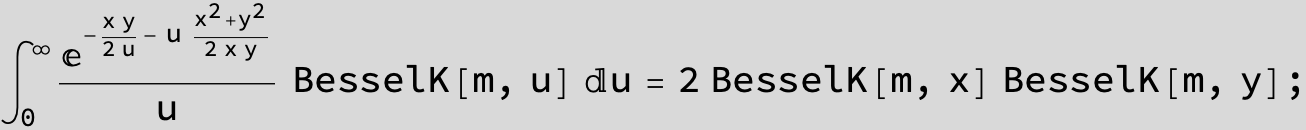


![]()
![]()
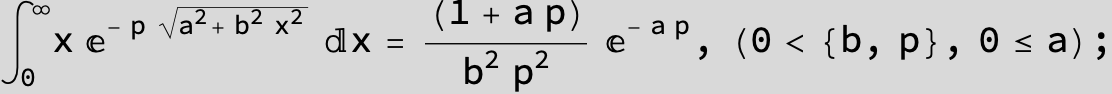
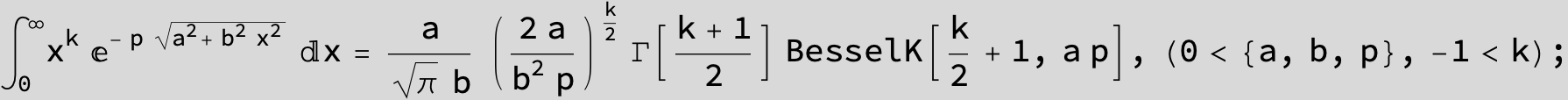

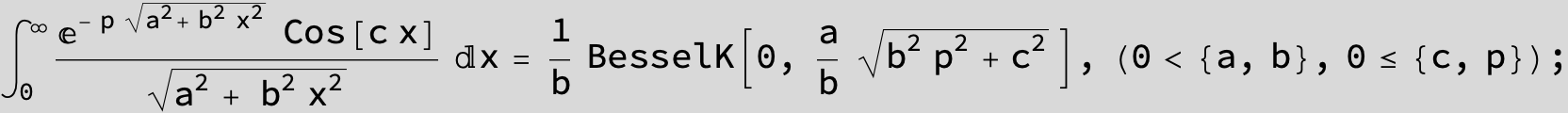
…this is a special case of the next integral below (m = -1 / 2).

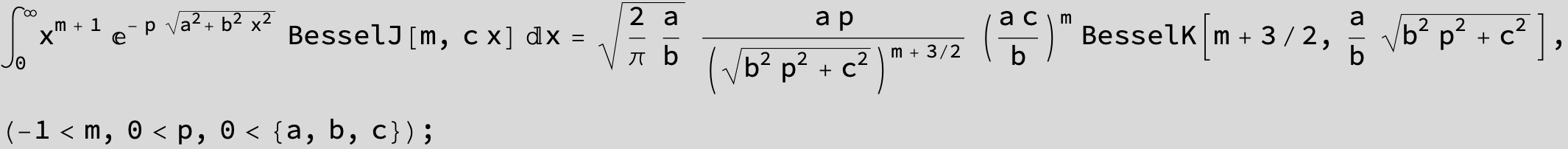



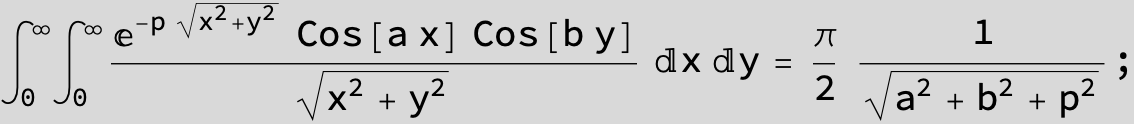
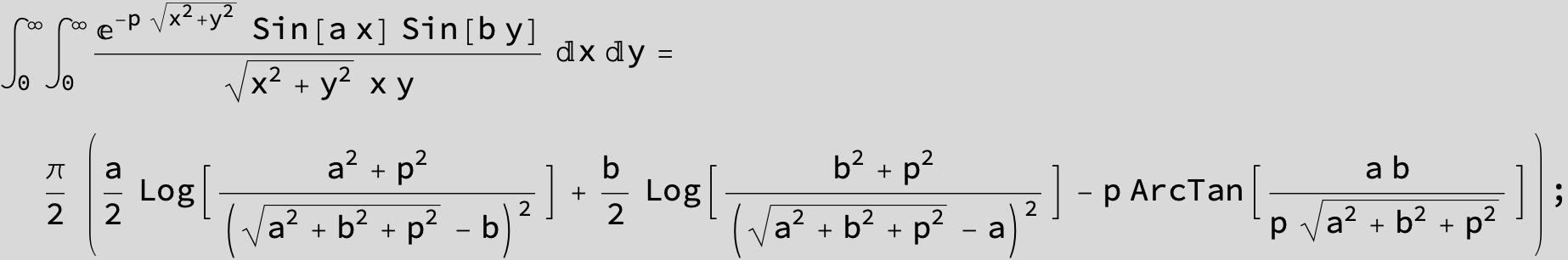
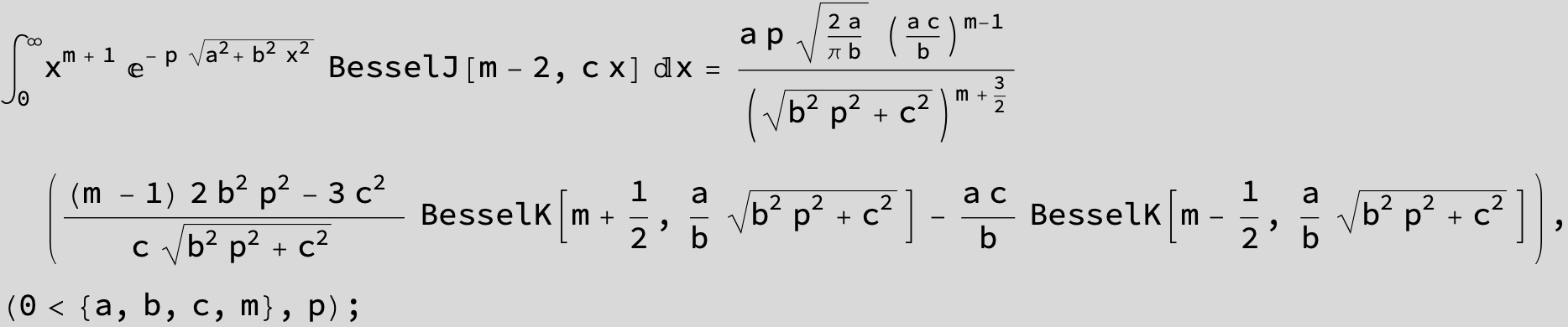
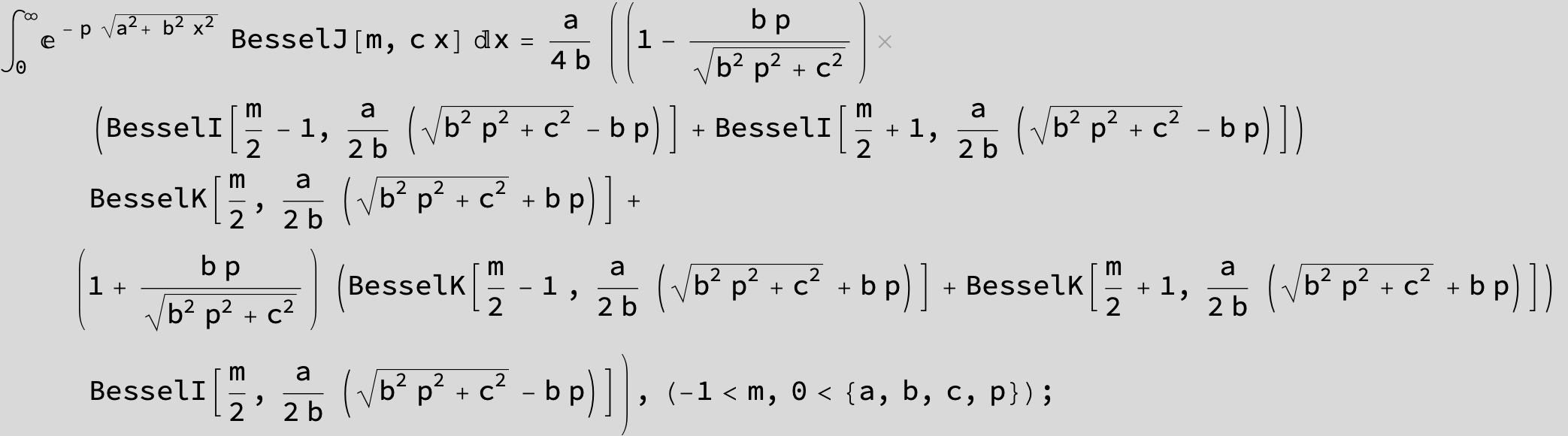
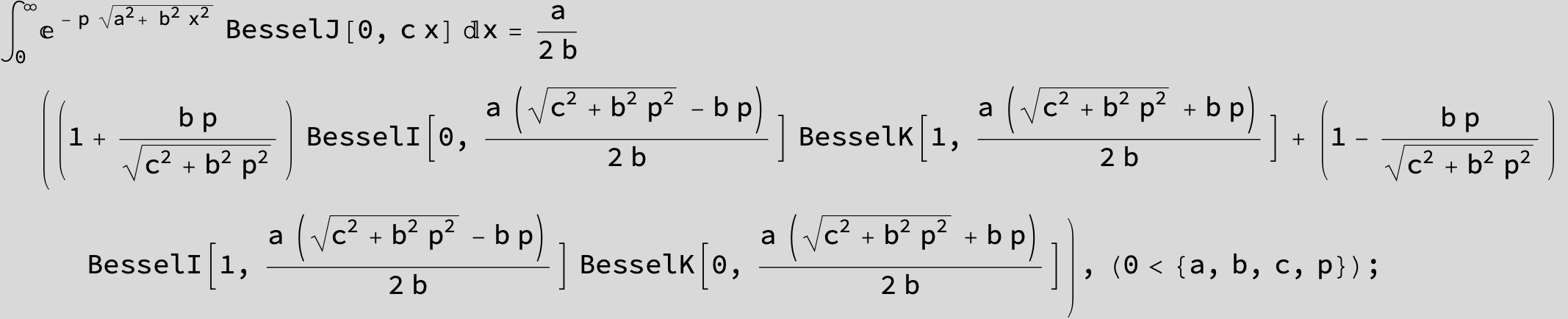
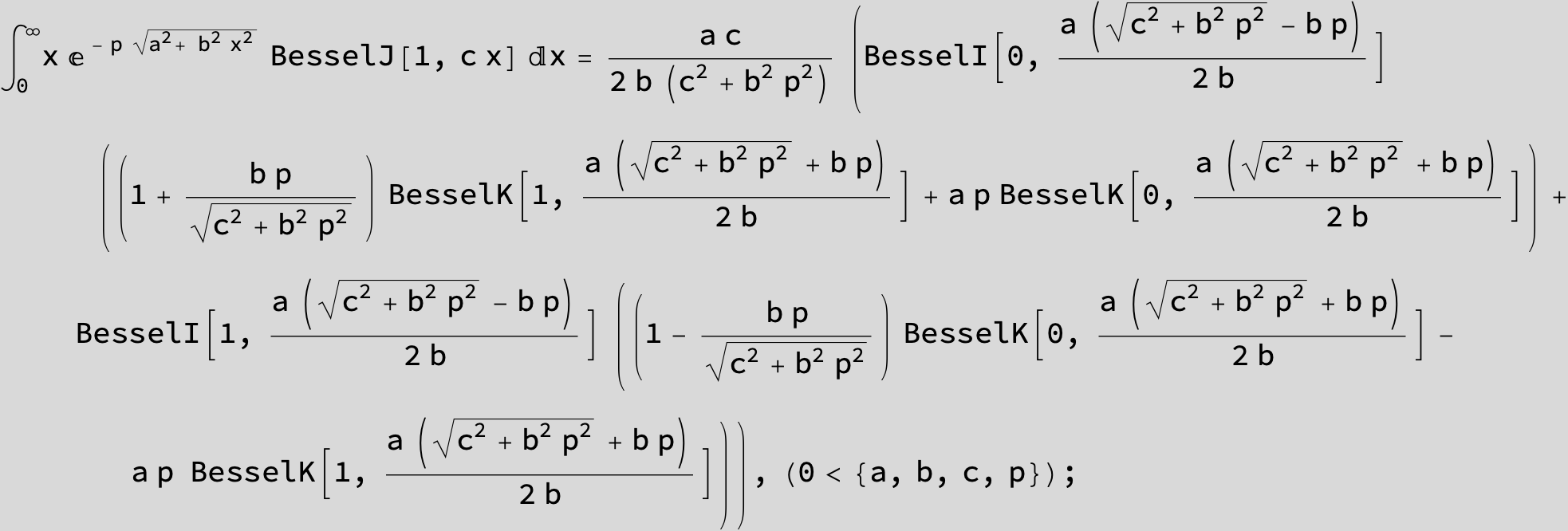
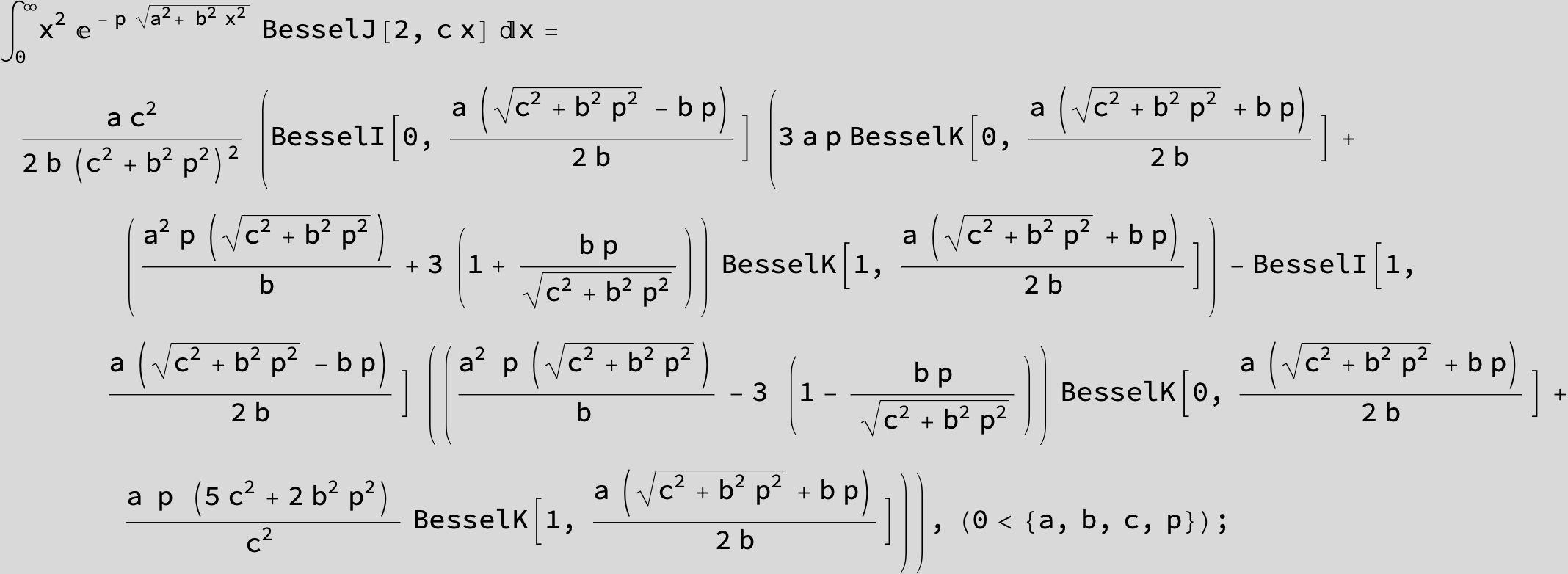
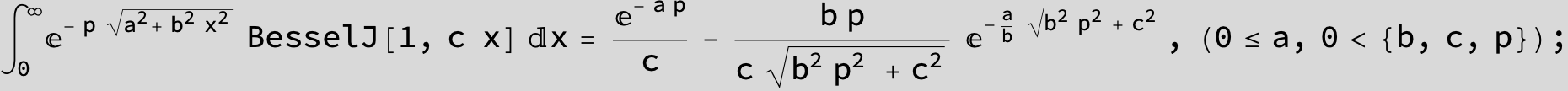
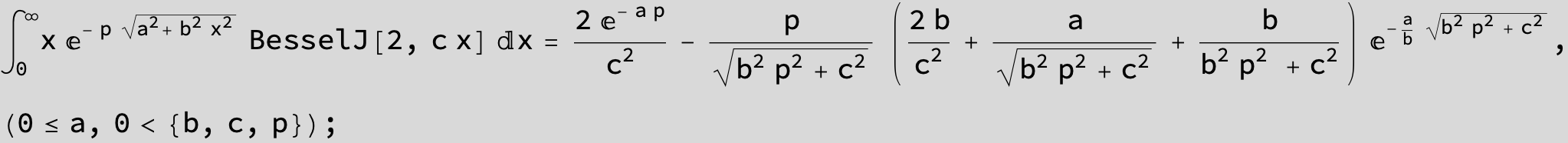
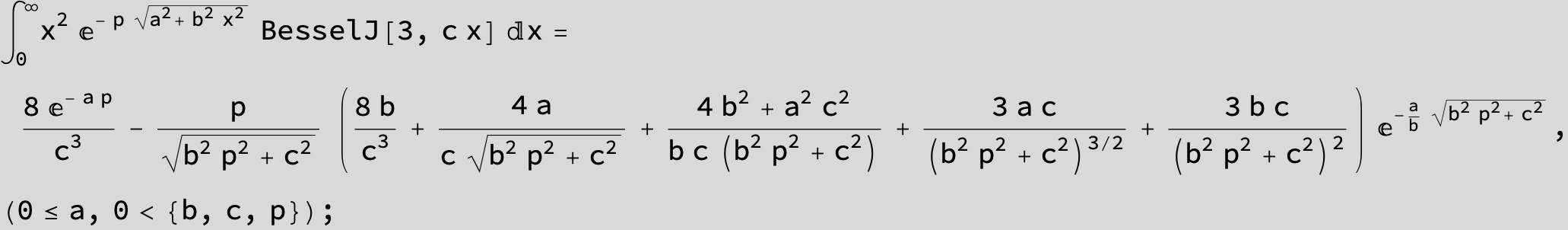
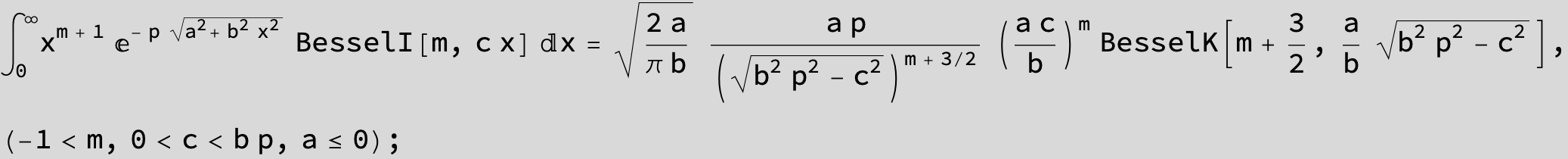

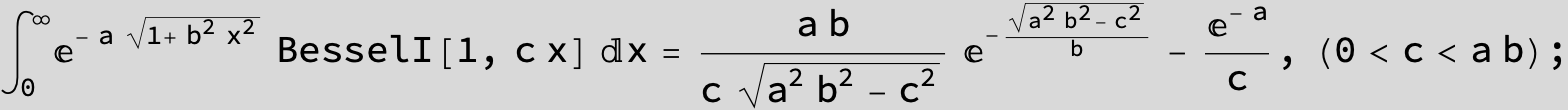
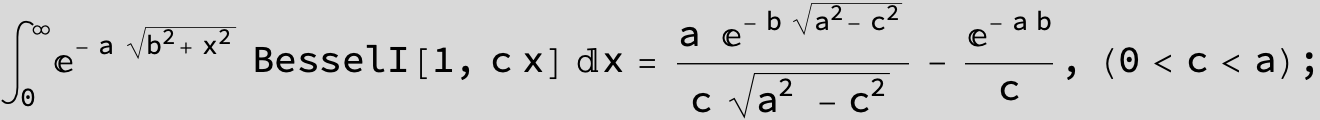

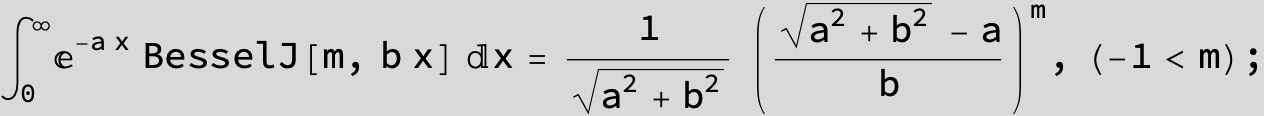
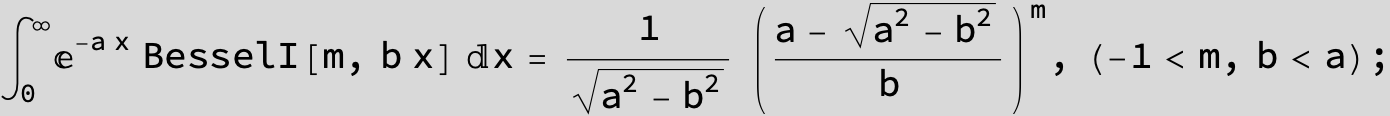

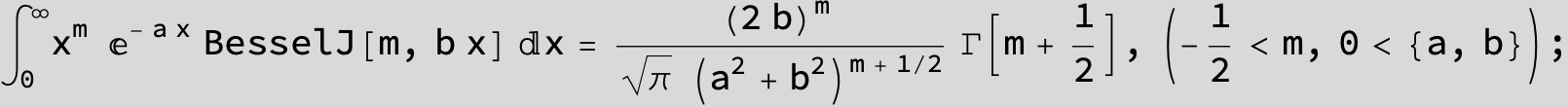
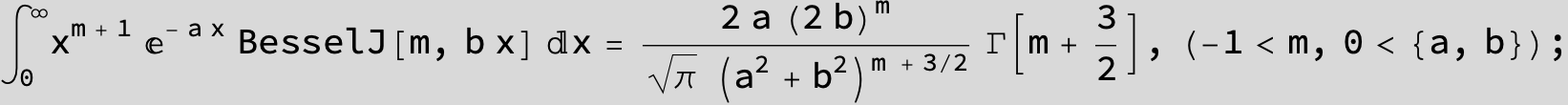
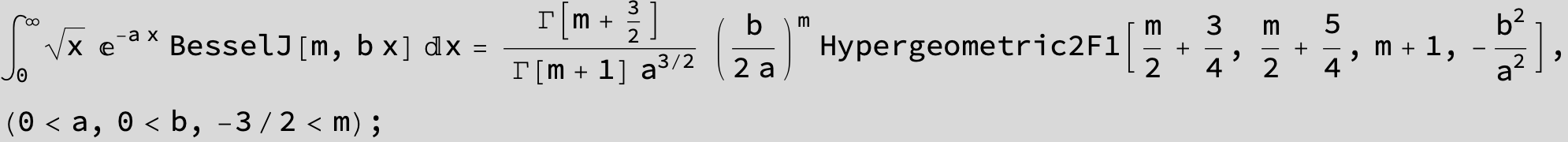
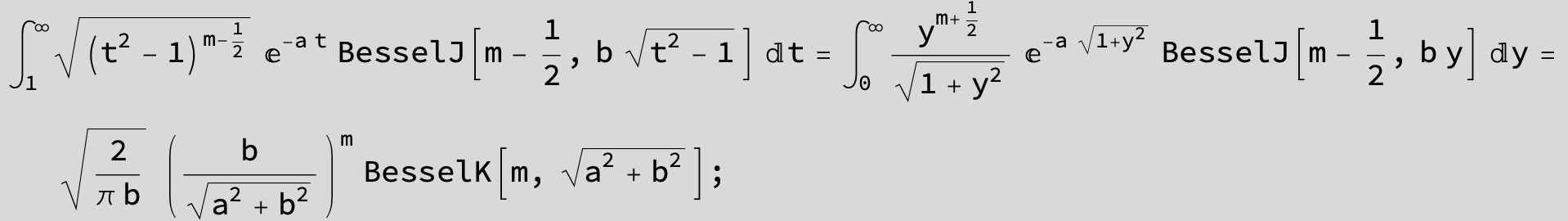
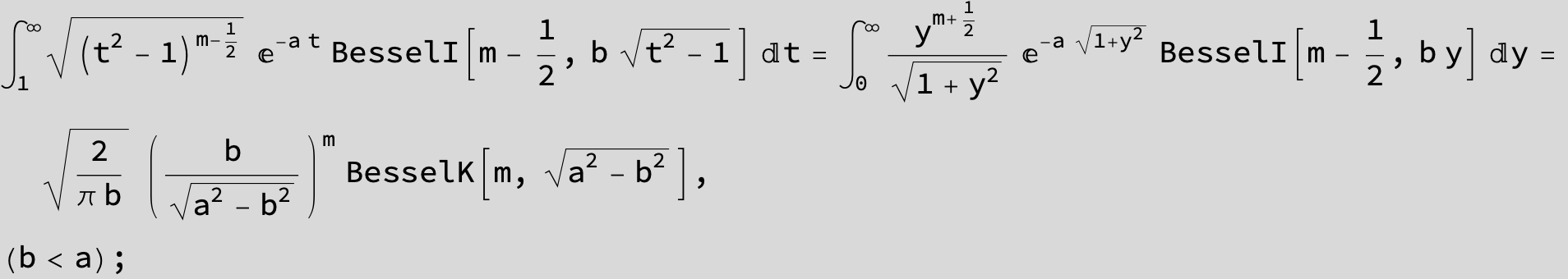
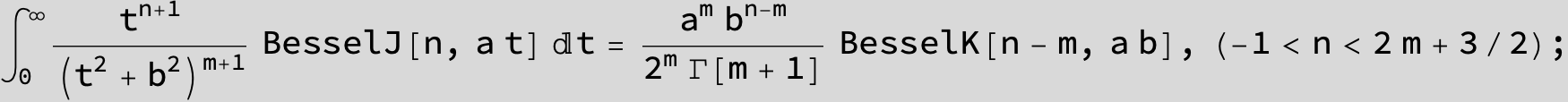
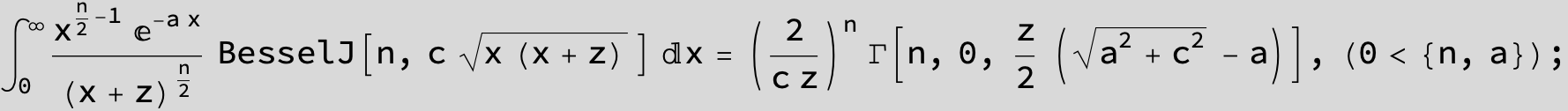
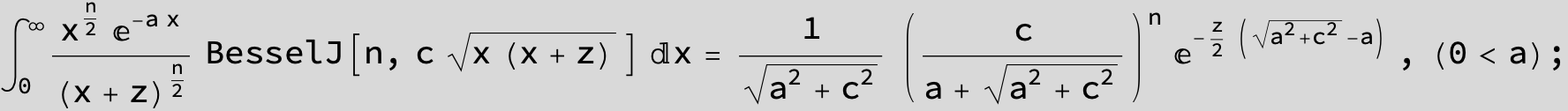
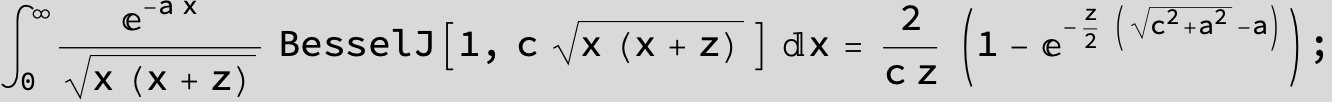
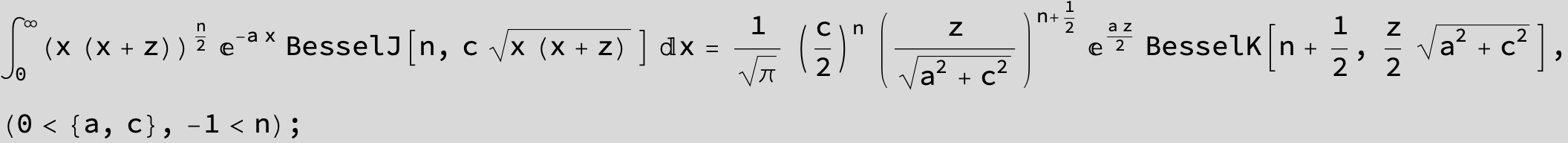
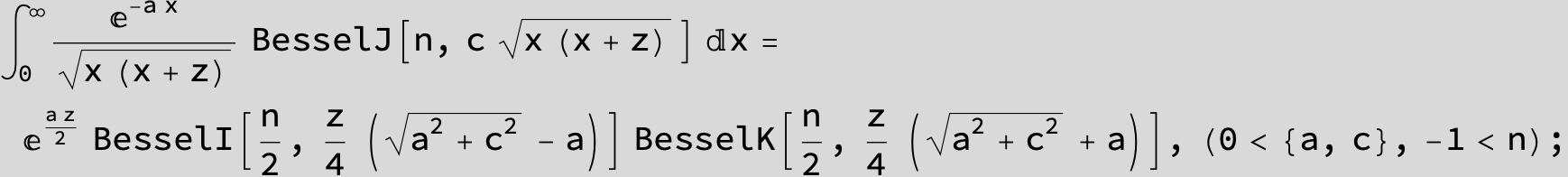
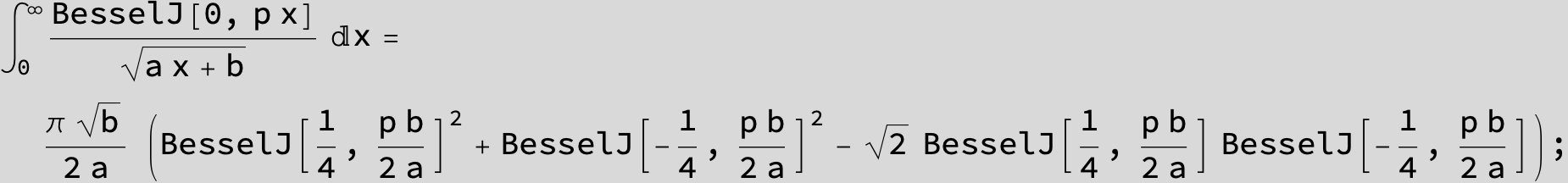


![]()
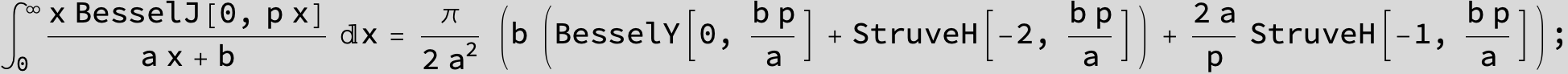
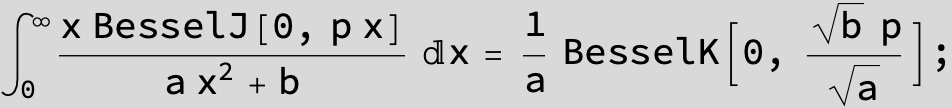
![]()

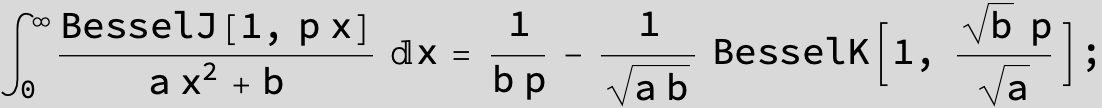
![]()
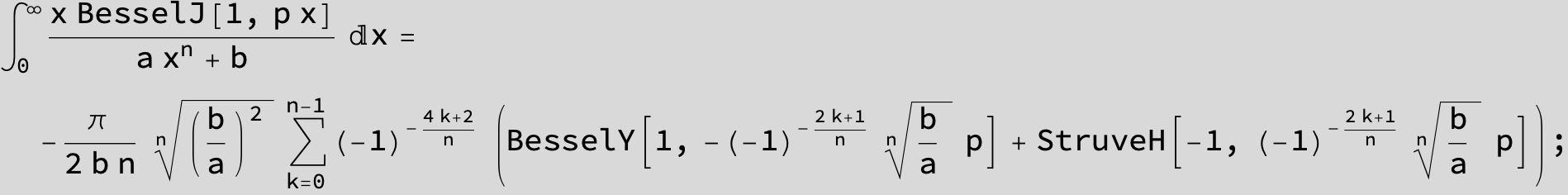
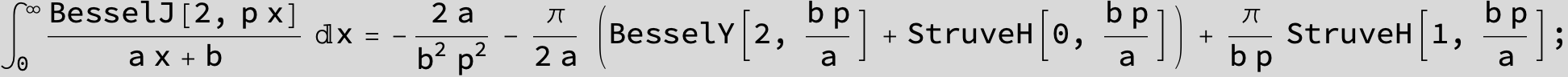
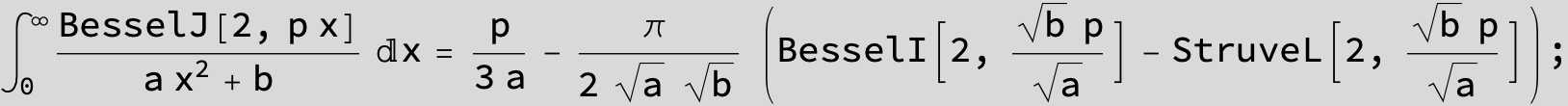
![]()
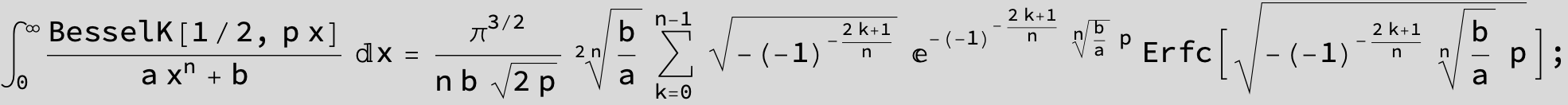
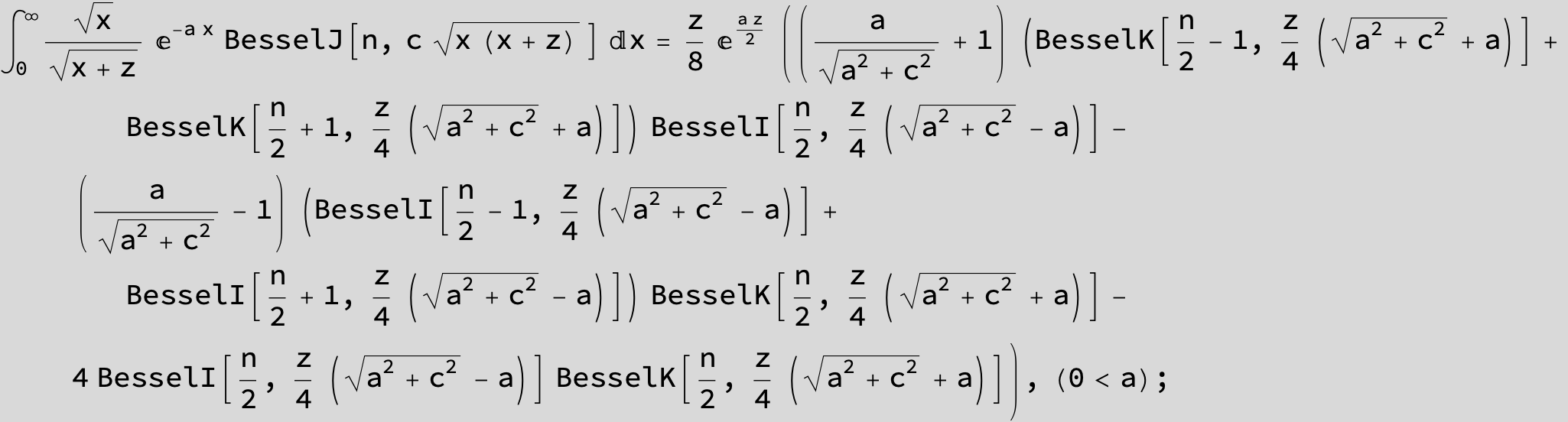
![]()

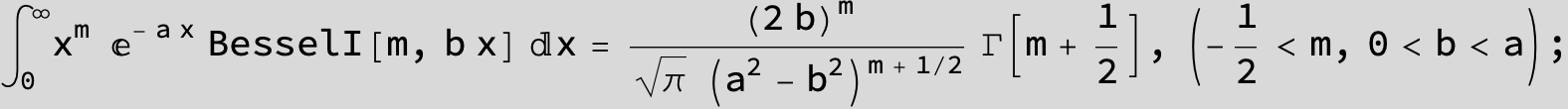
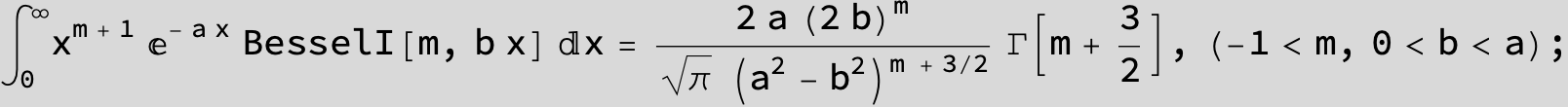
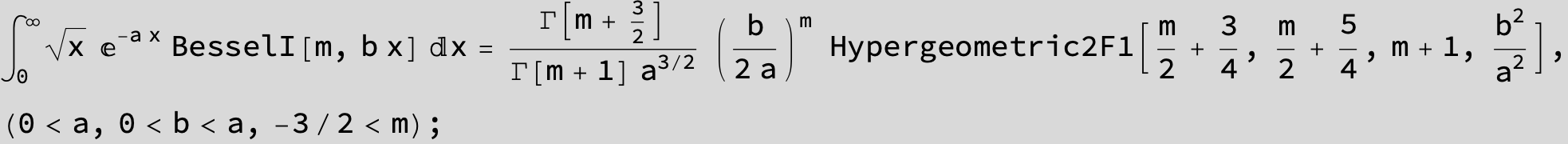
![]()


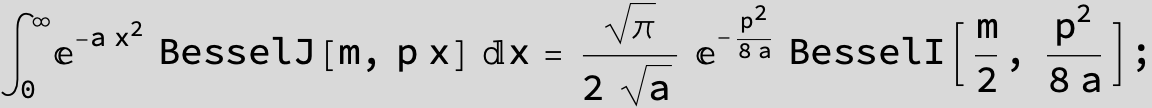
![]()
![]()
![]()
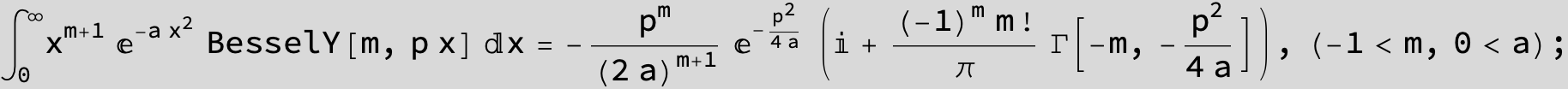
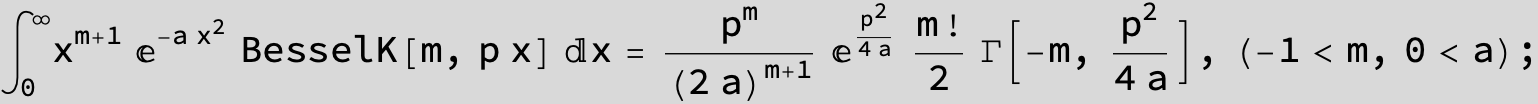
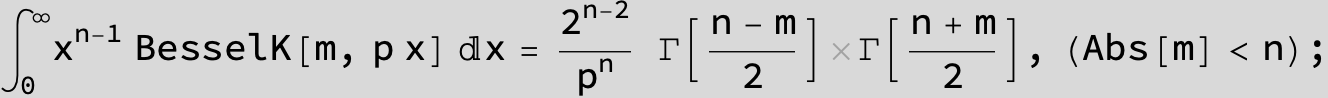
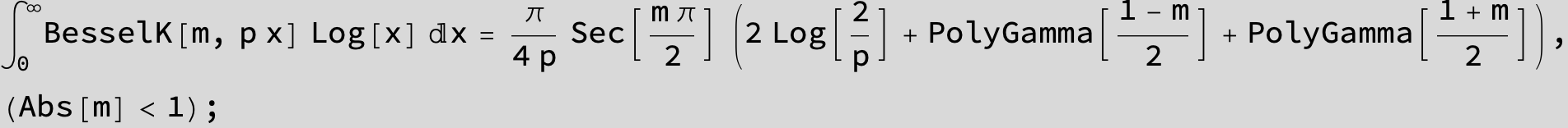
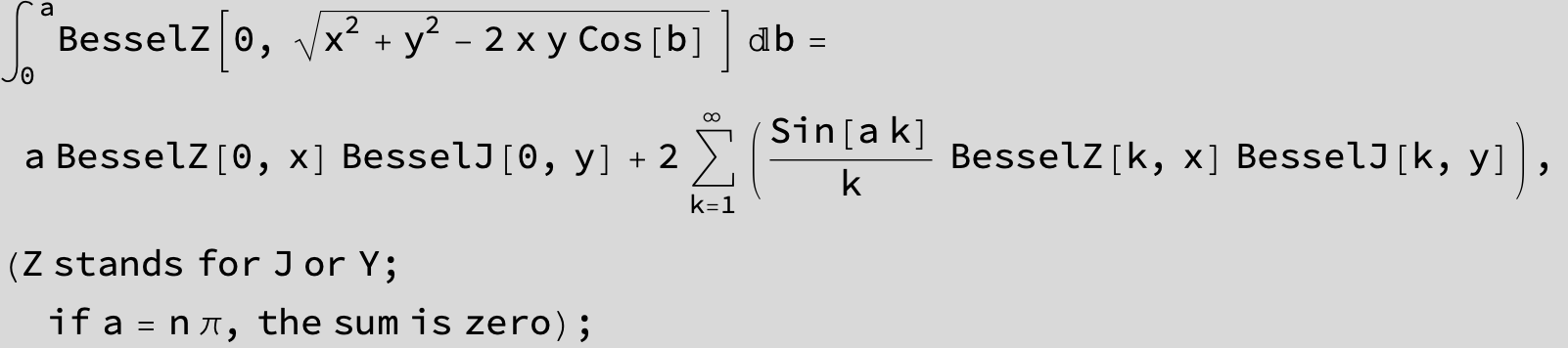
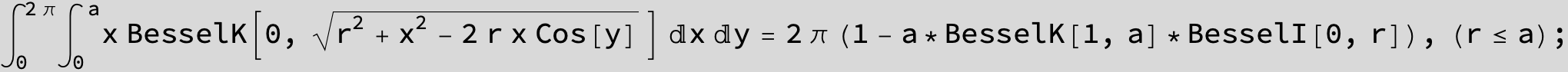
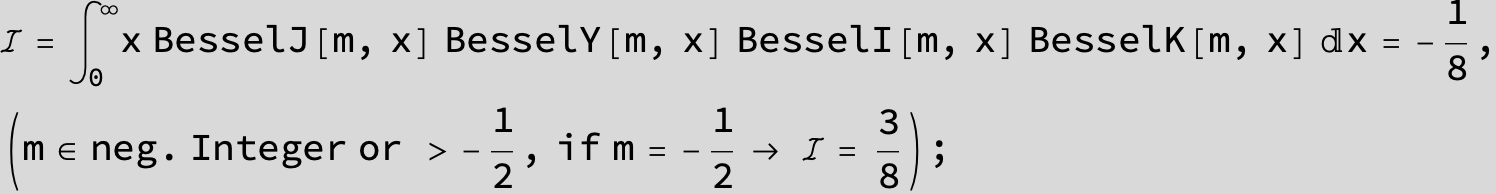

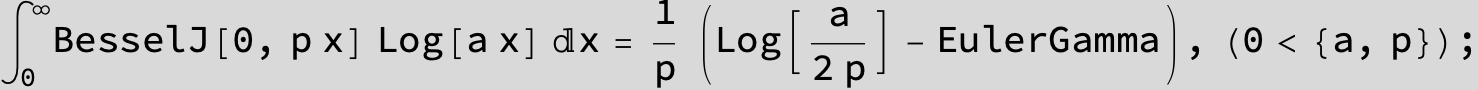
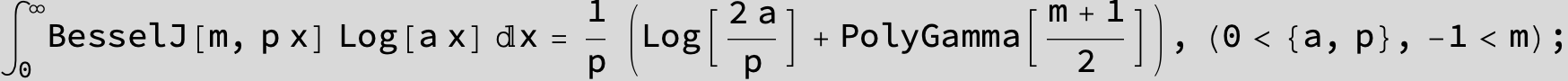
![]()


![]()

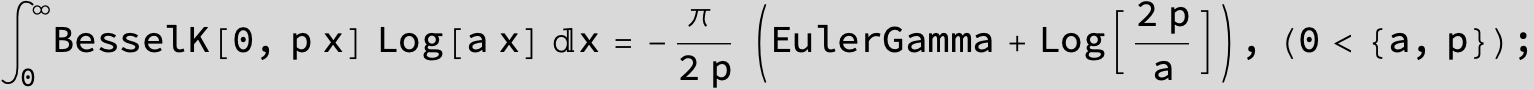
![]()
![]()
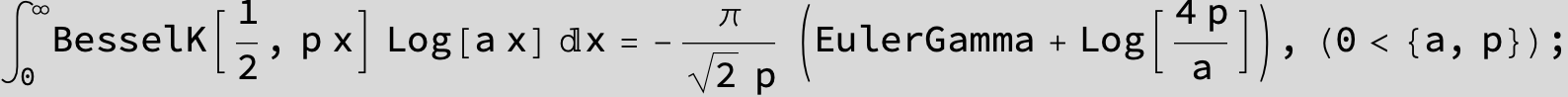

![]()
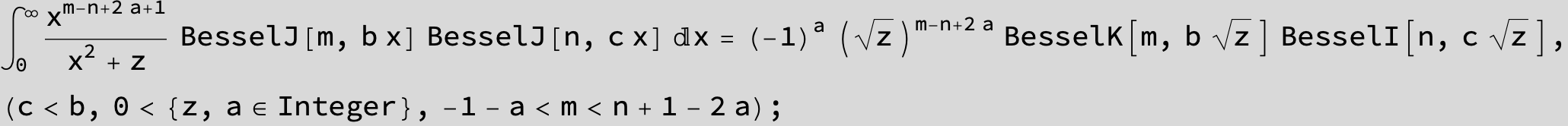
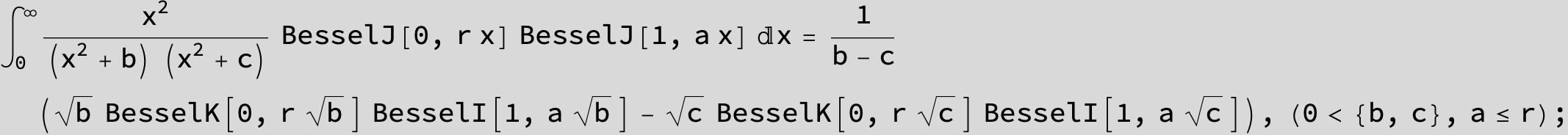
![]()
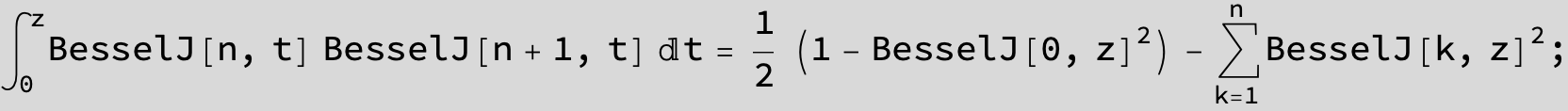
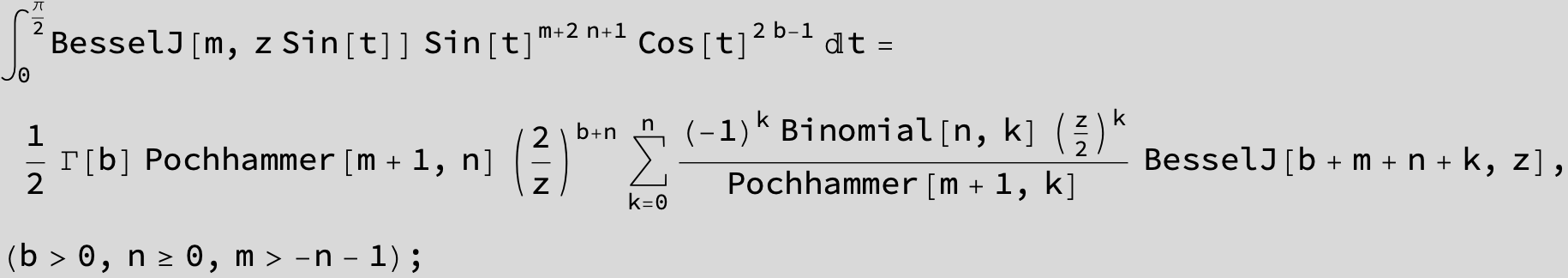
![]()
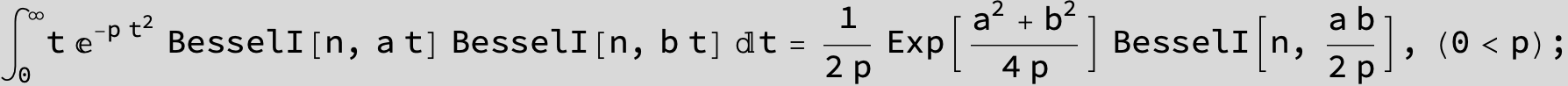
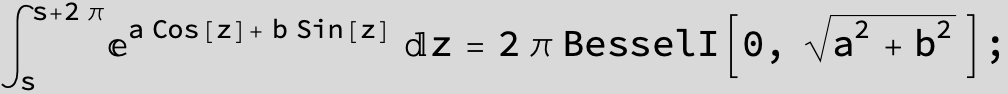
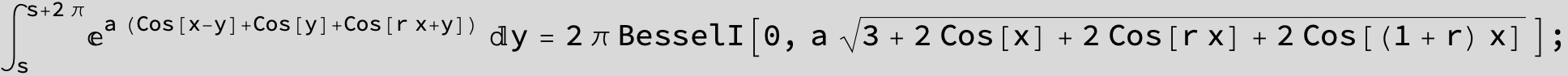
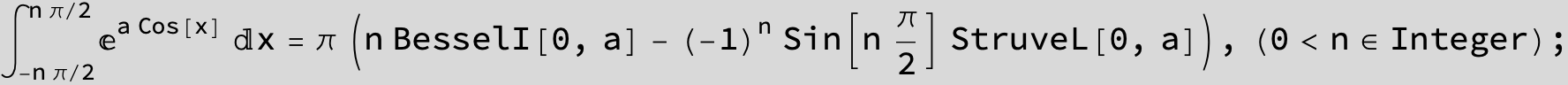

![]()
![]()

![]()
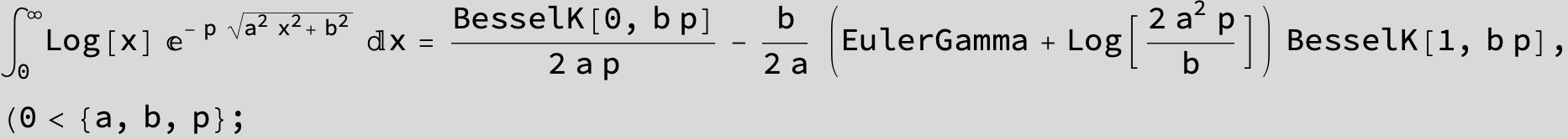

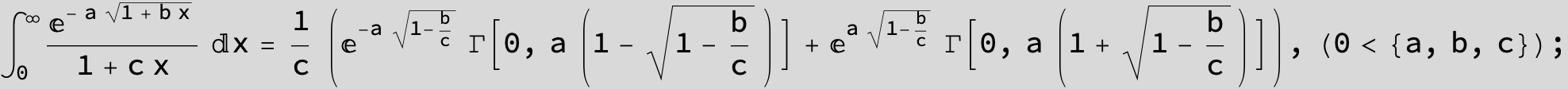
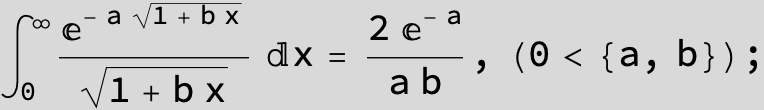
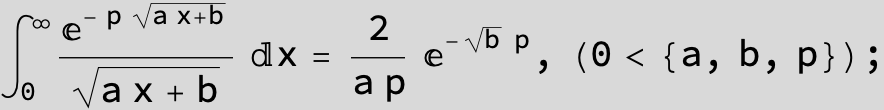
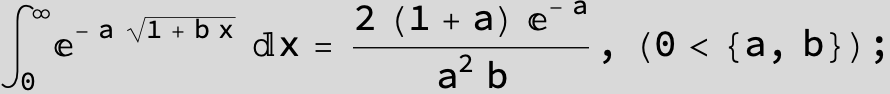
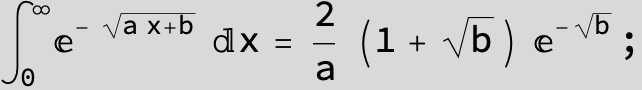

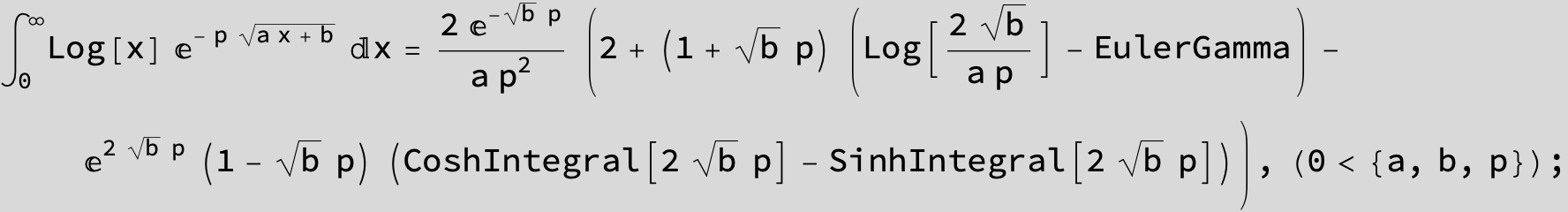

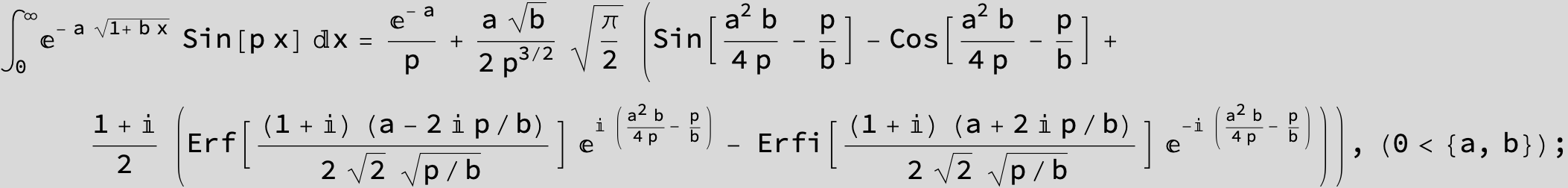
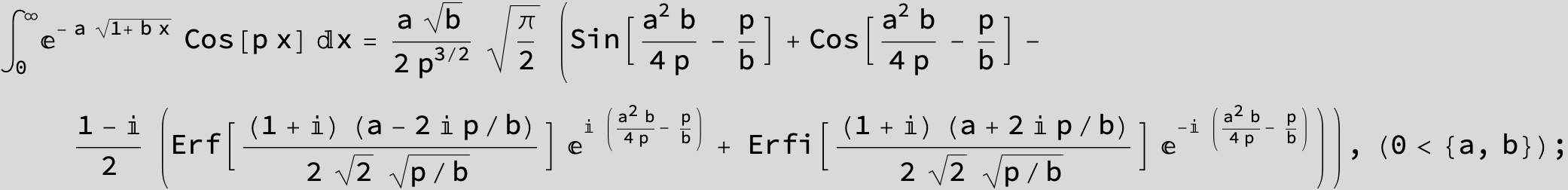
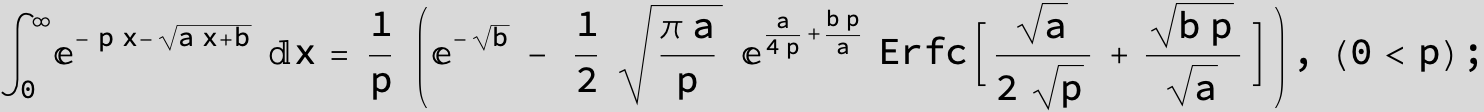
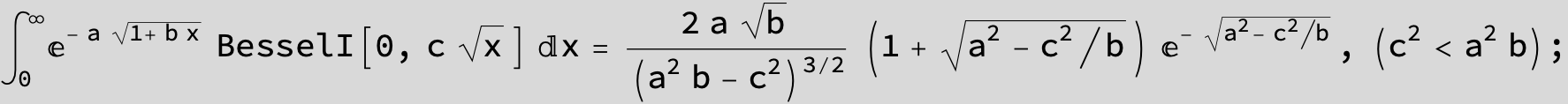
![]()

![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
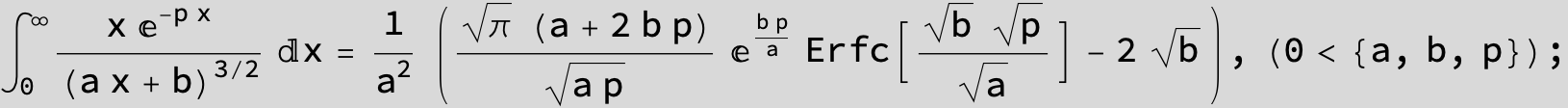
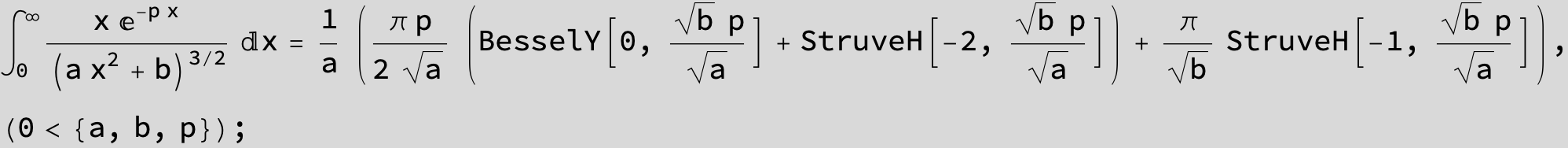
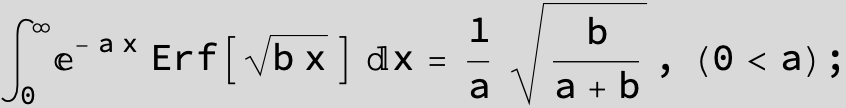
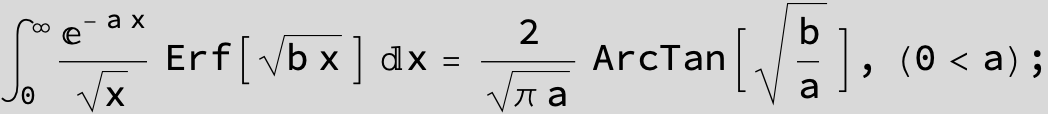

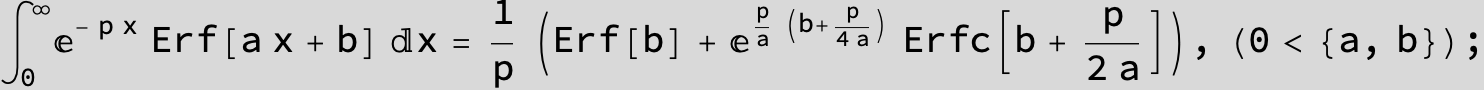

![]()
![]()
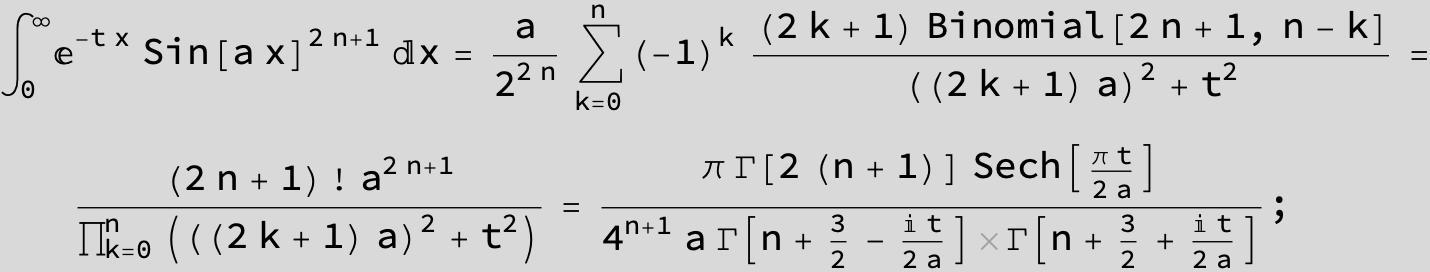
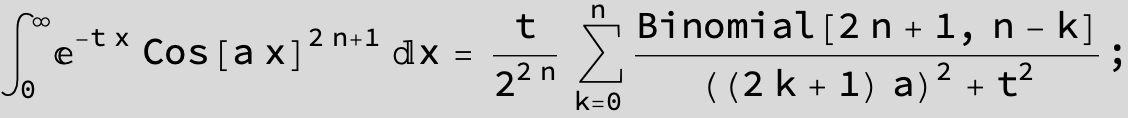
![]()
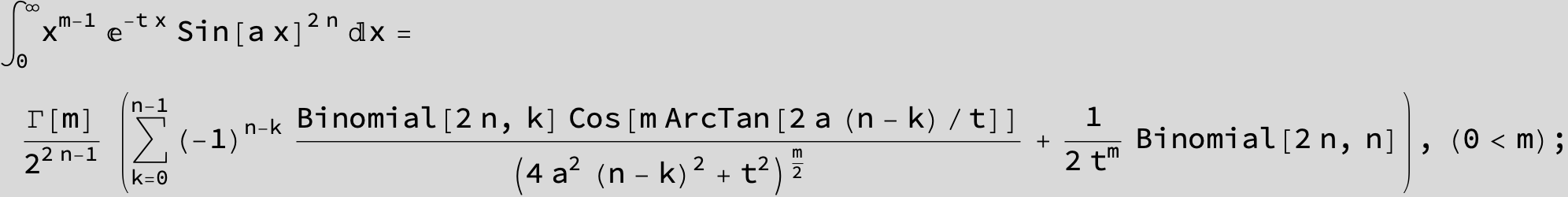



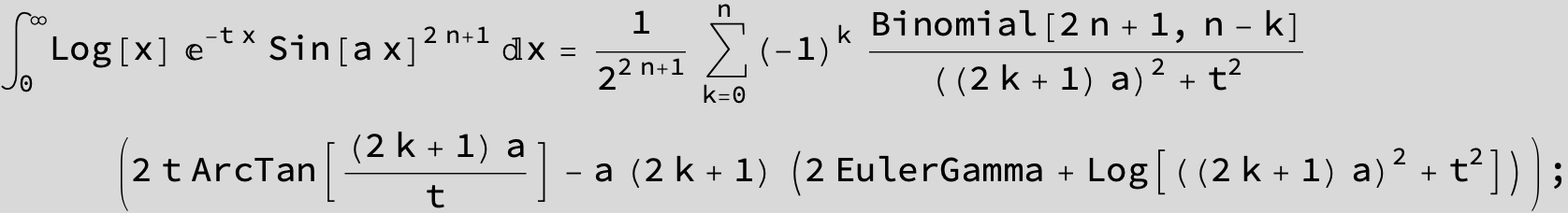
![]()
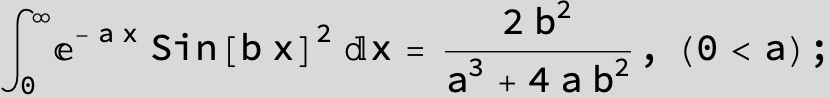
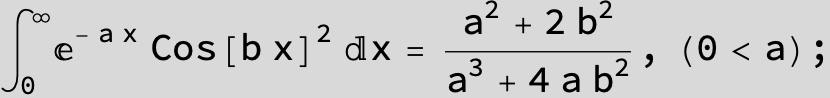
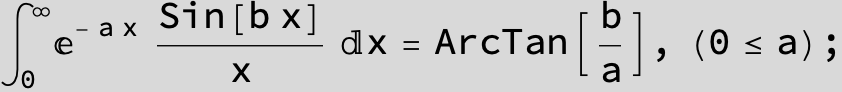
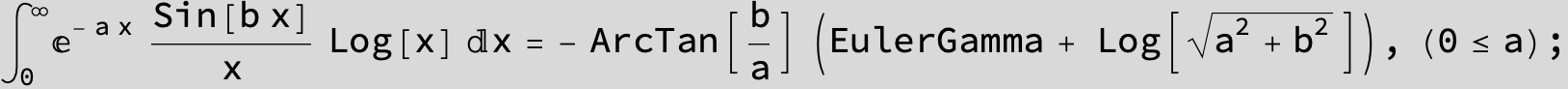
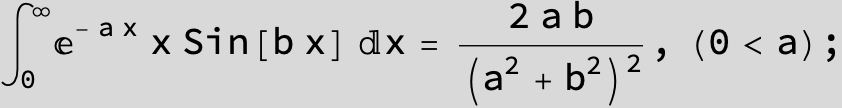
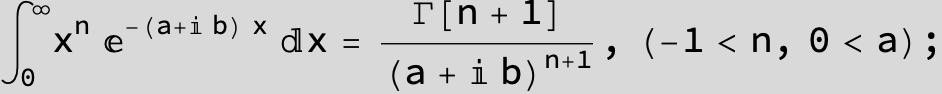

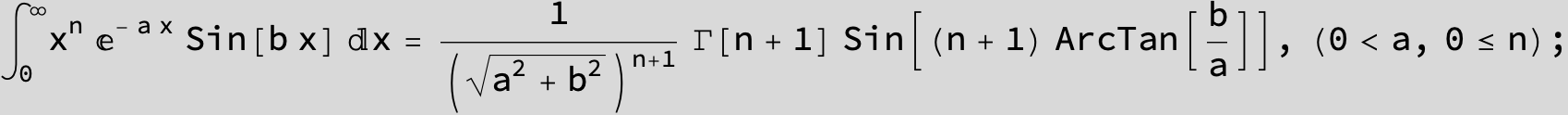

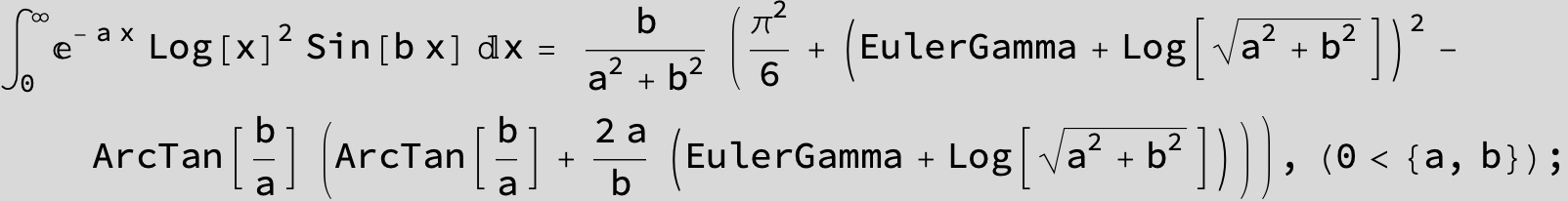
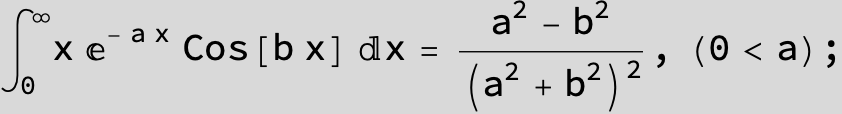
![]()


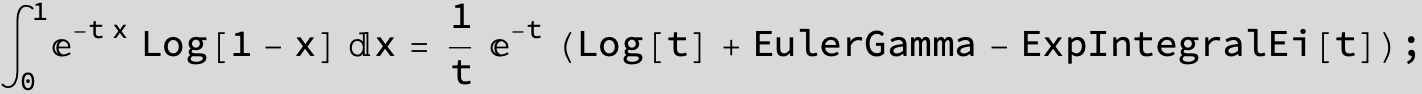

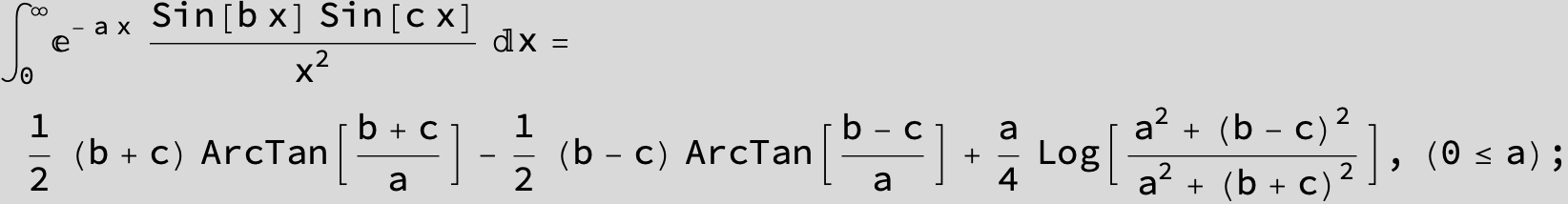
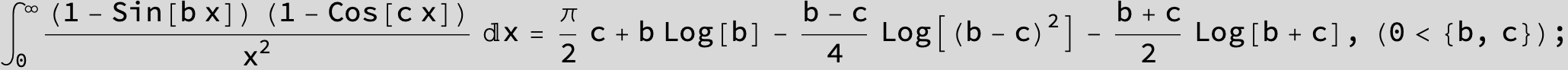
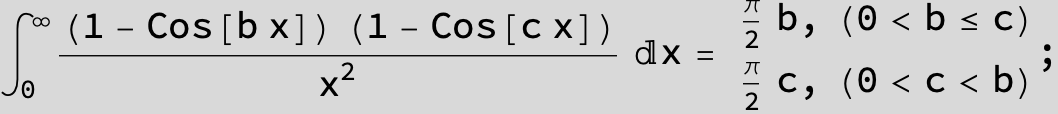
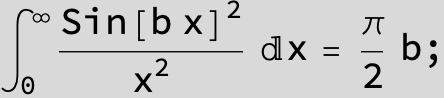

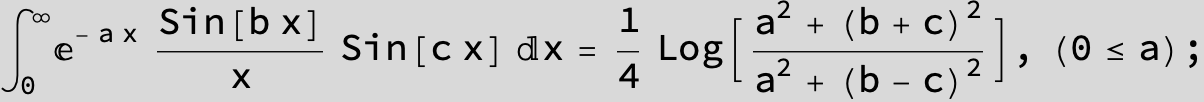
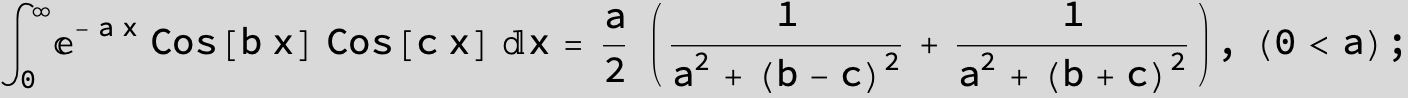
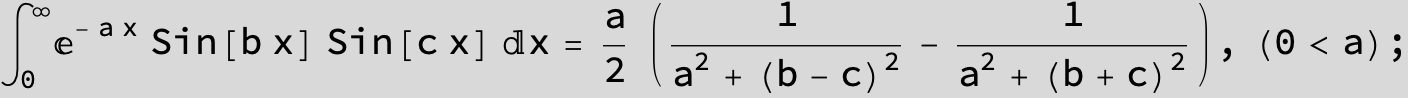
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
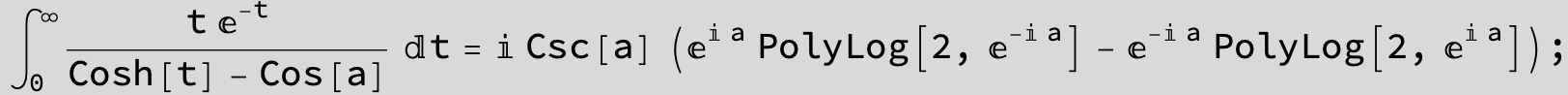
![]()
![]()





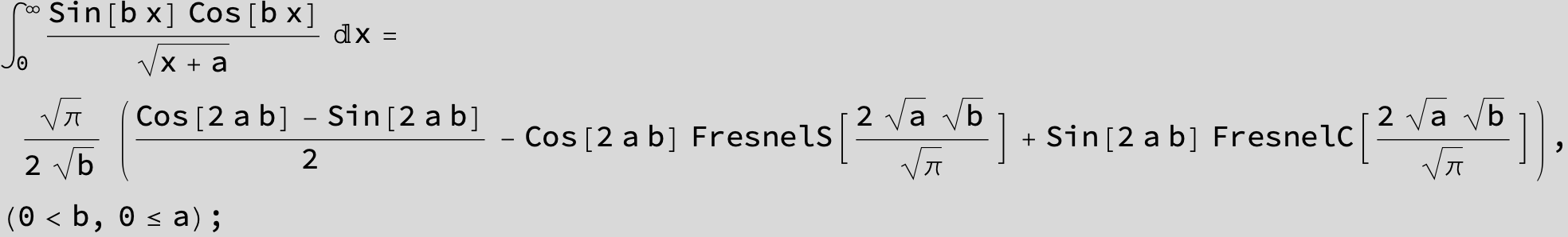

![]()
![]()

![]()
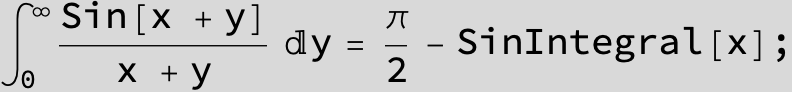
![]()
![]()
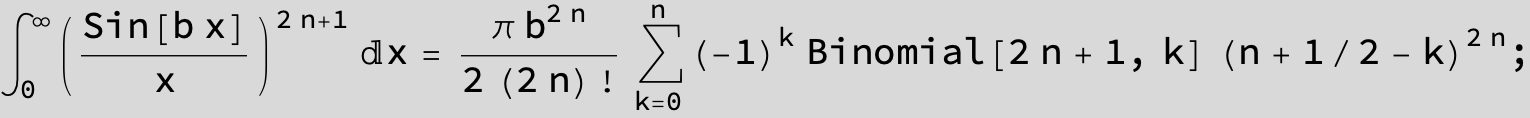
![]()
![]()
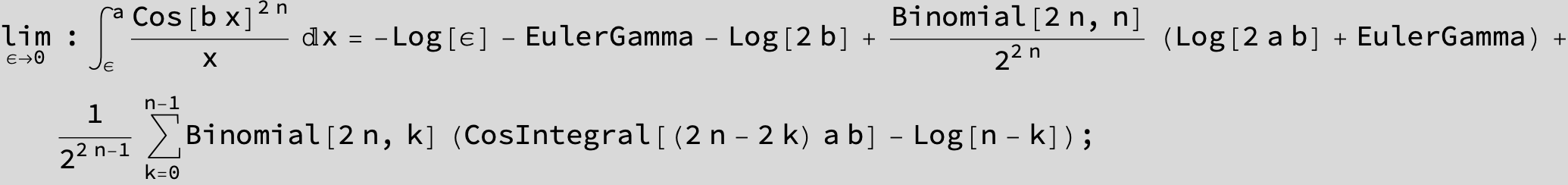

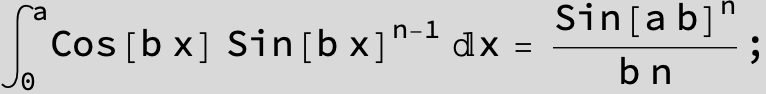

![]()
![]()
![]()
Arclength of of a helix around a torus with major radius R, minor radius r and number of windings n :

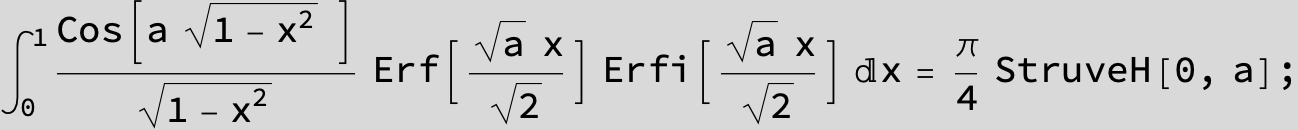


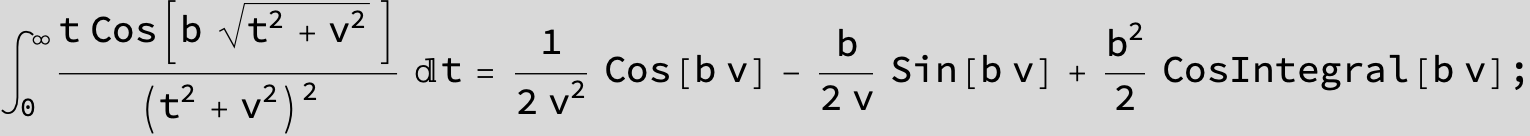

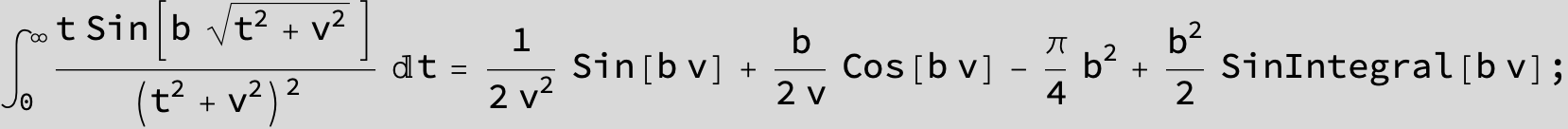
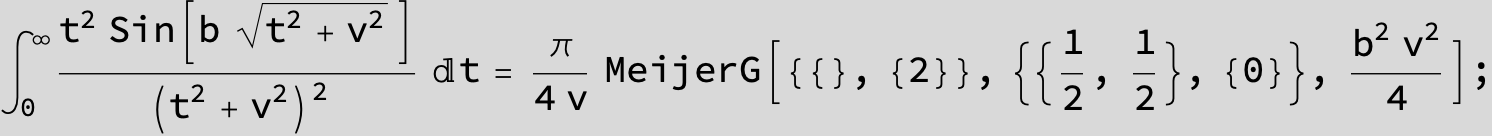
![]()
![]()
![]()
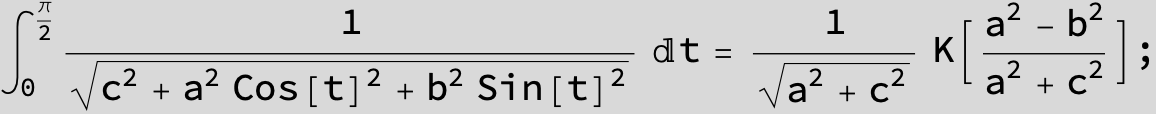
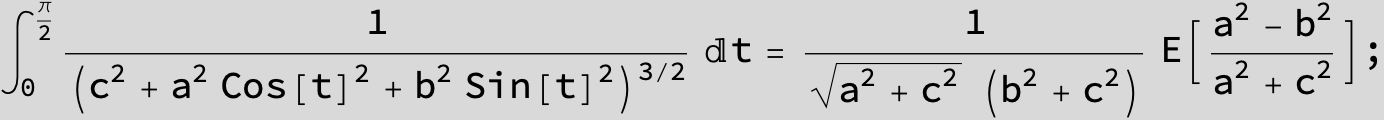
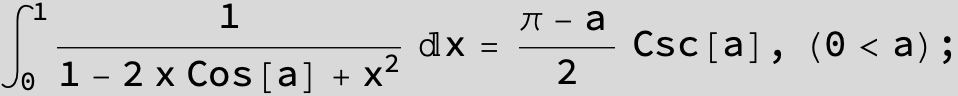

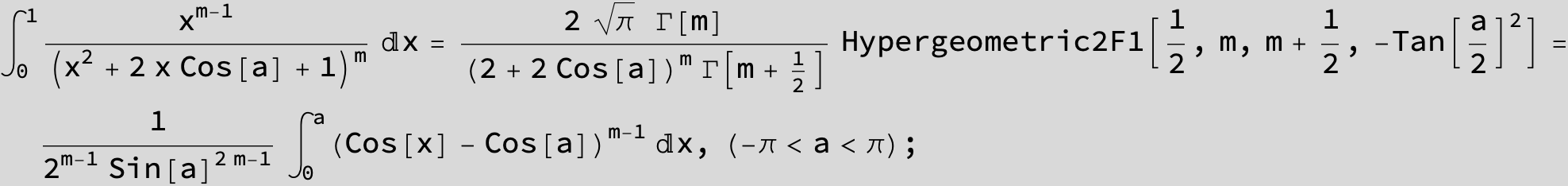

![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()



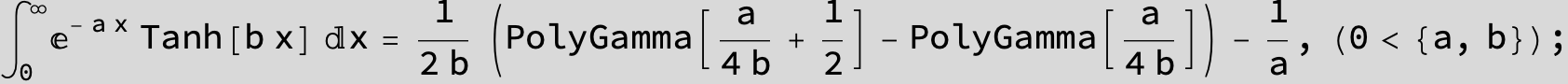
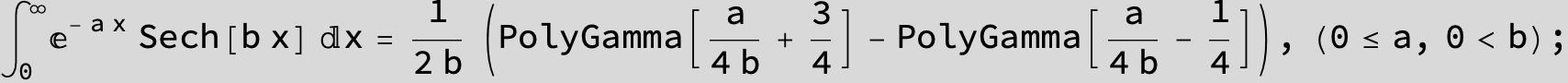
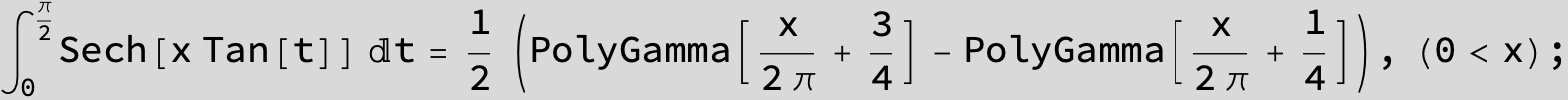
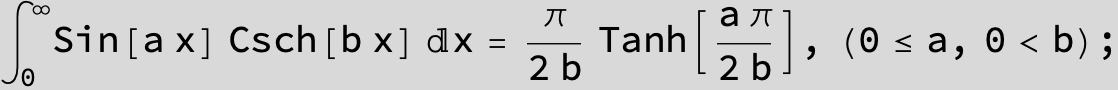
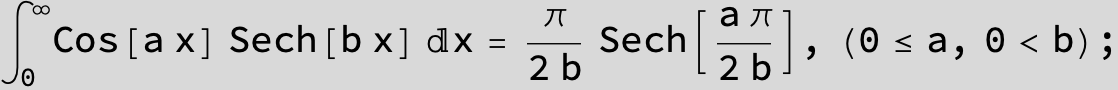
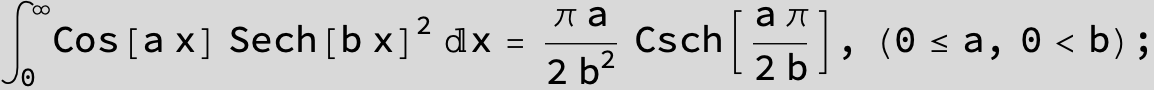
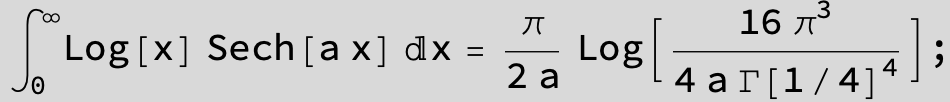
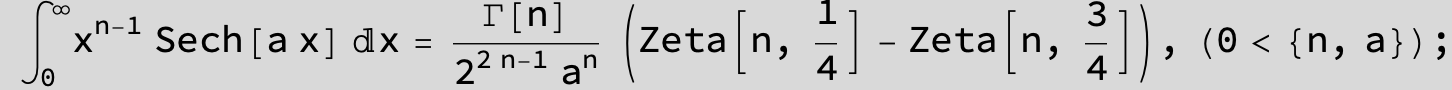
![]()
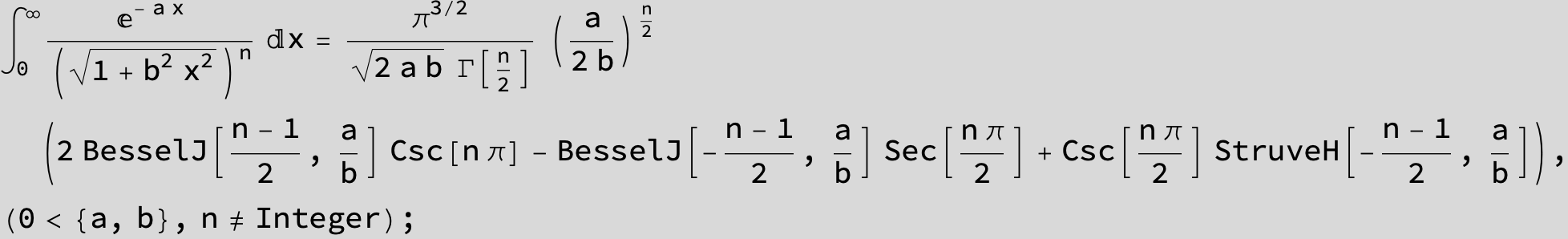
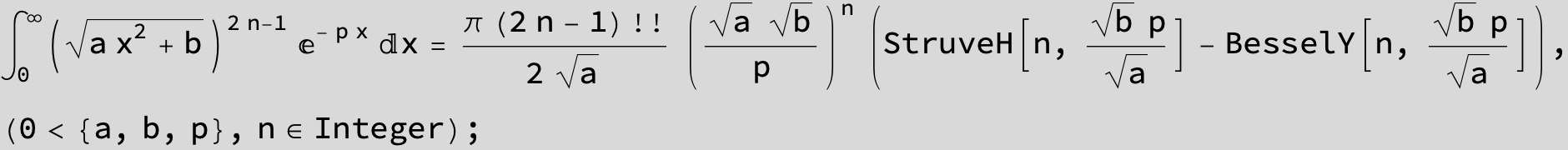
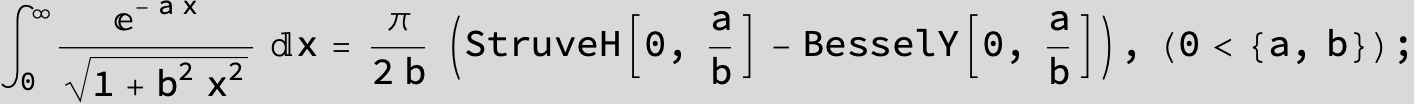
-- 4 ![]() times the above integral gives the circumference of Cassini' s curve --
times the above integral gives the circumference of Cassini' s curve --
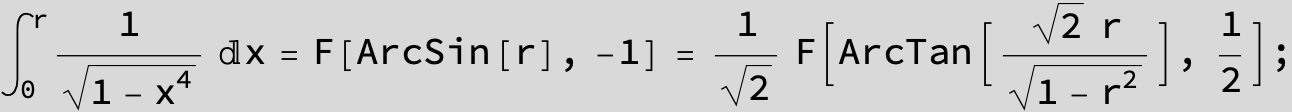
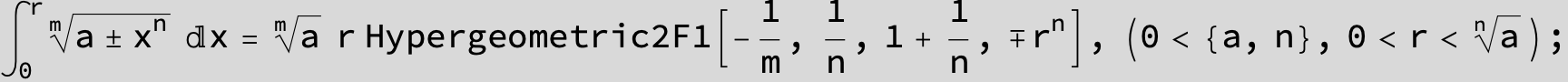
![]()
![]()
![]()
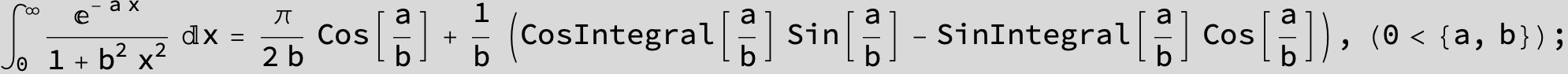
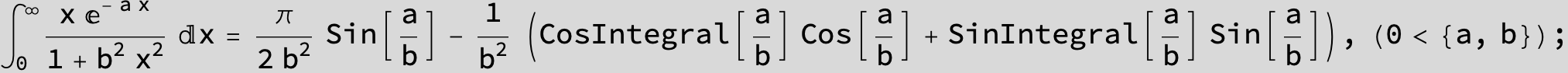



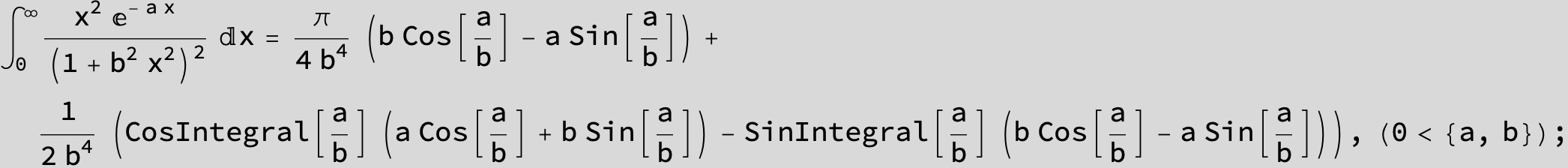

![]()
![]()
![]()

![]()
![]()
![]()
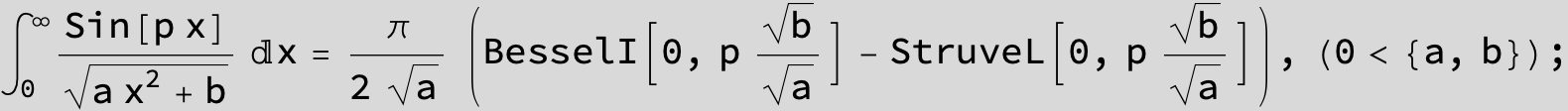
![]()
![]()


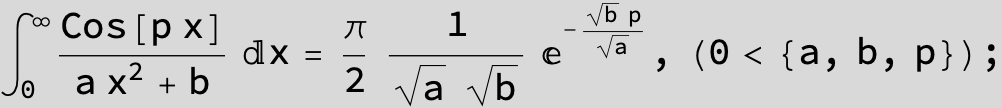


![]()

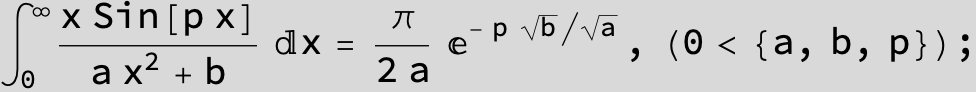
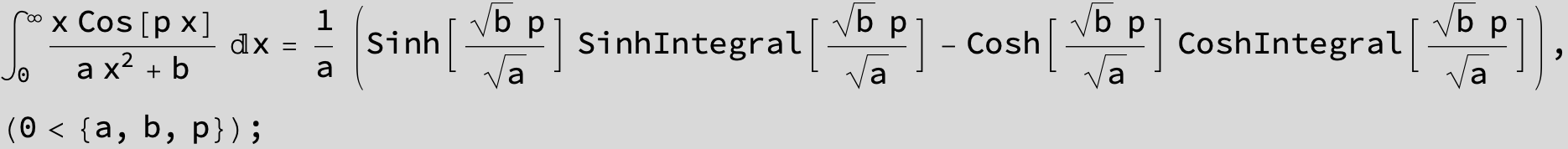
![]()
![]()
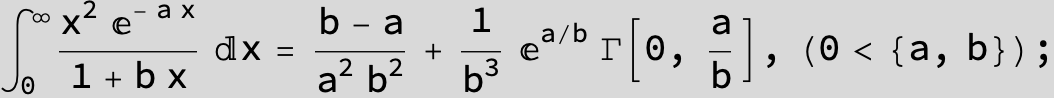

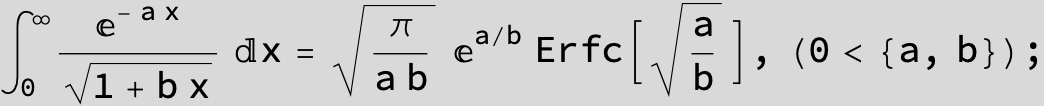
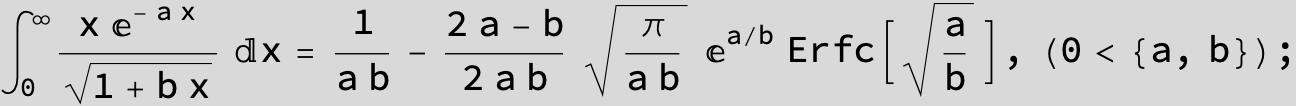
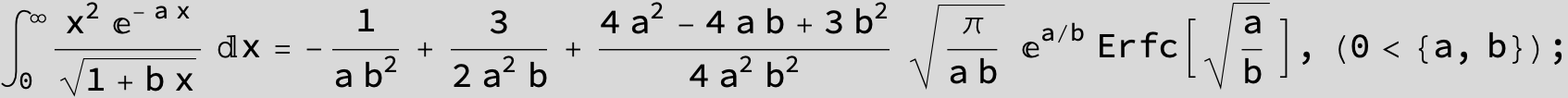
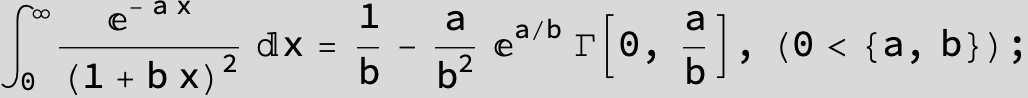
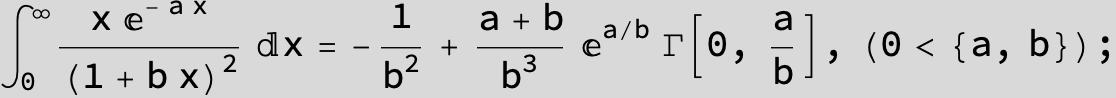
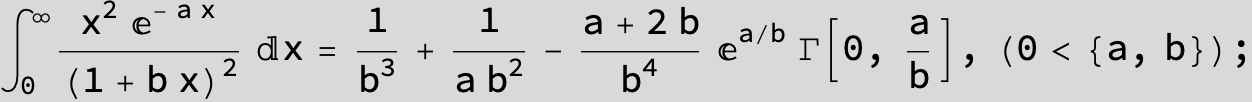
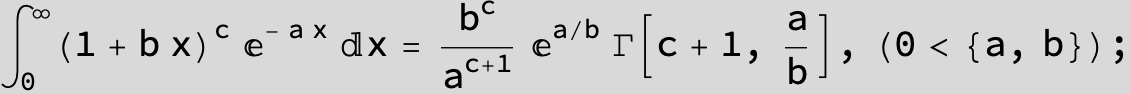

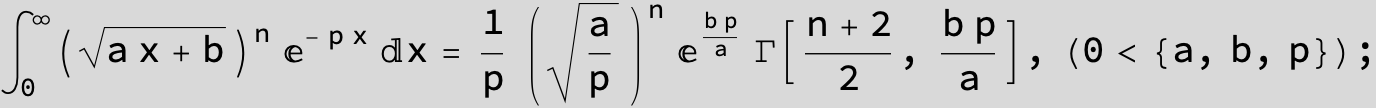
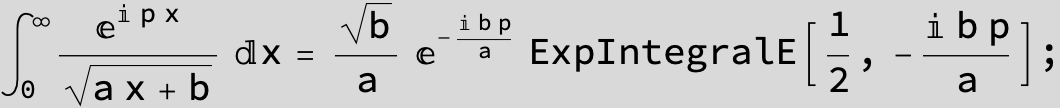
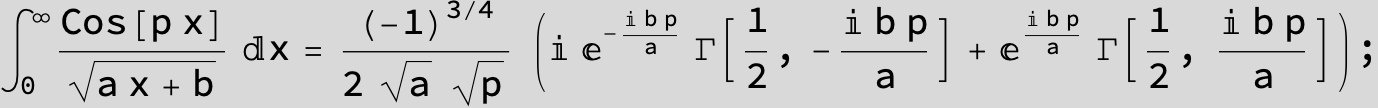
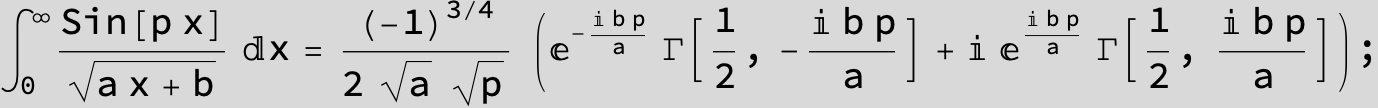


![]()
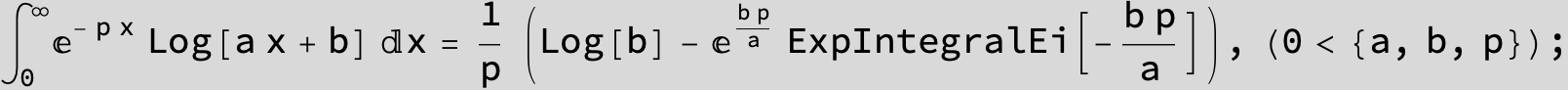
![]()
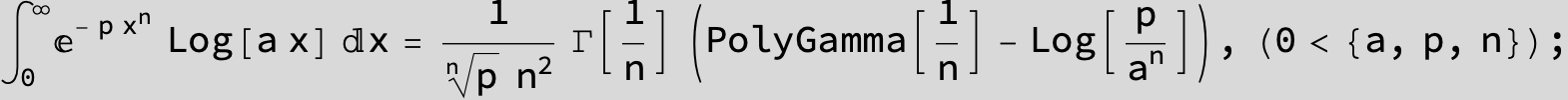
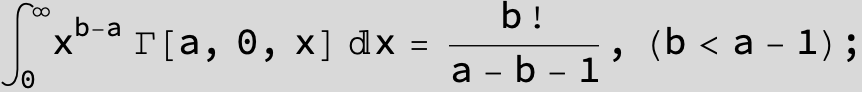
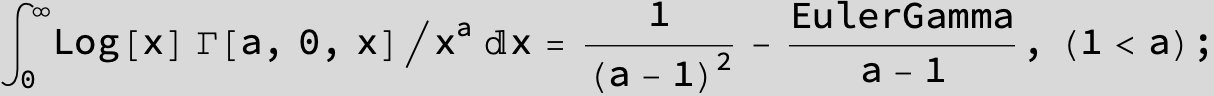
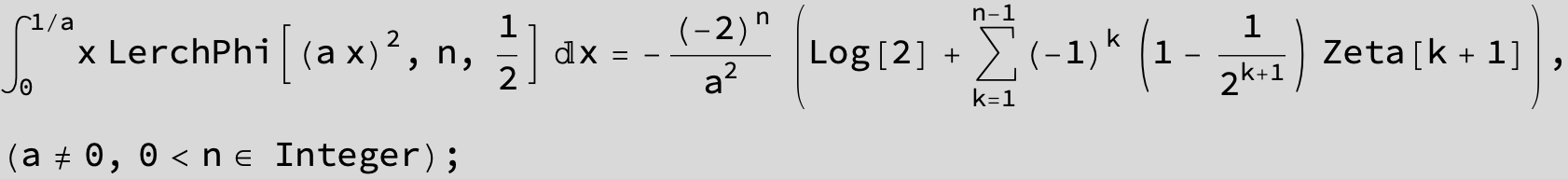
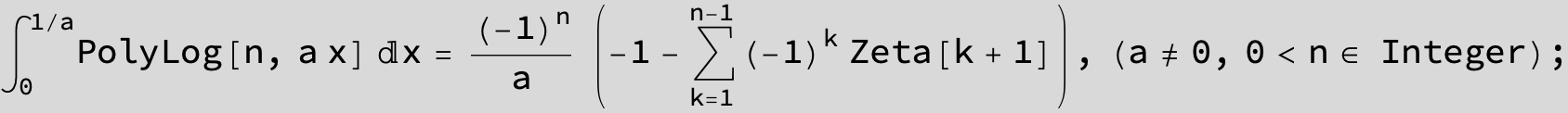
![]()
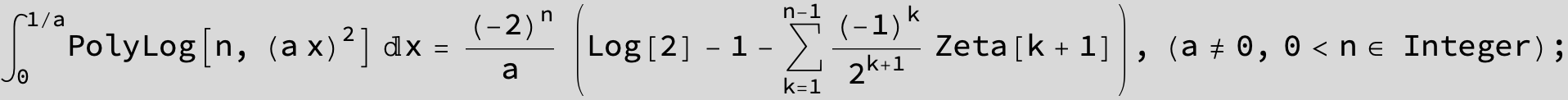
![]()
![]()
![]()
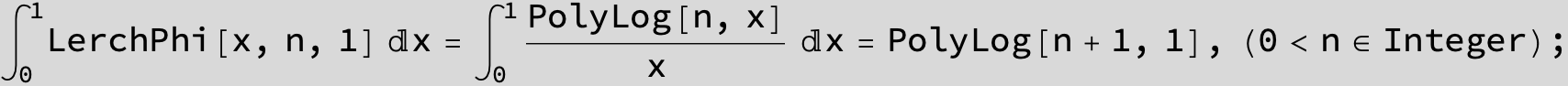
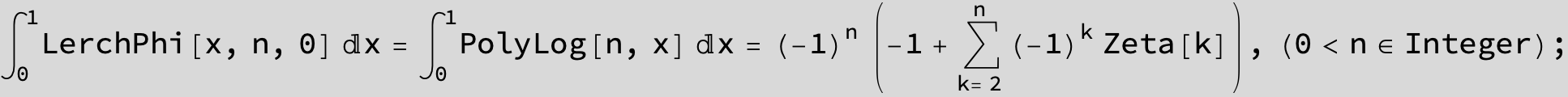

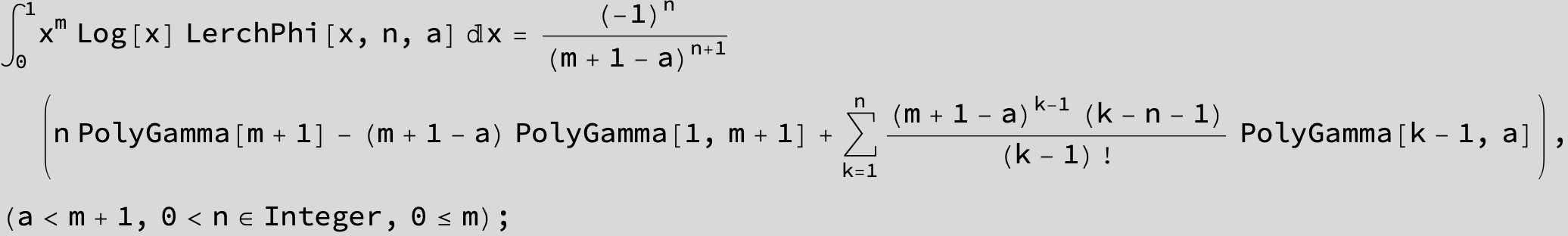
![]()
![]()
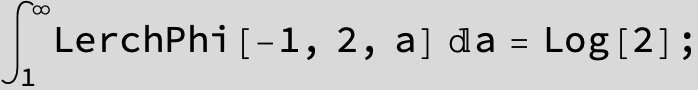
![]()


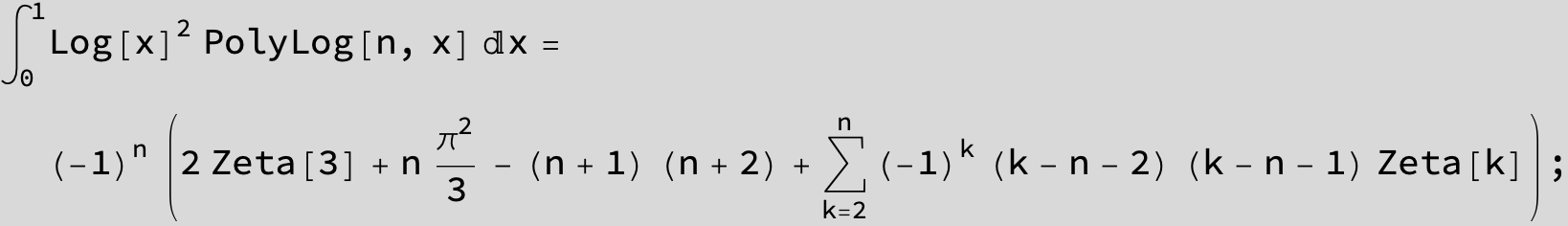
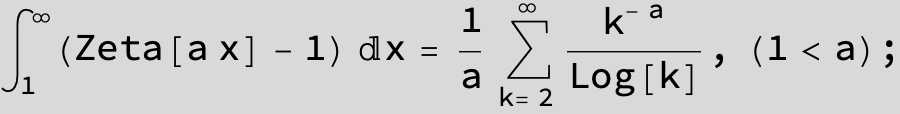
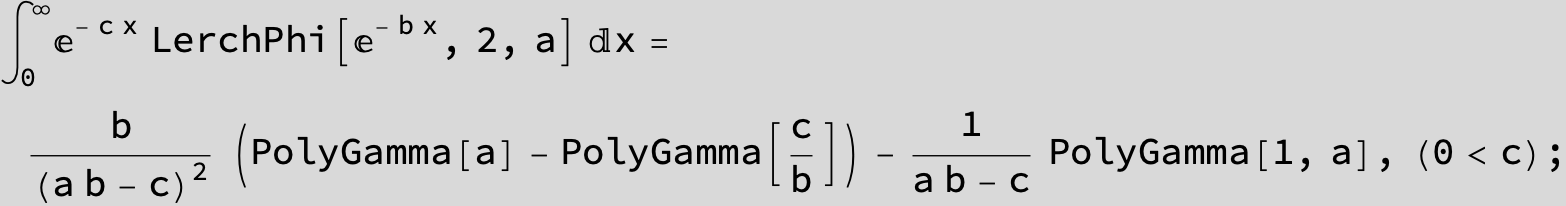
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()

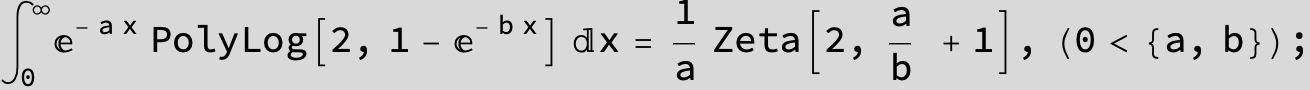
![]()
![]()
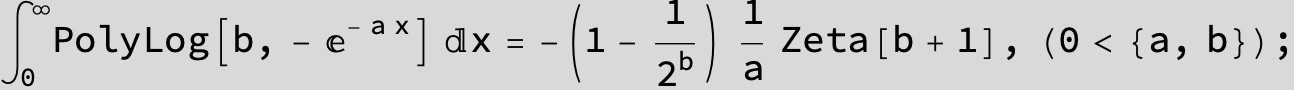
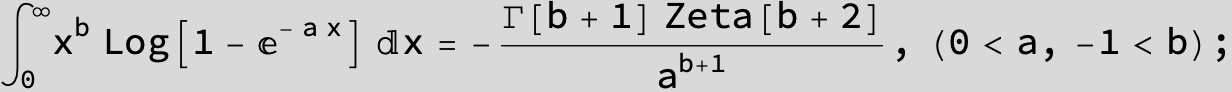

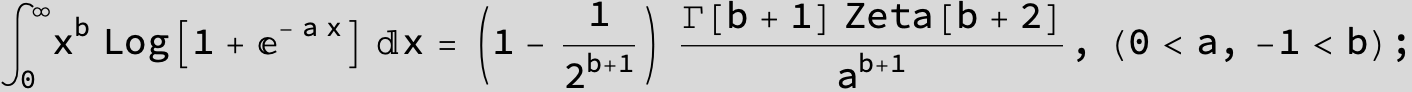
![]()
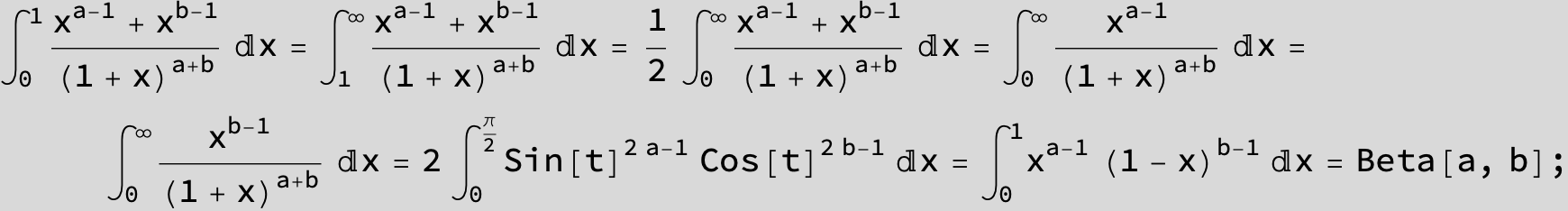
![]()
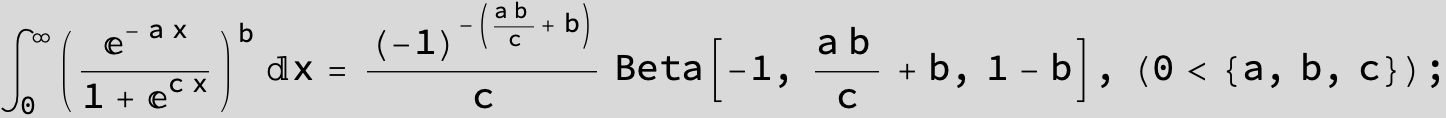
![]()
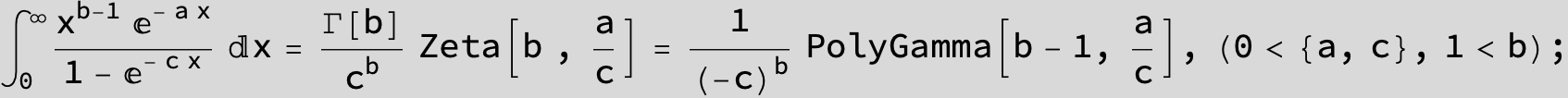
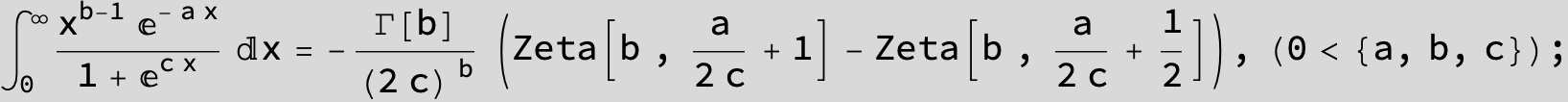
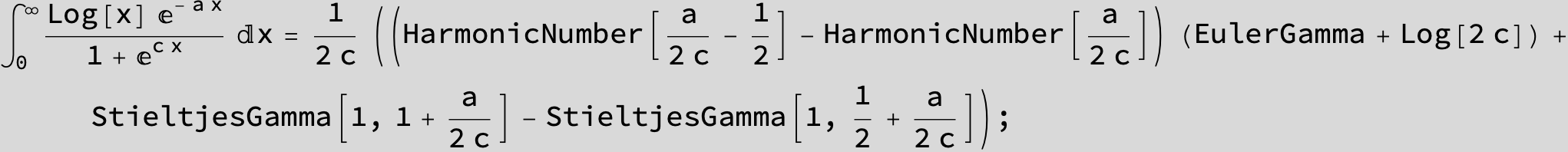
![]()
![]()
![]()
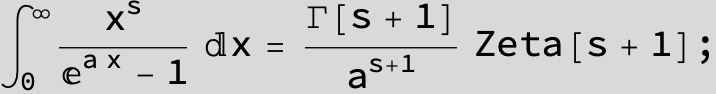
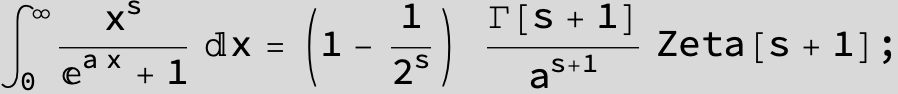
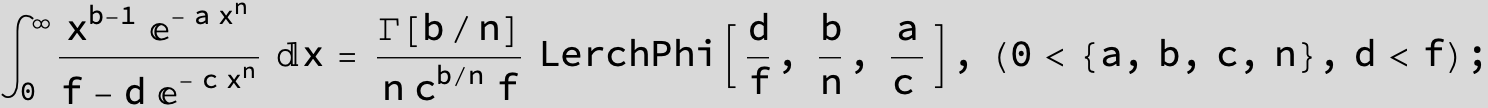
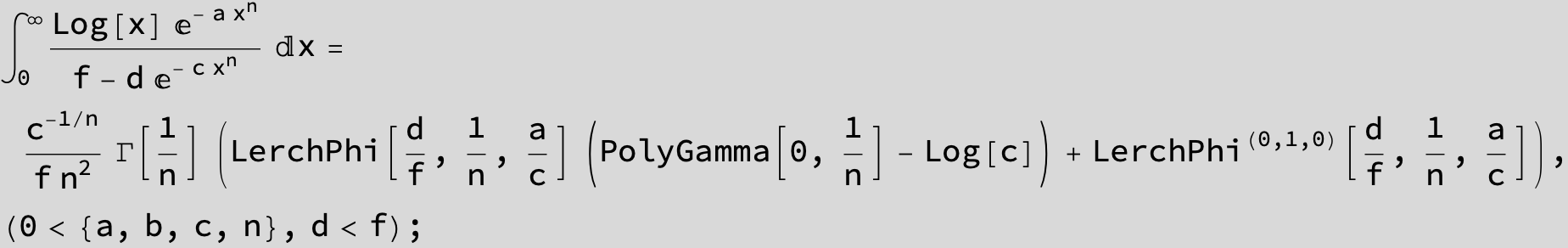
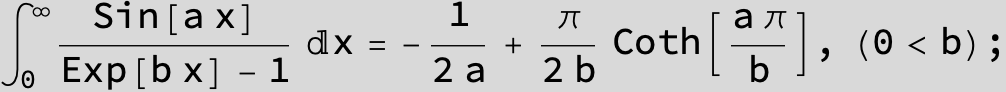
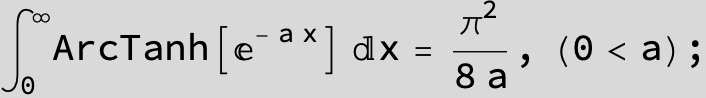
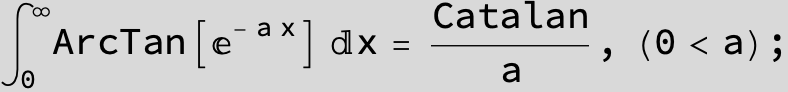
![]()
![]()
![]()
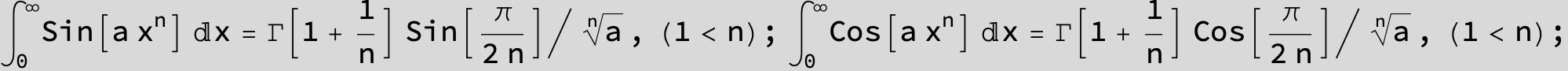
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
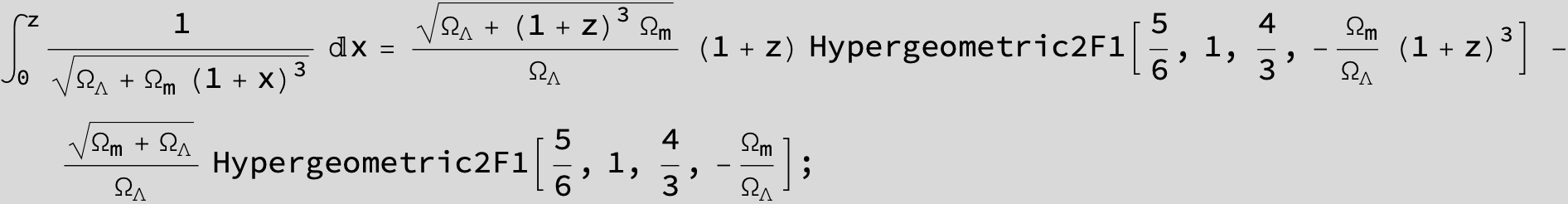
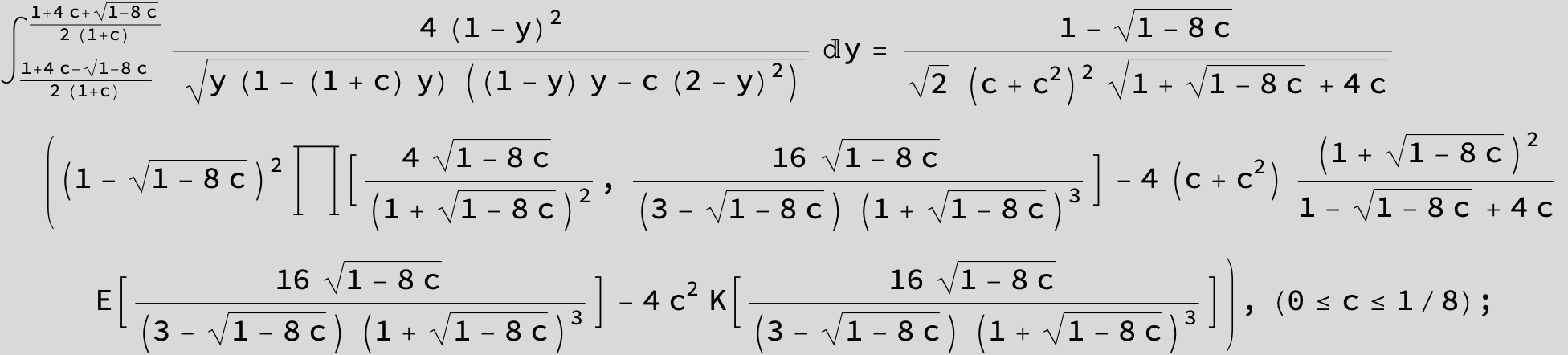
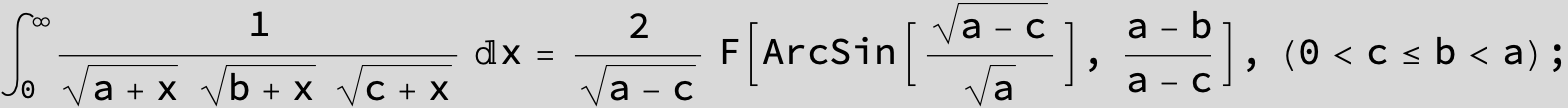
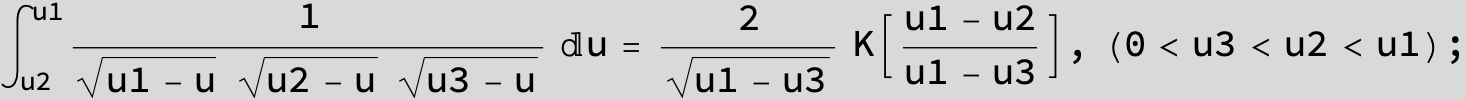
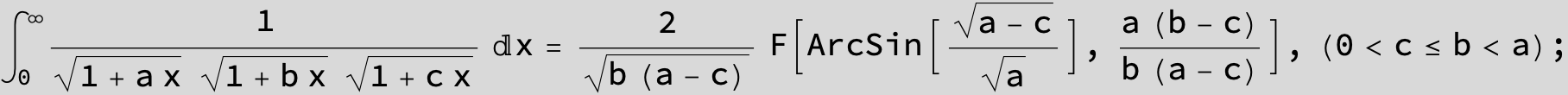
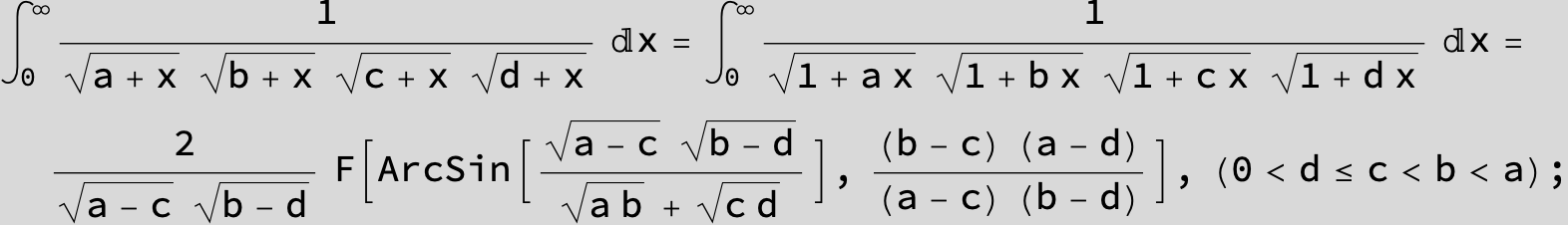
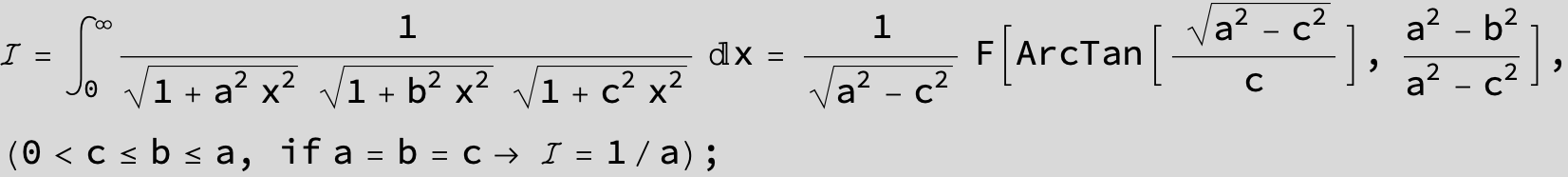
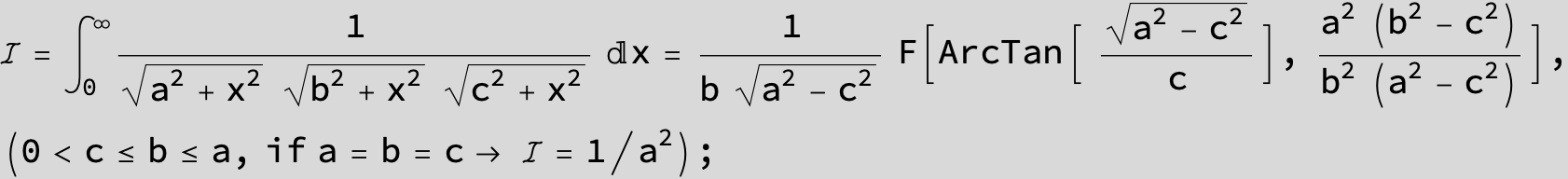
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
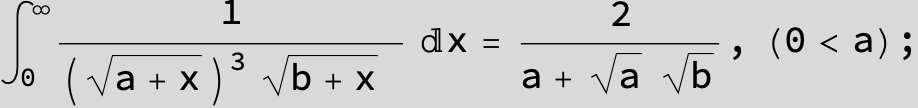
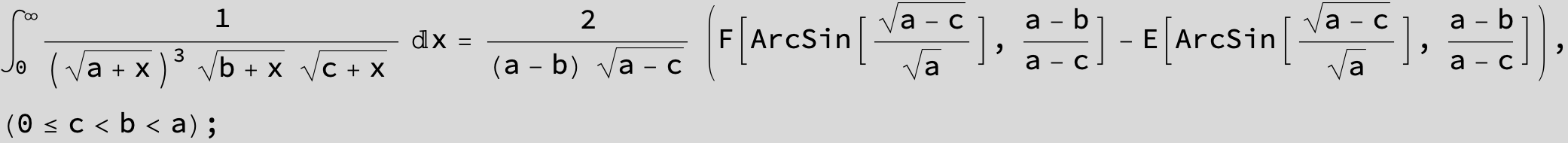
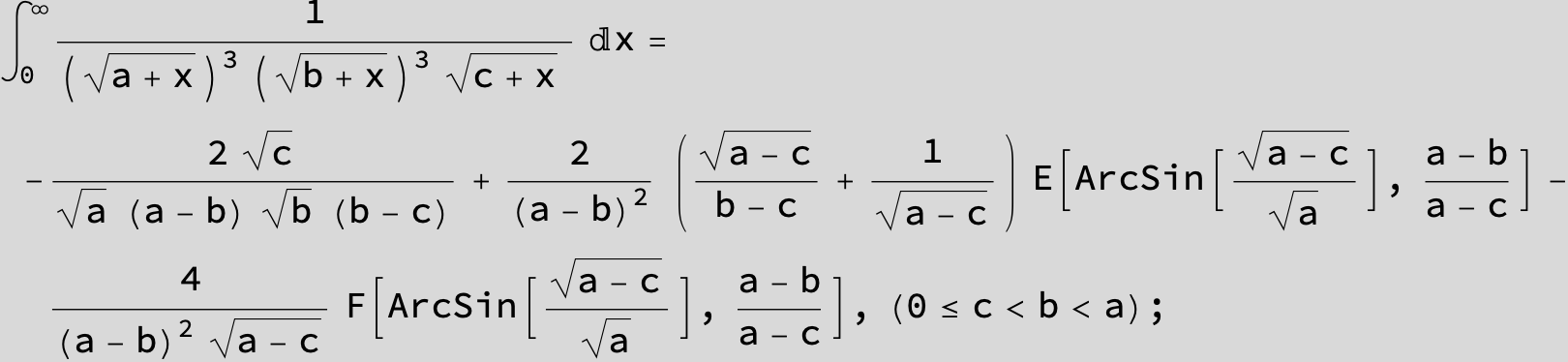
![]()
![]()
![]()
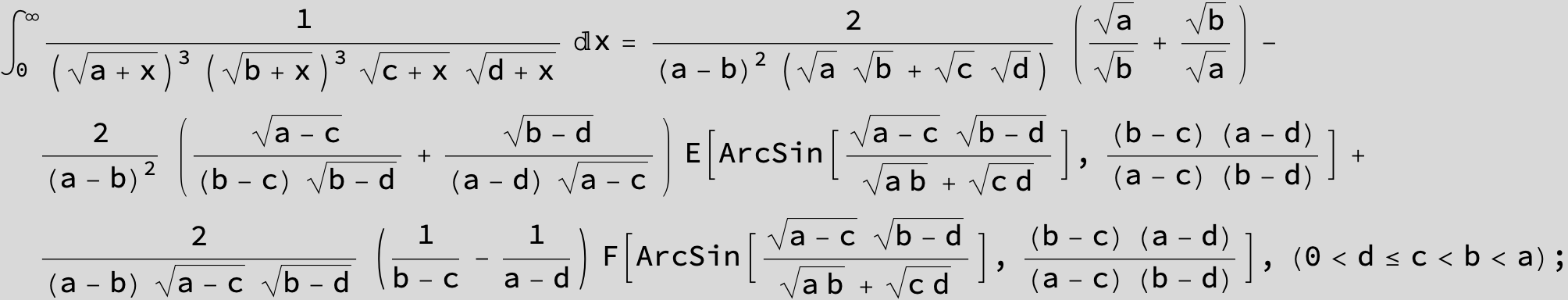
![]()
![]()
![]()
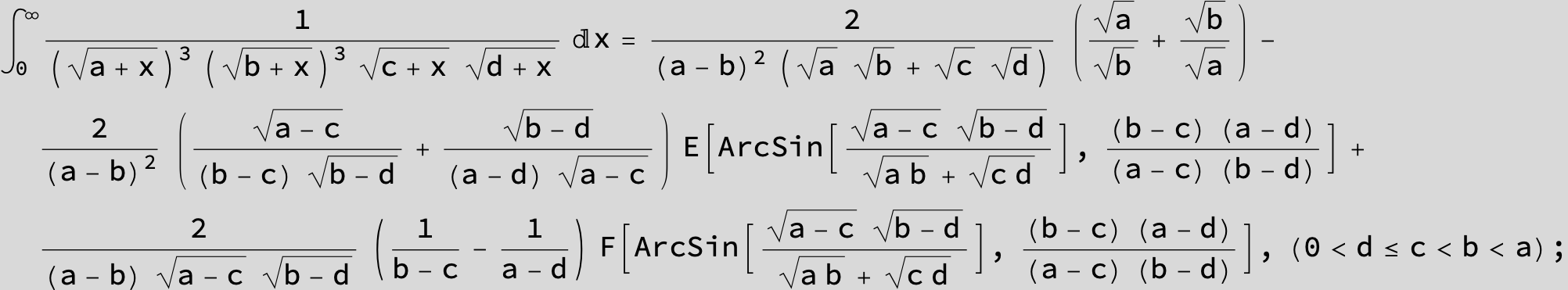
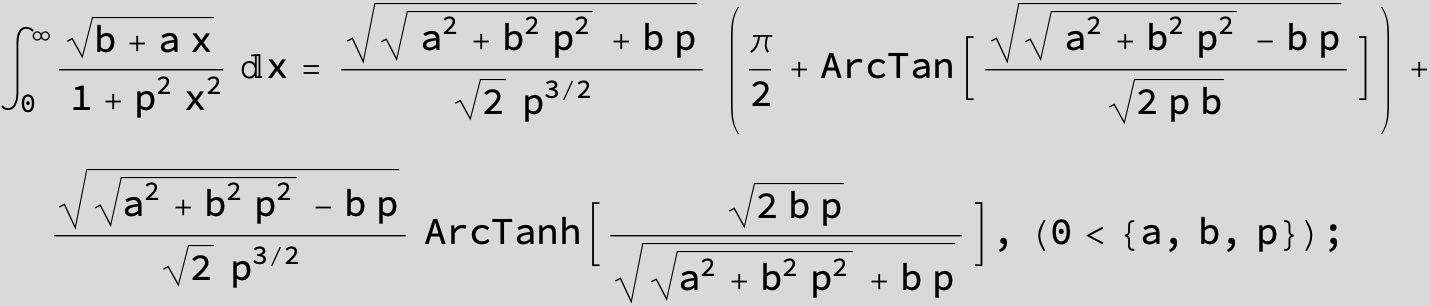
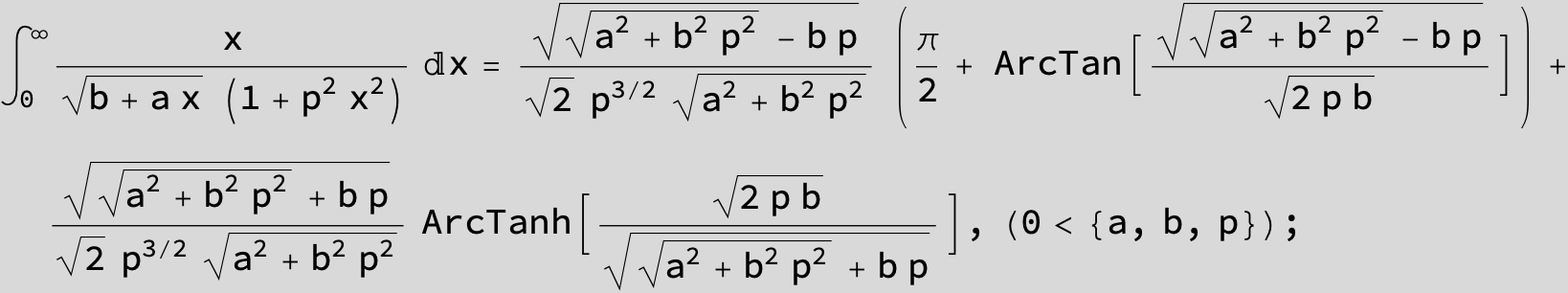
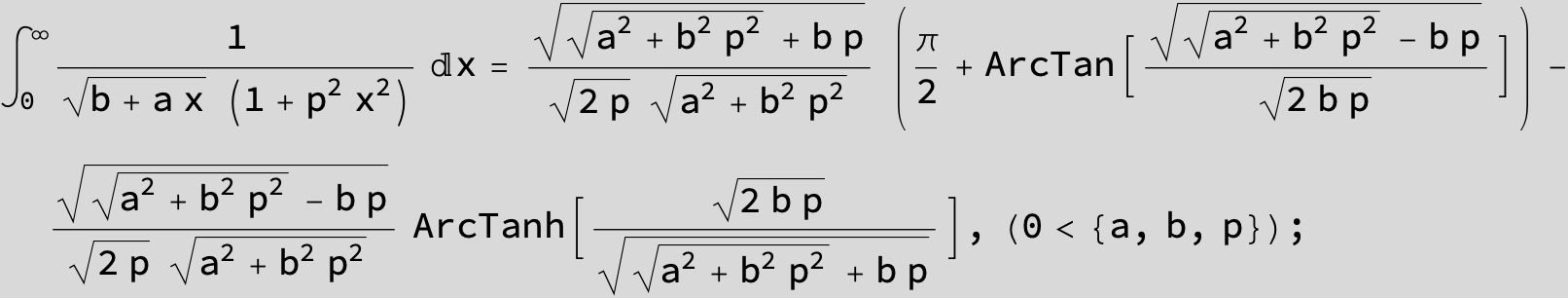
![]()
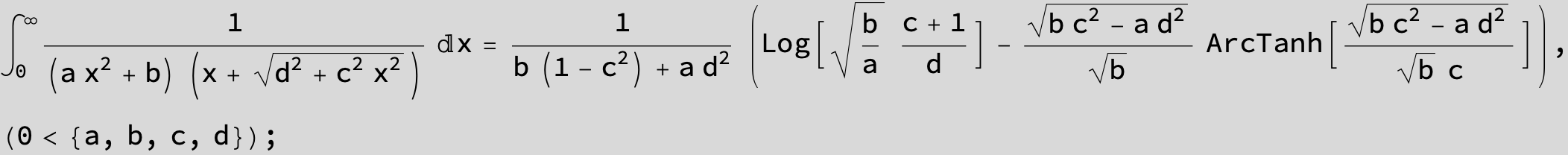
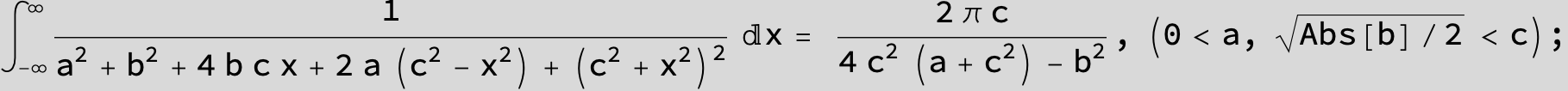
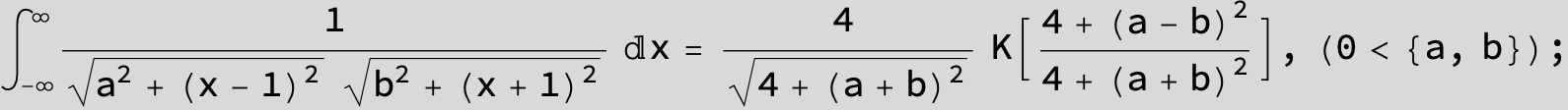
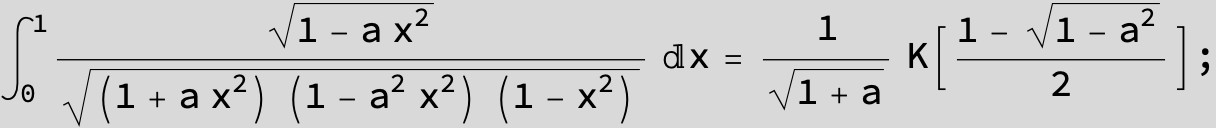
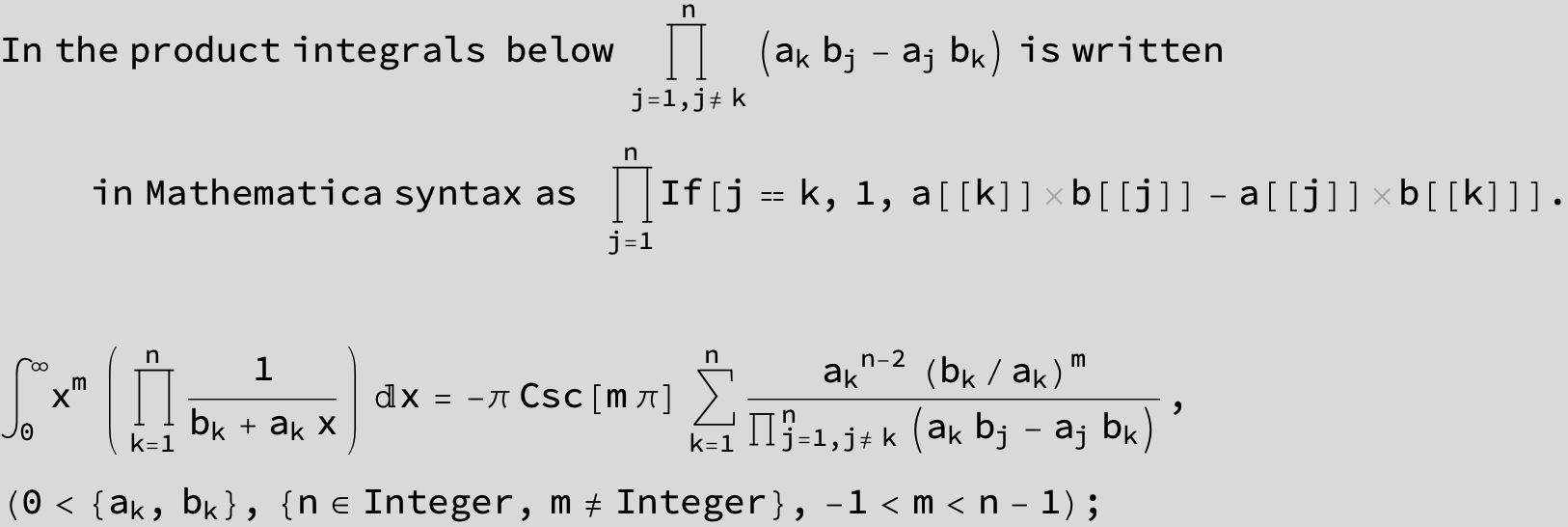
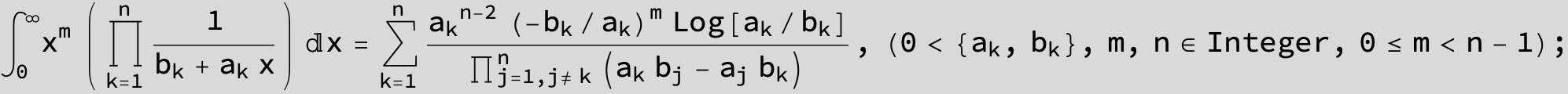
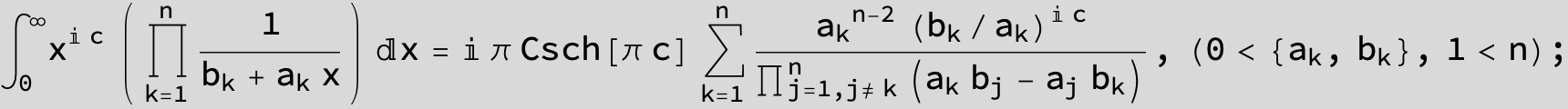
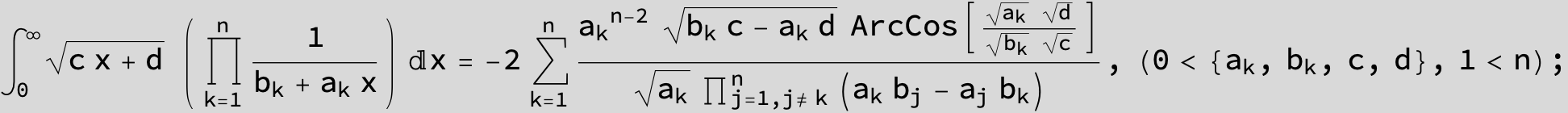
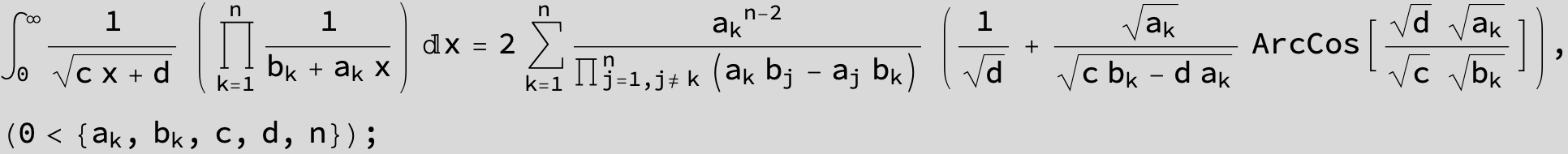
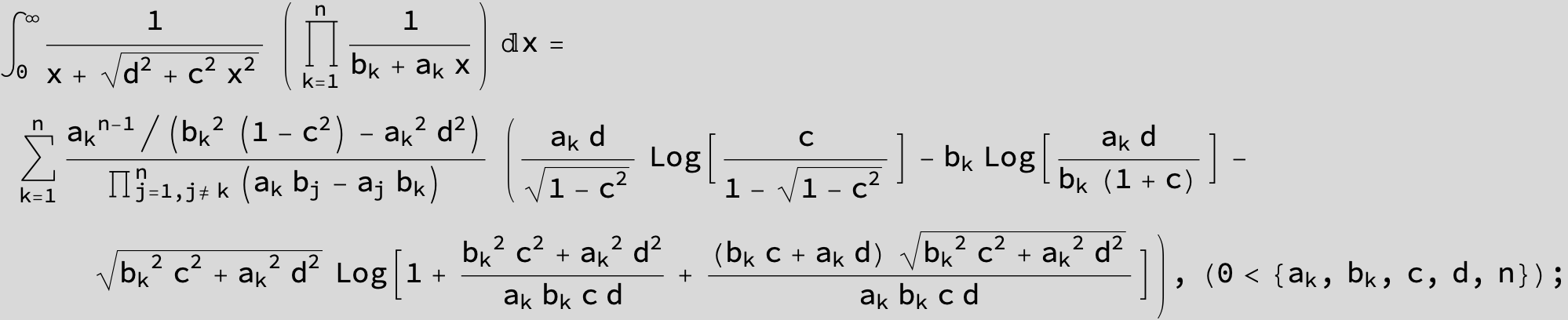
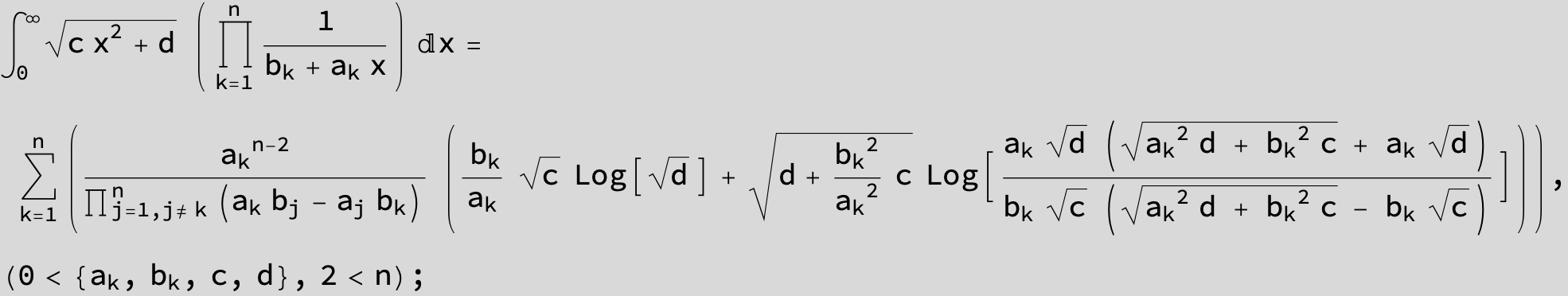
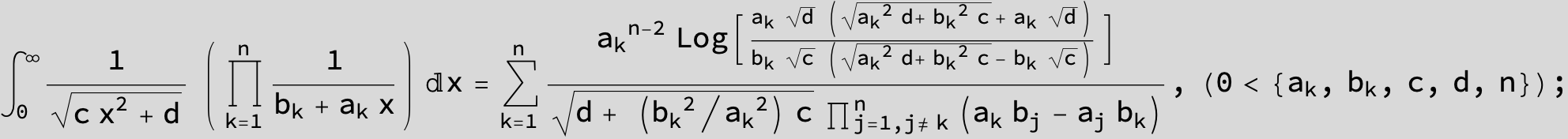
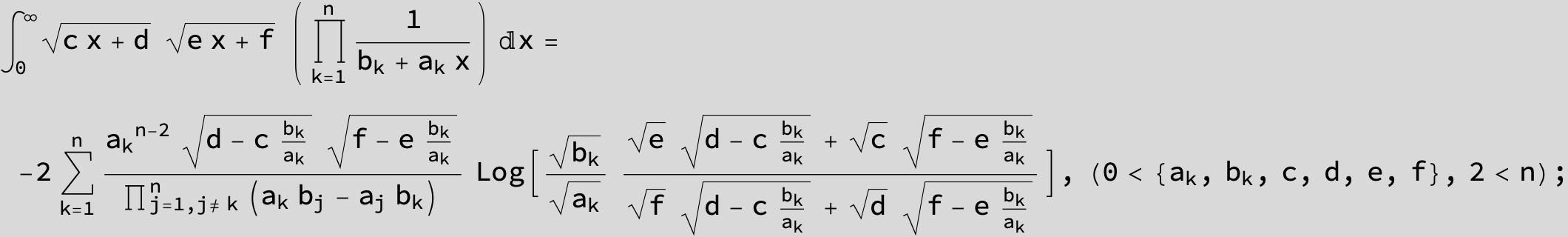
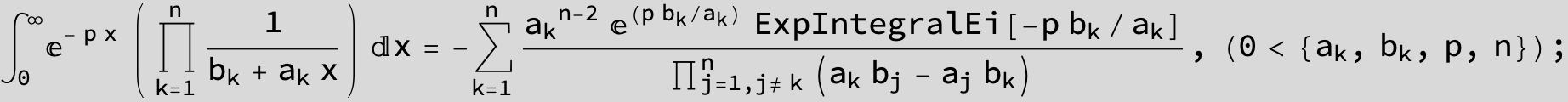
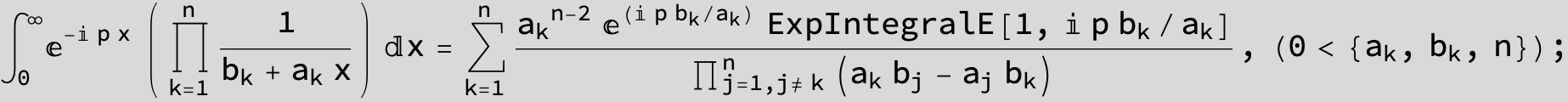
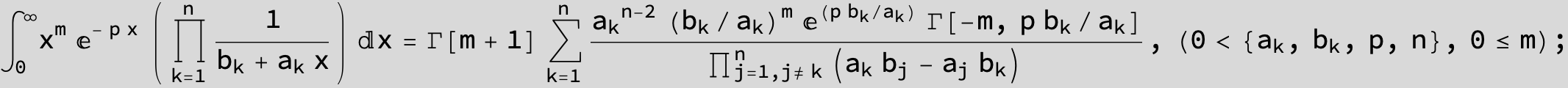
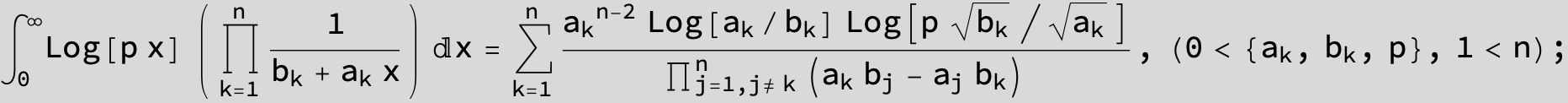

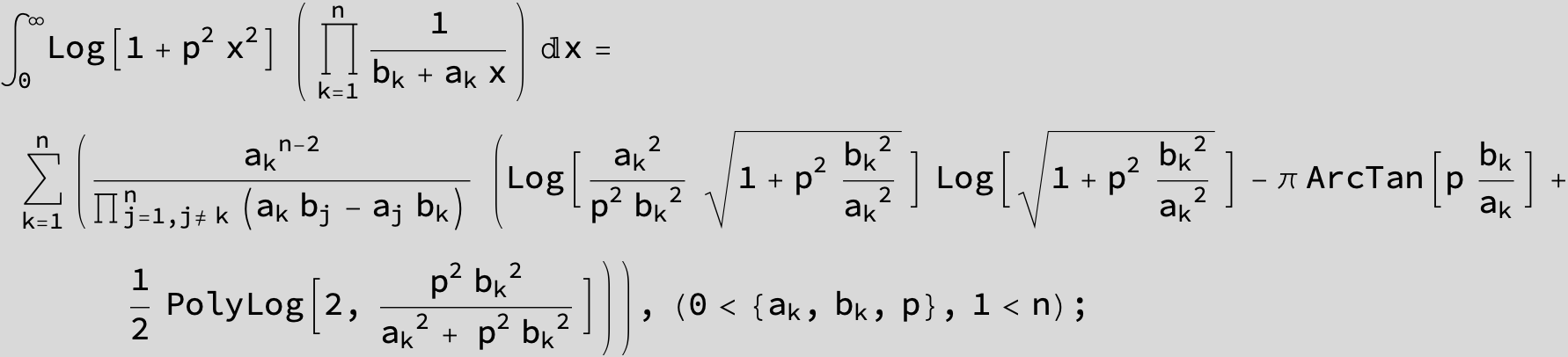
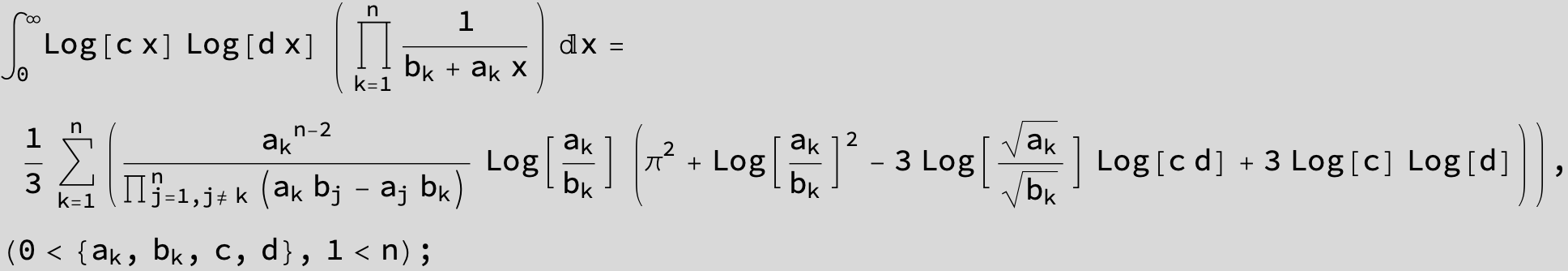
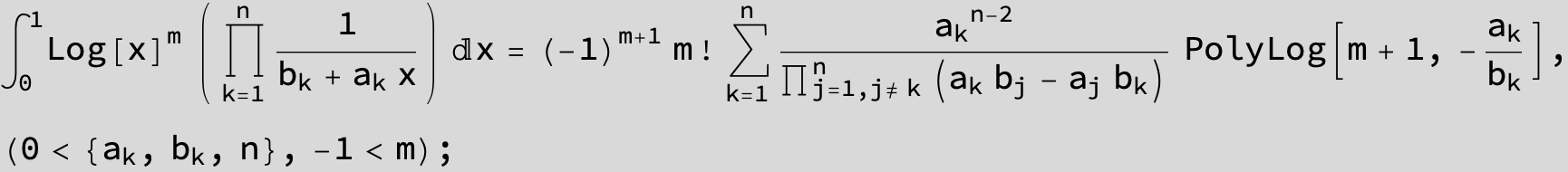


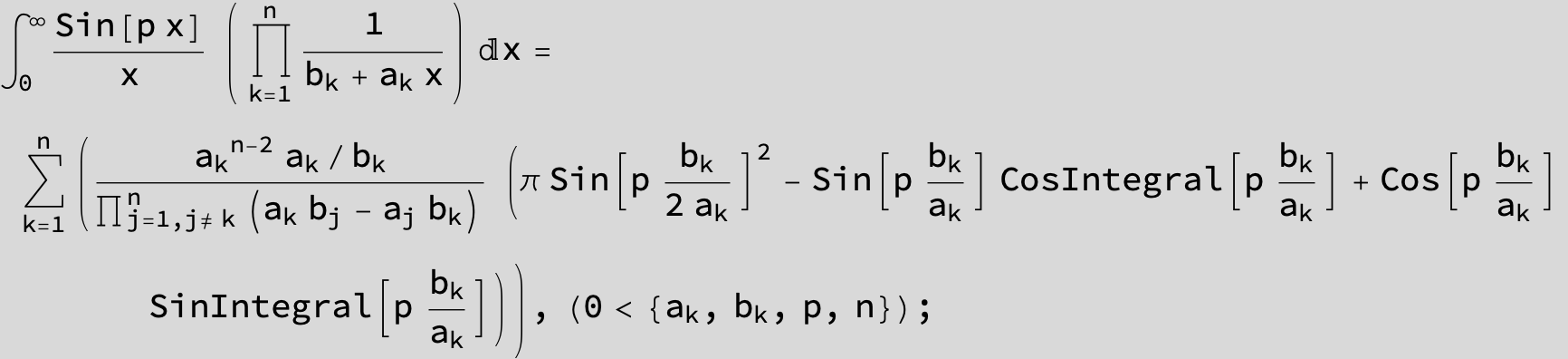
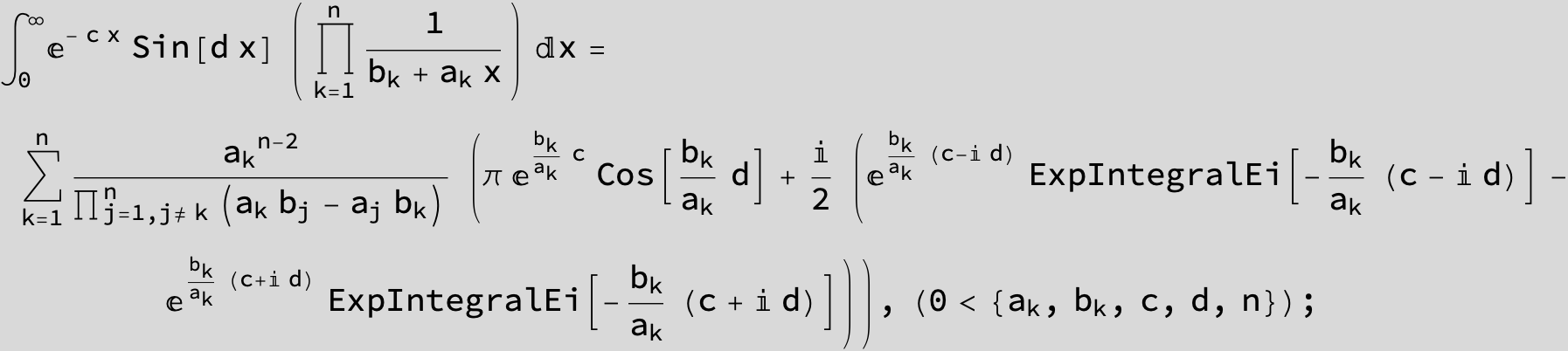
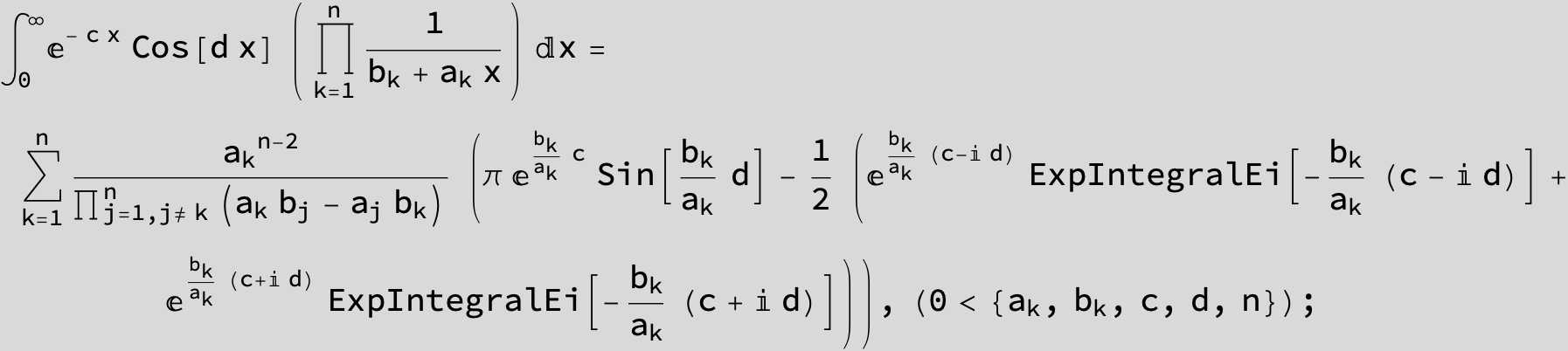
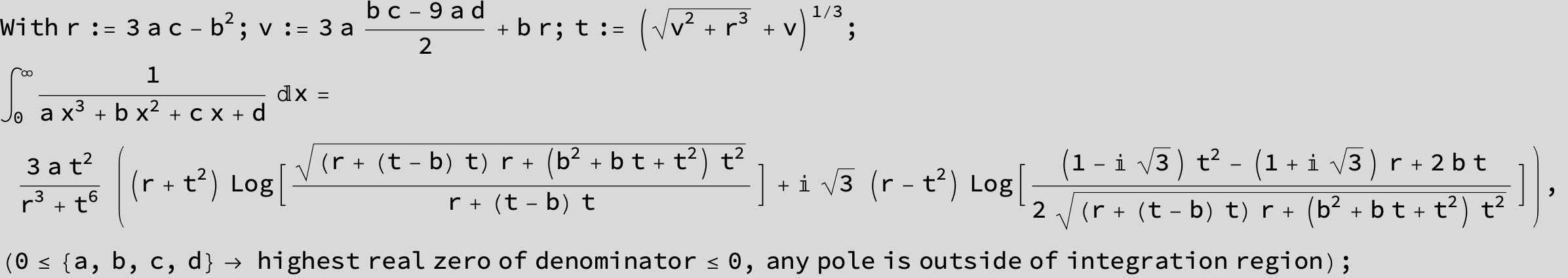
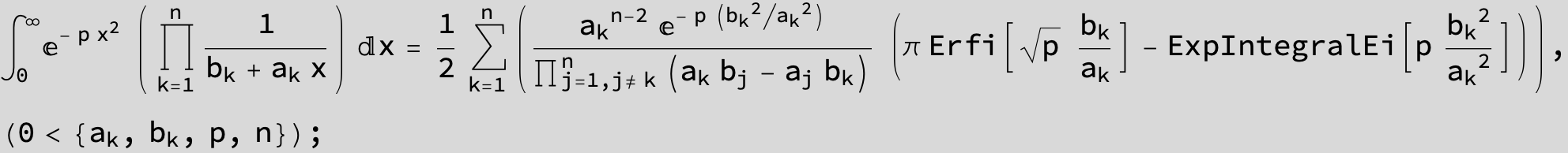
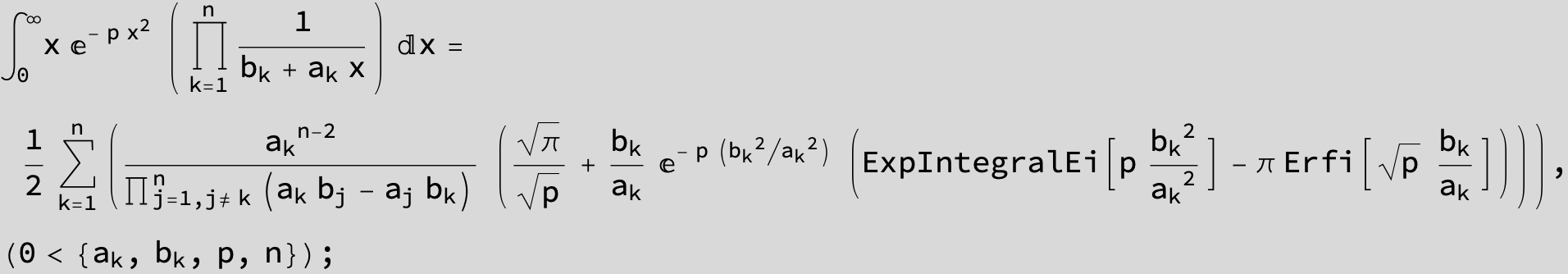
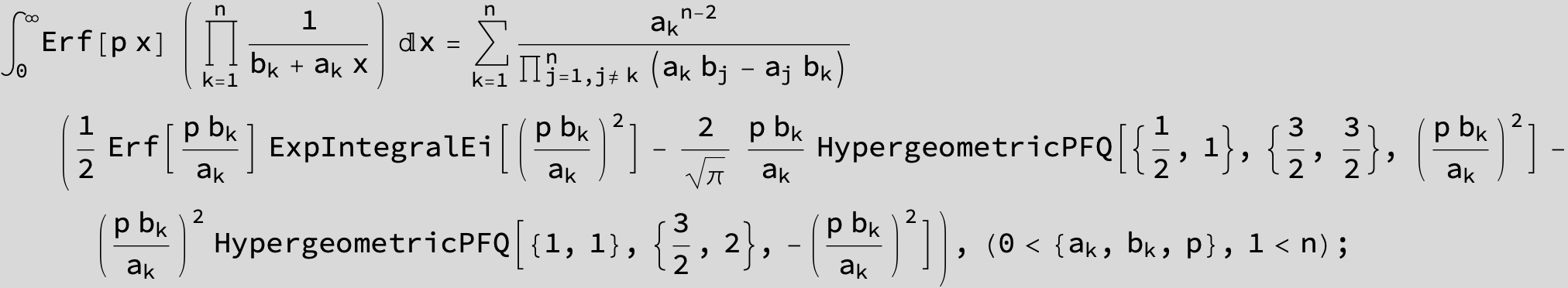

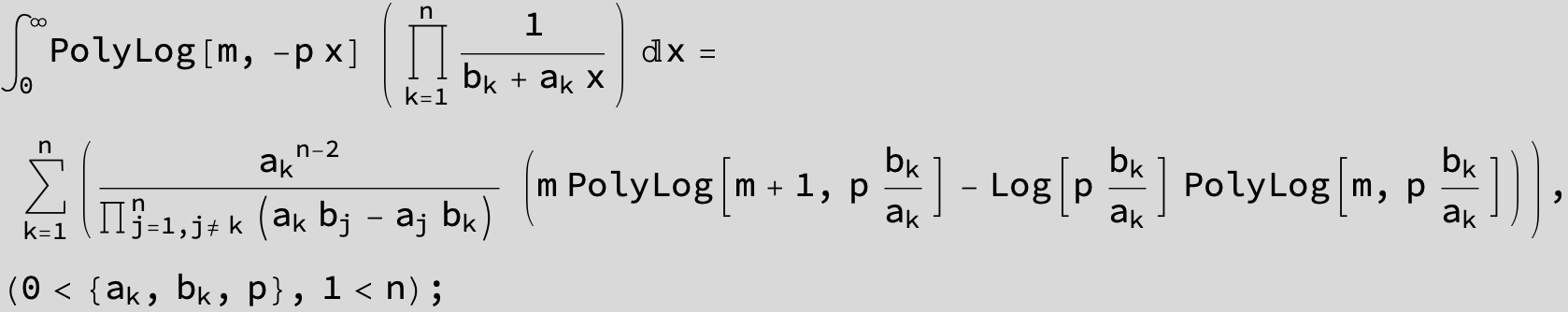
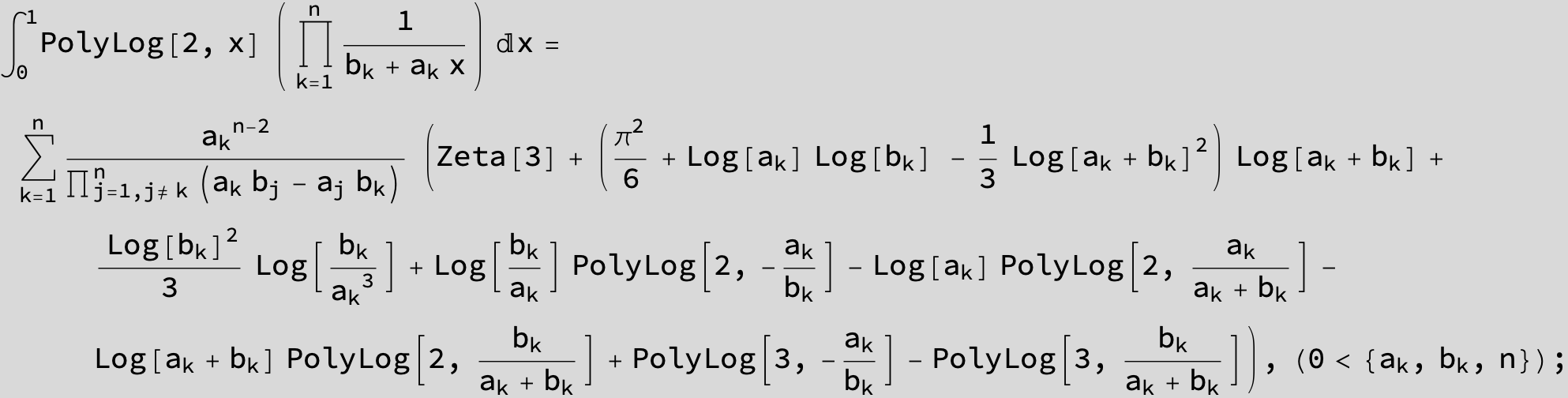

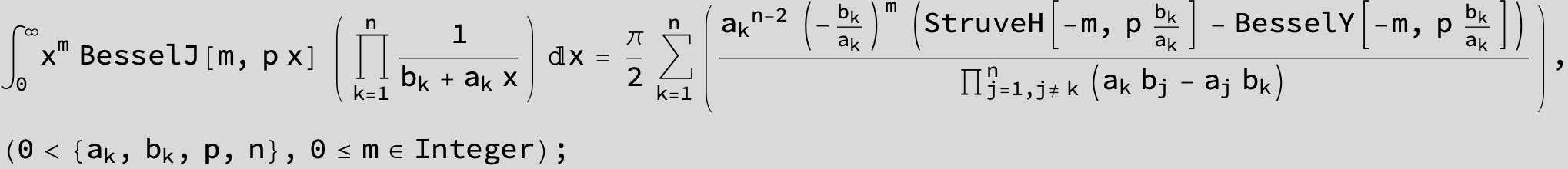


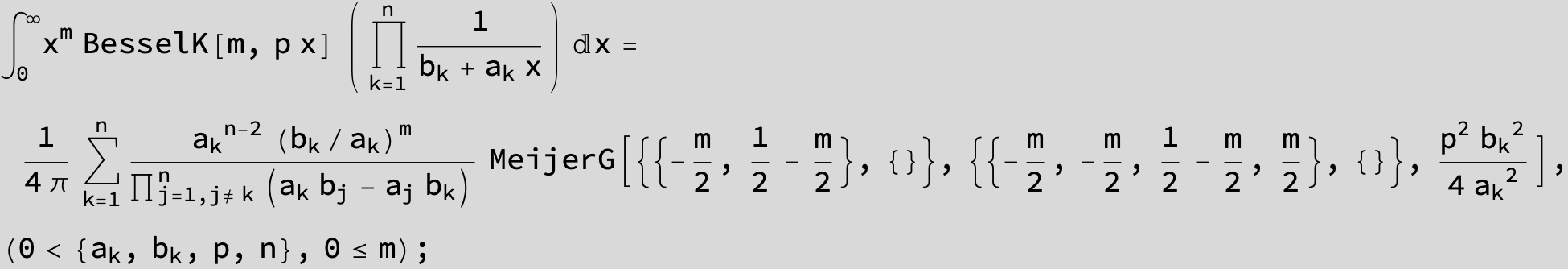
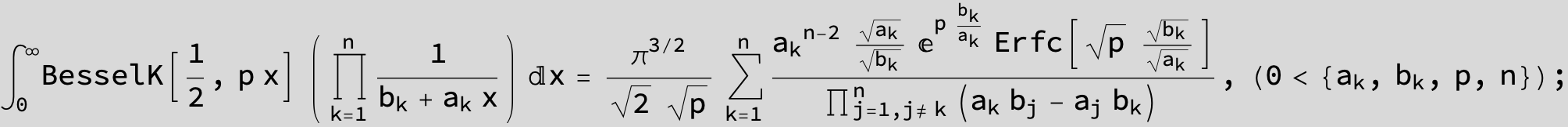
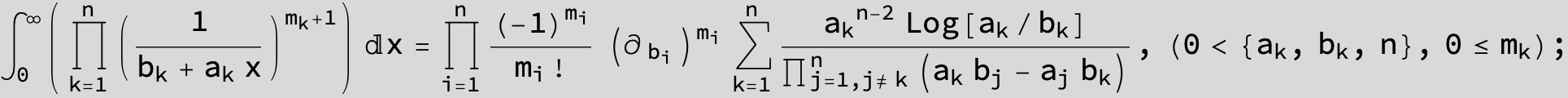

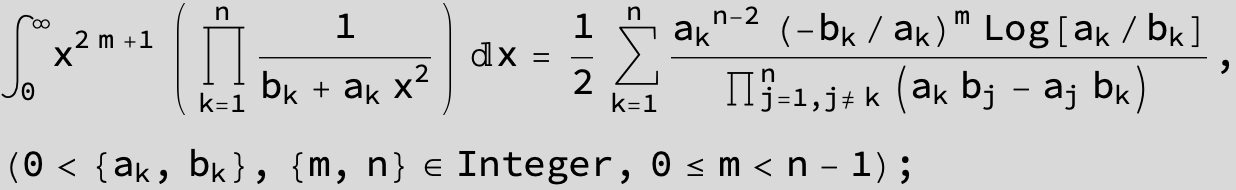
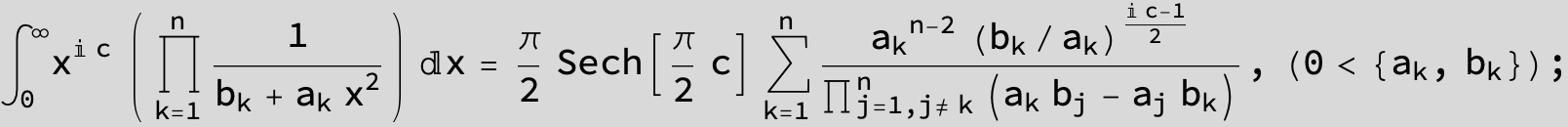
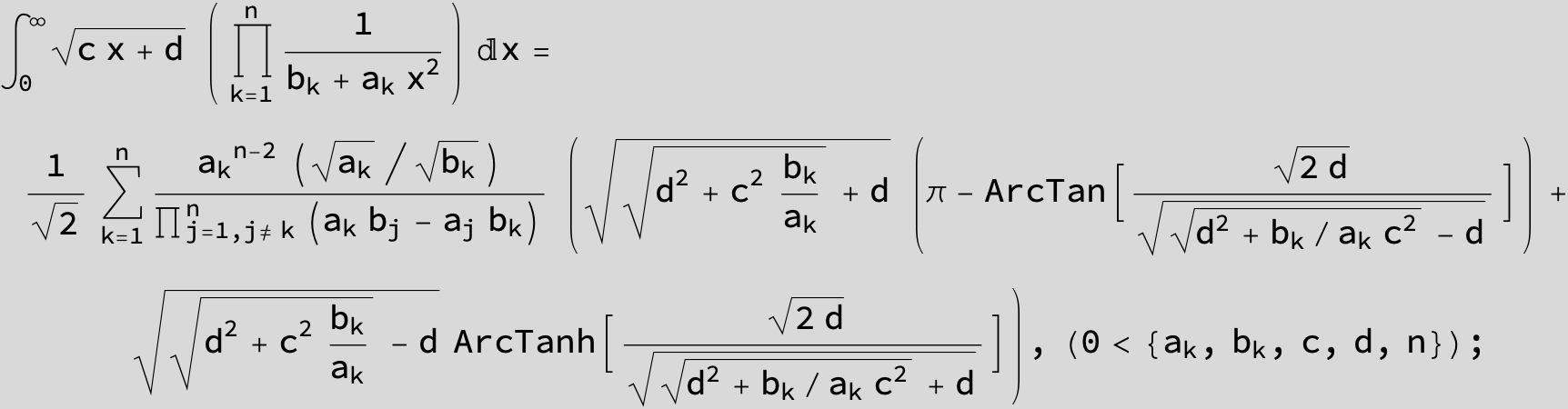

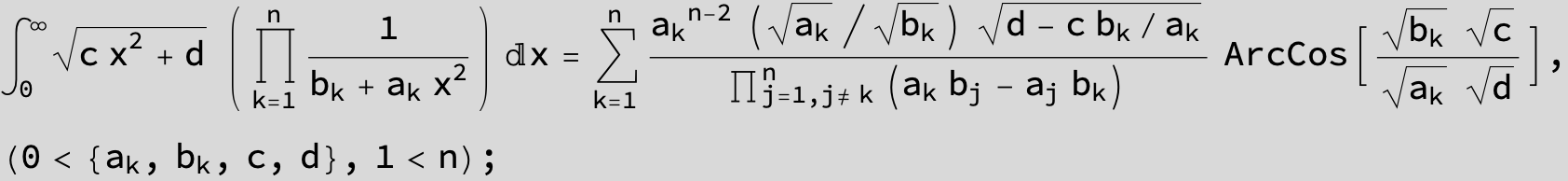
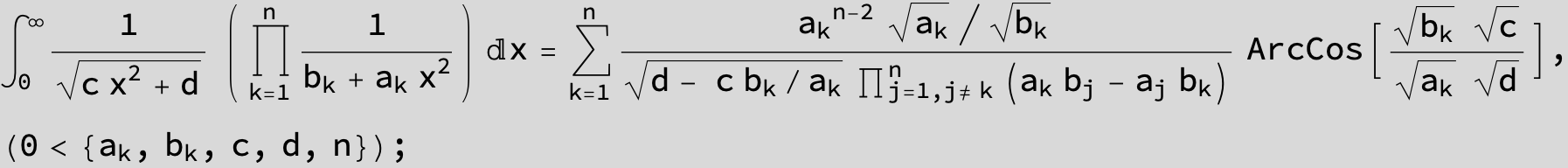

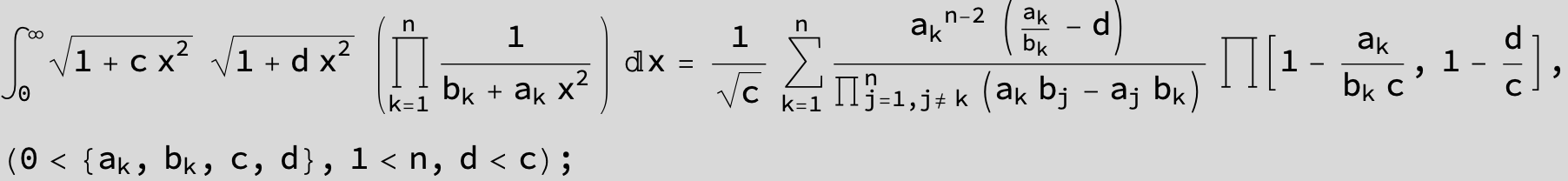
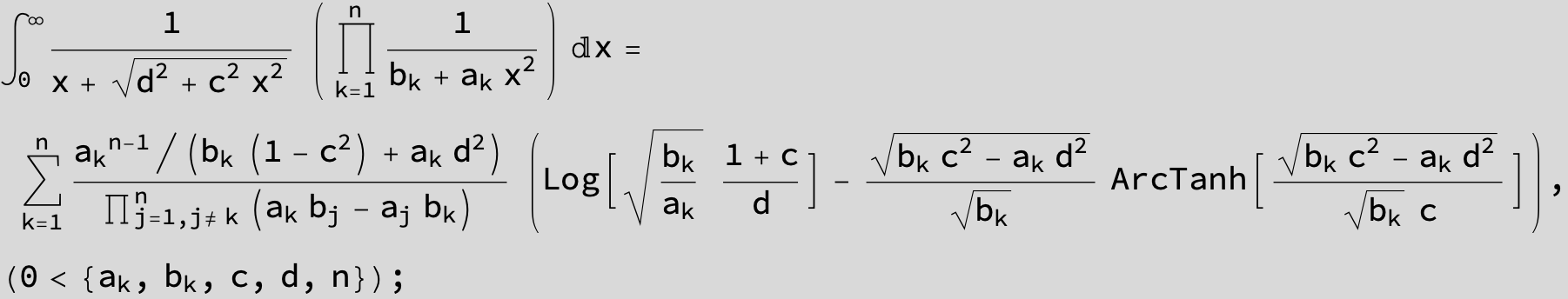
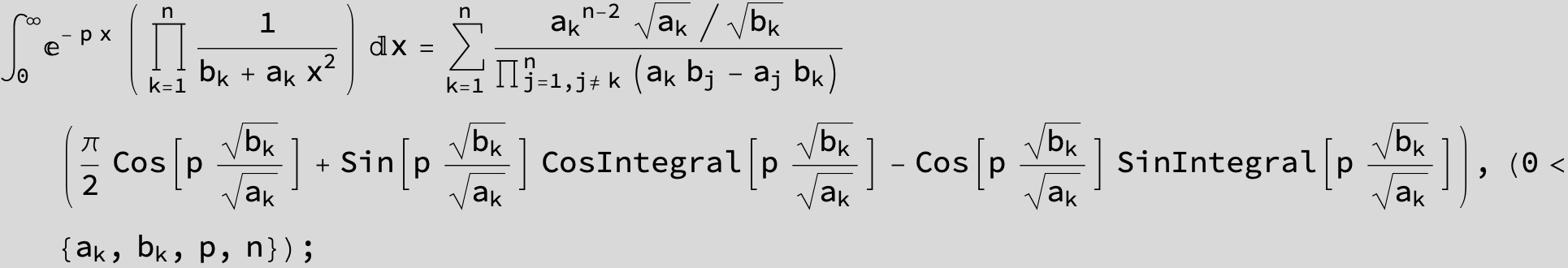
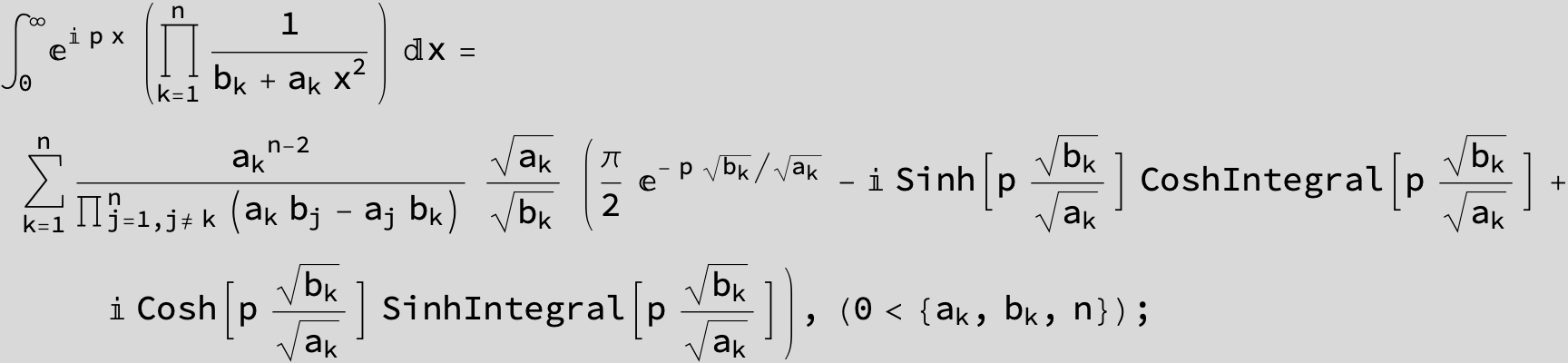
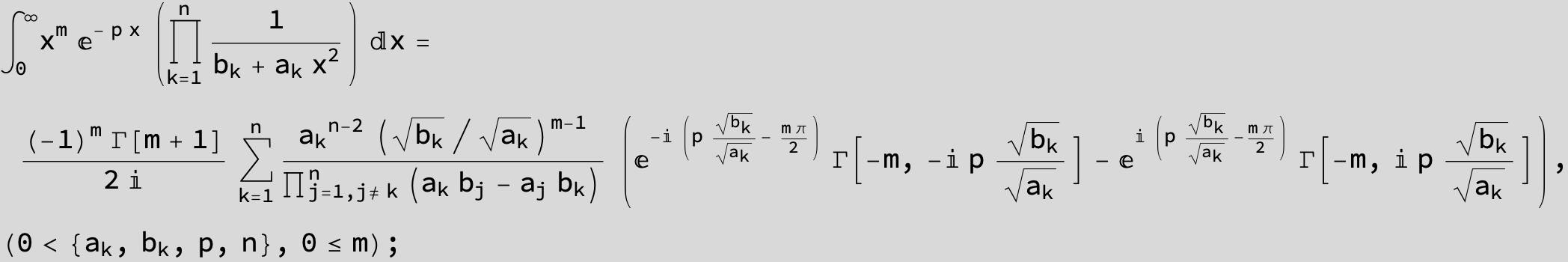
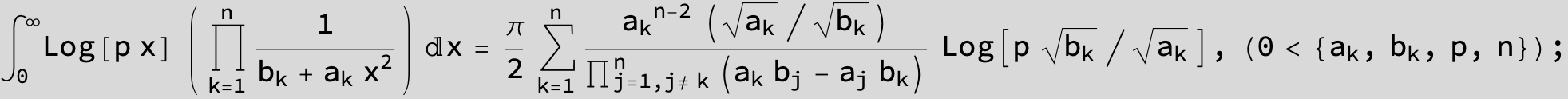
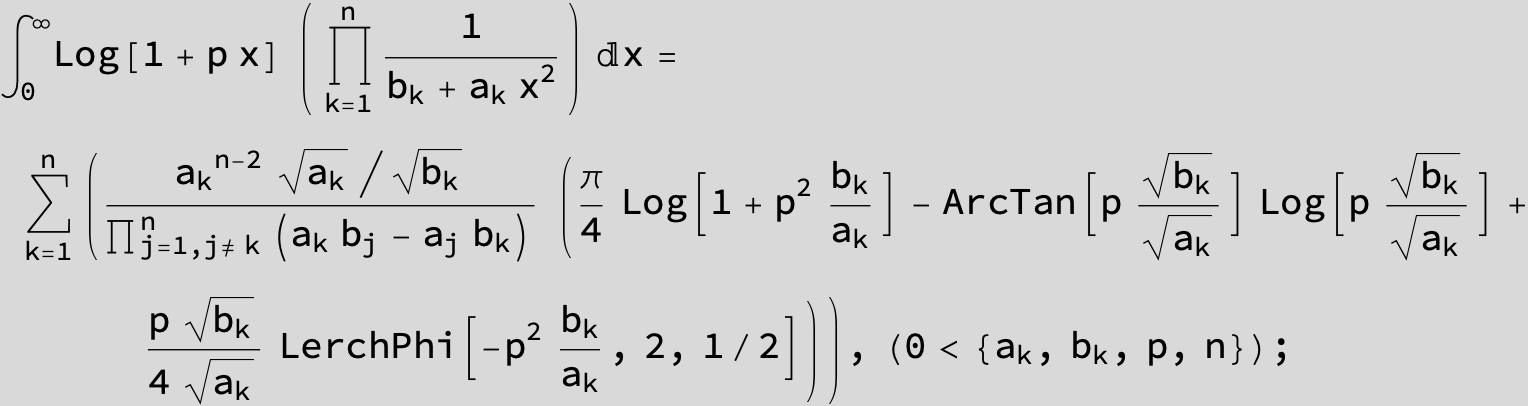
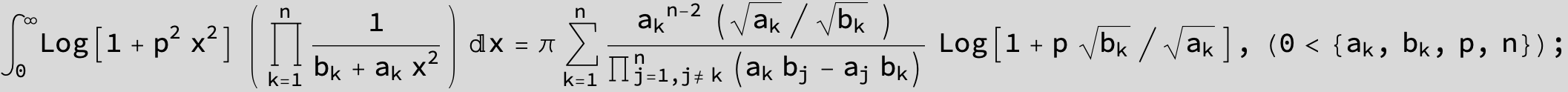
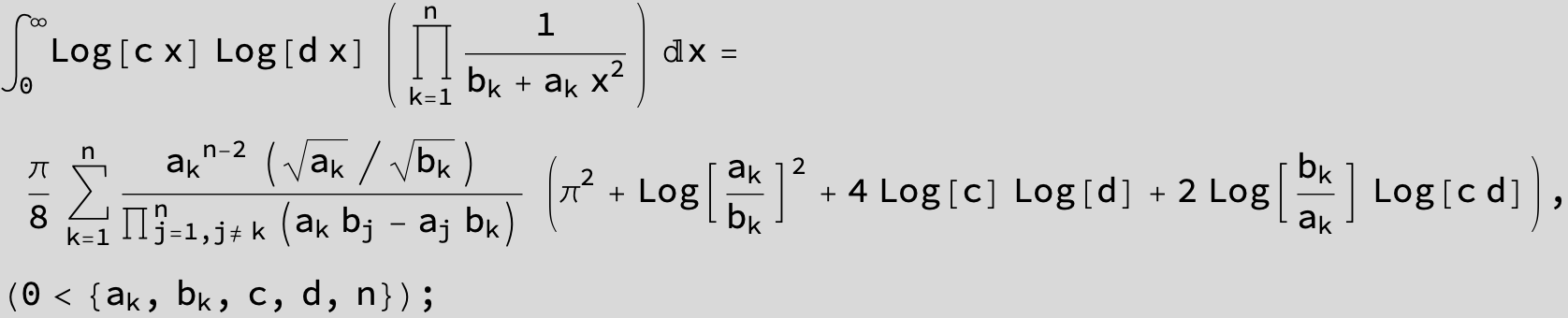
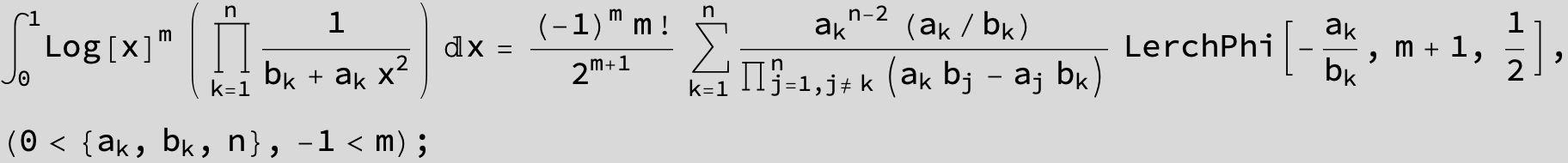
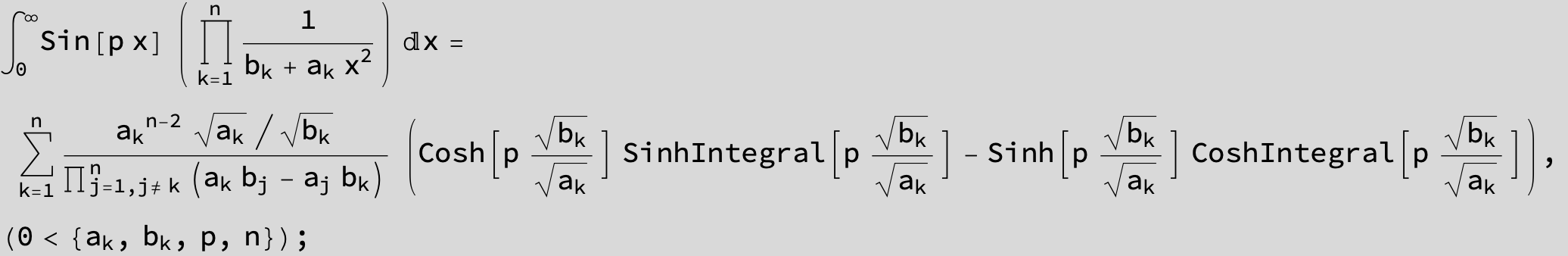
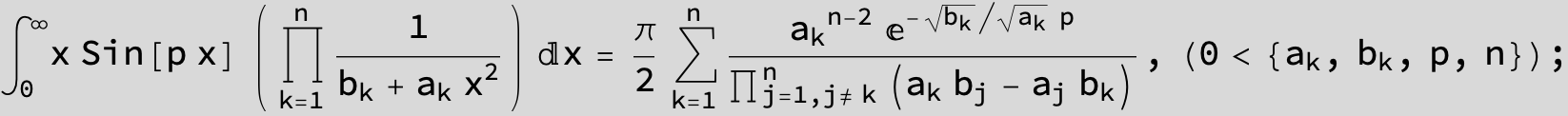
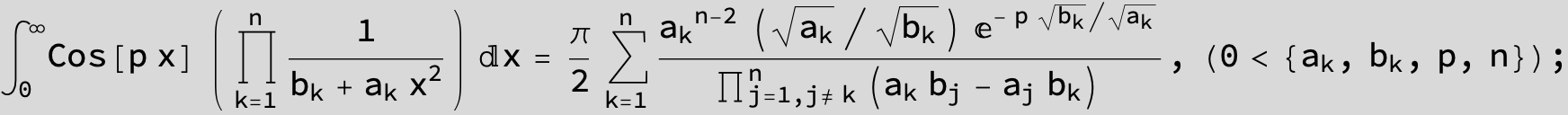
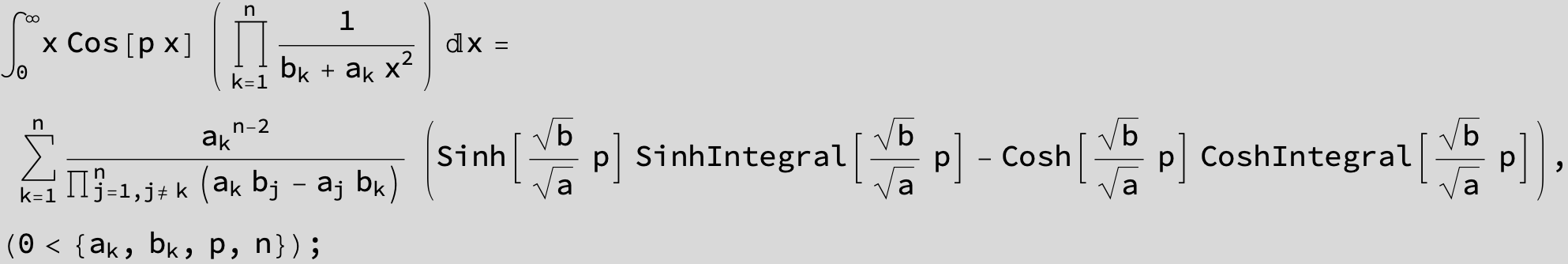
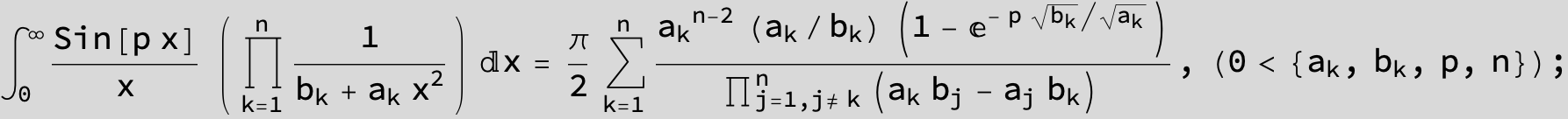
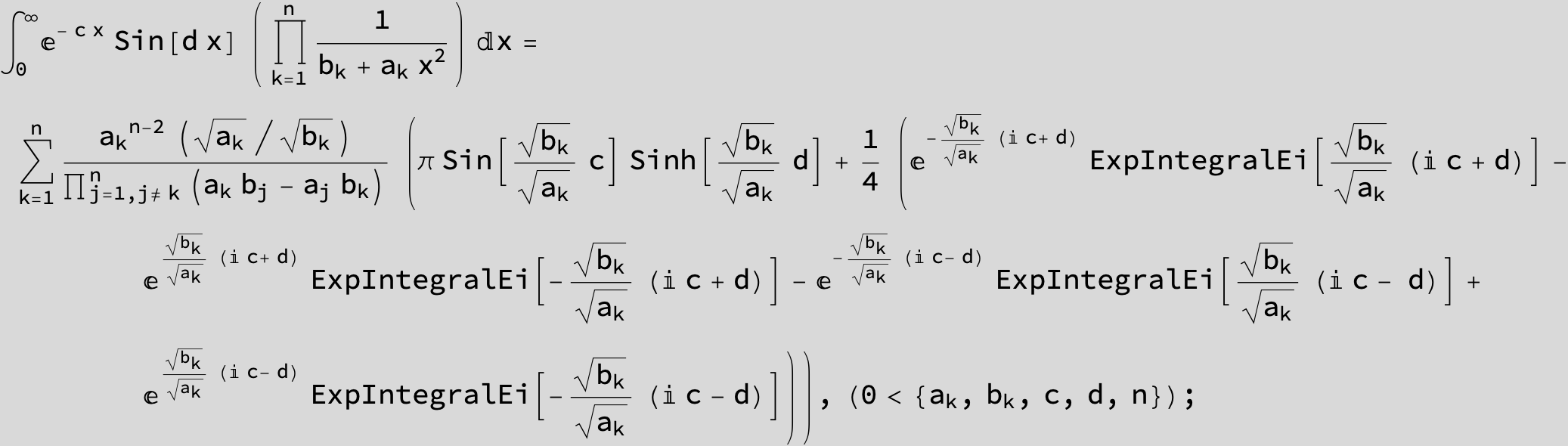
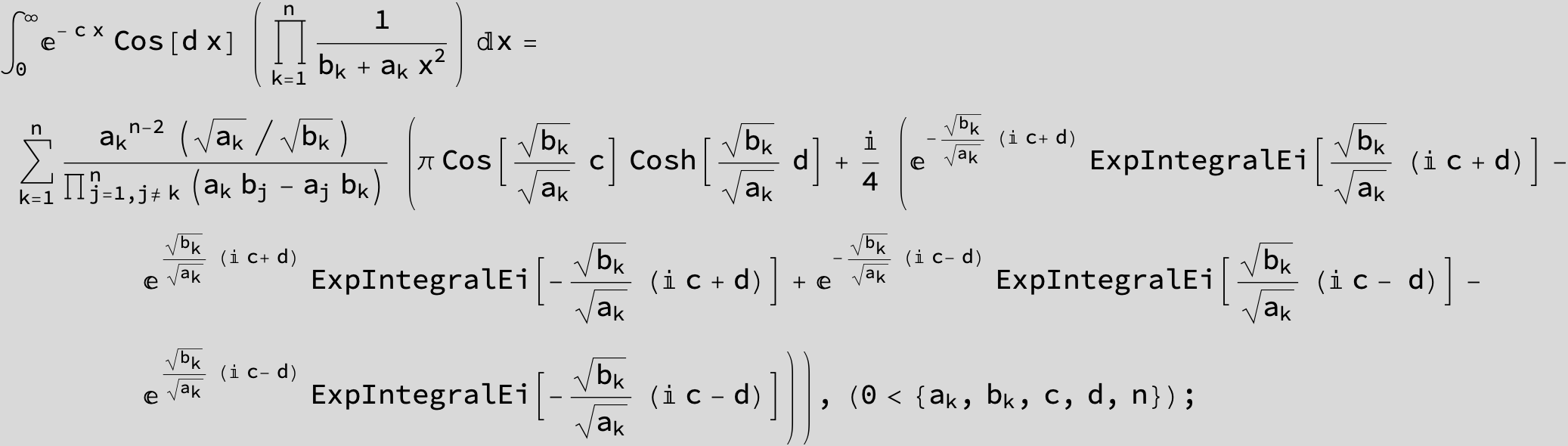

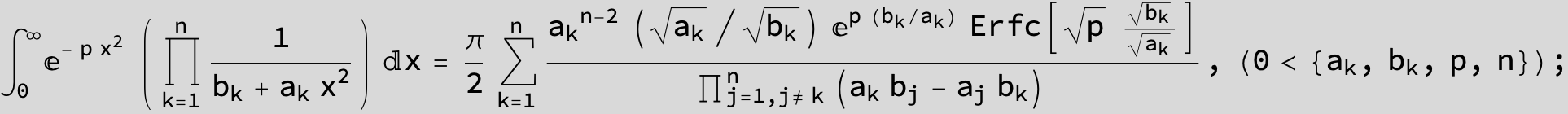
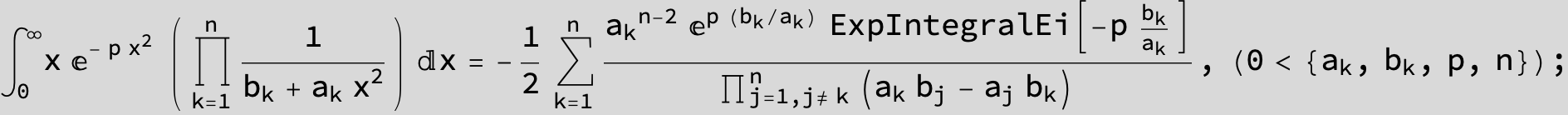
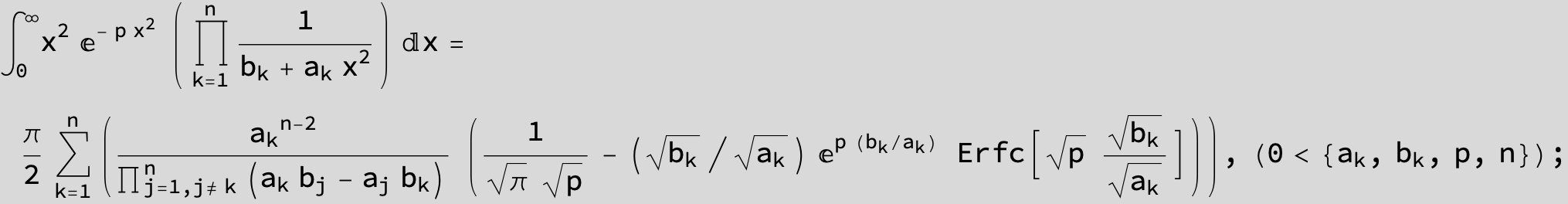
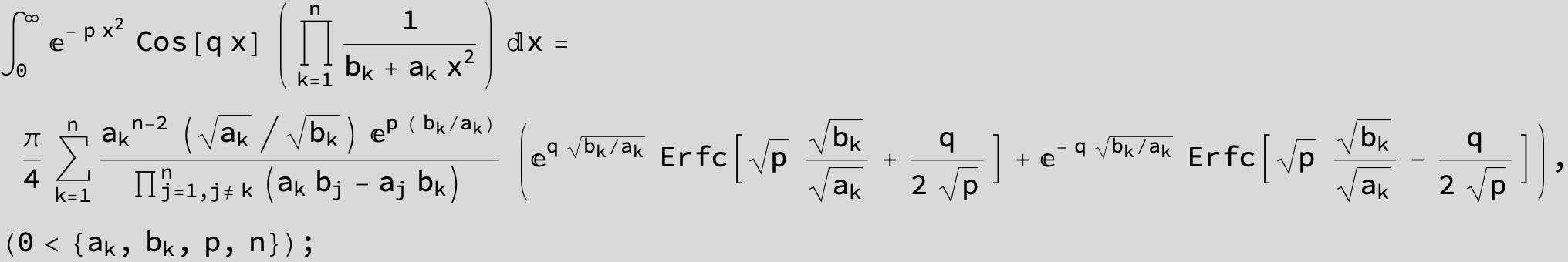

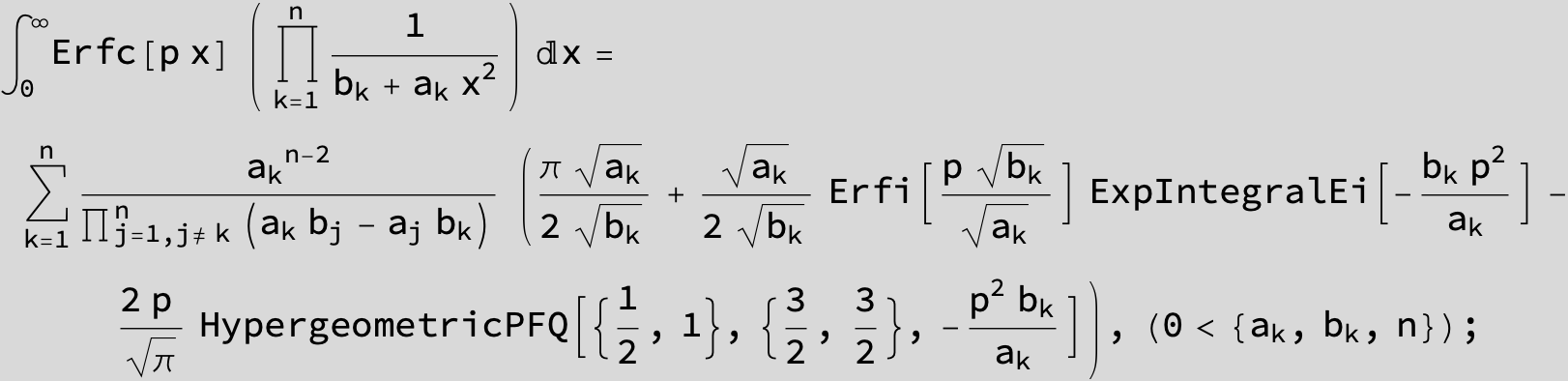
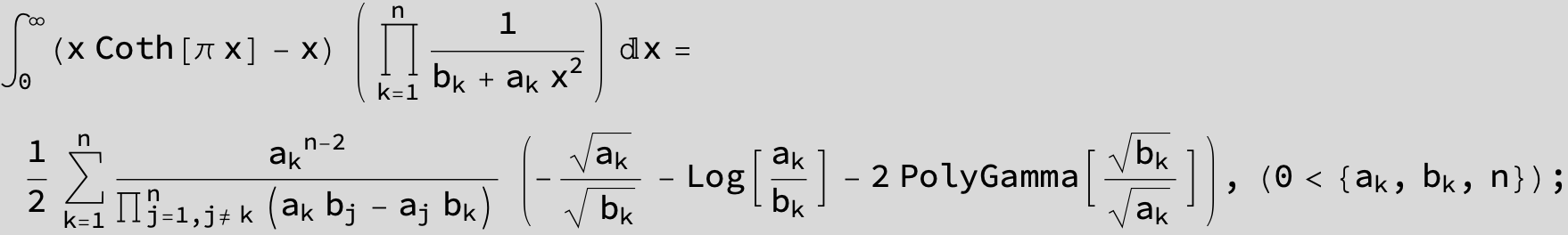
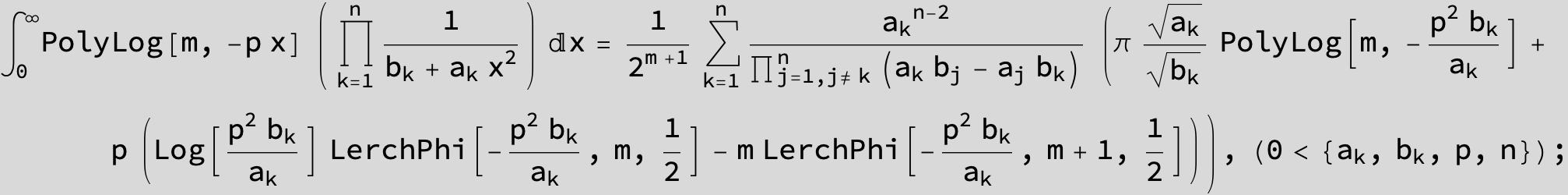

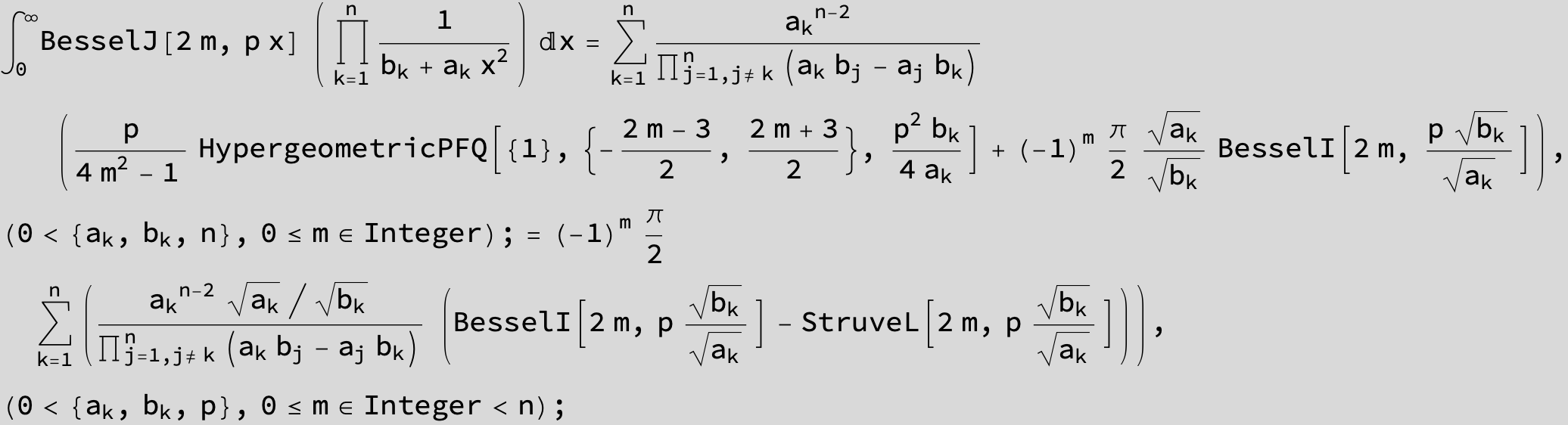
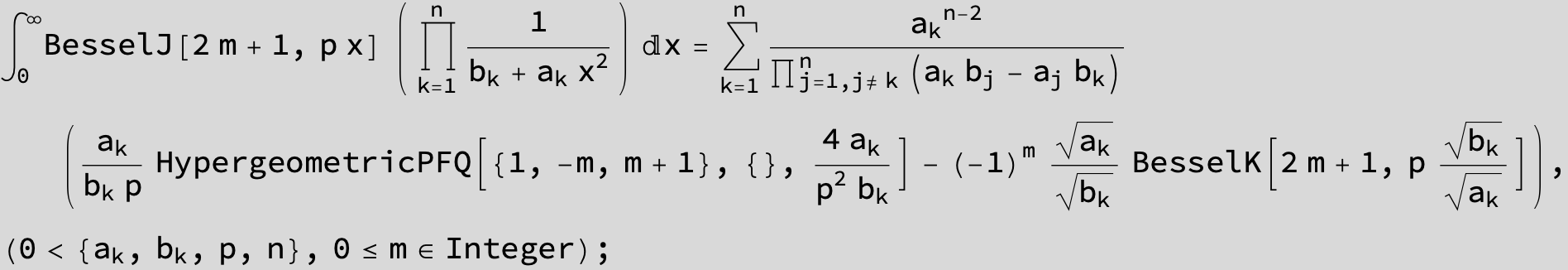
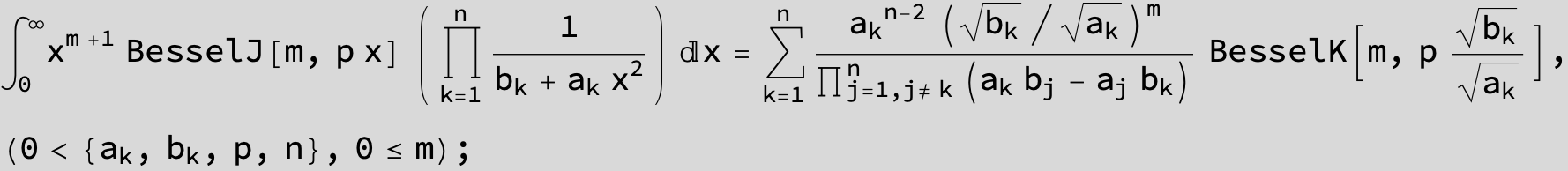


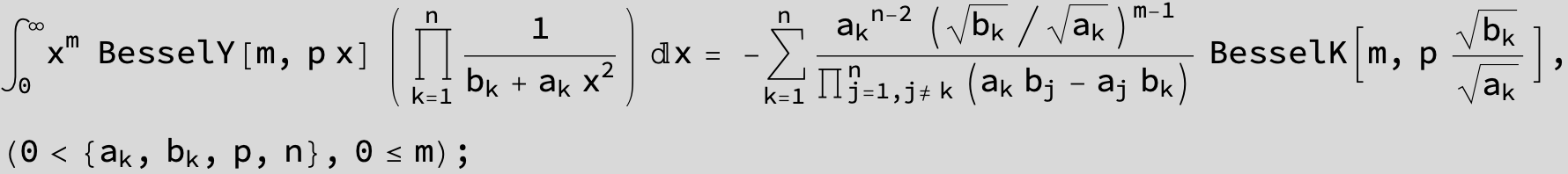
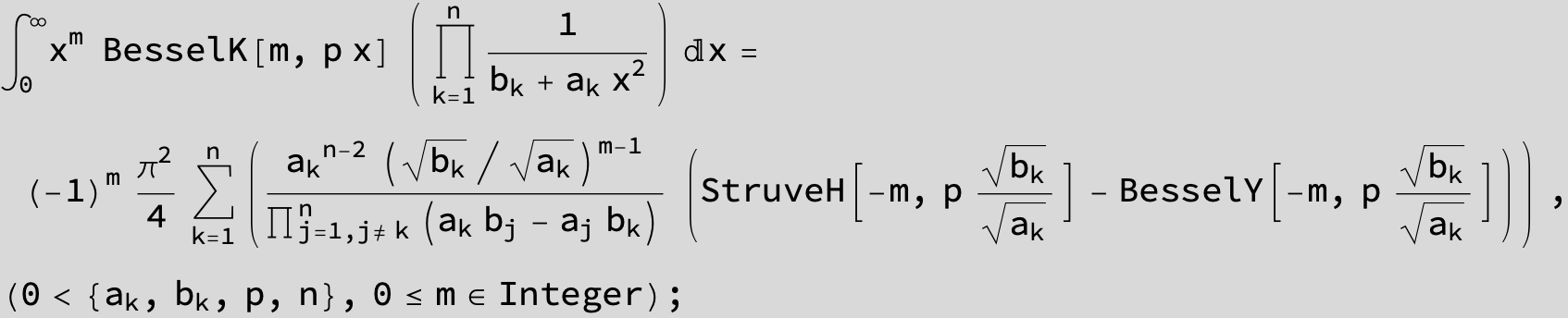
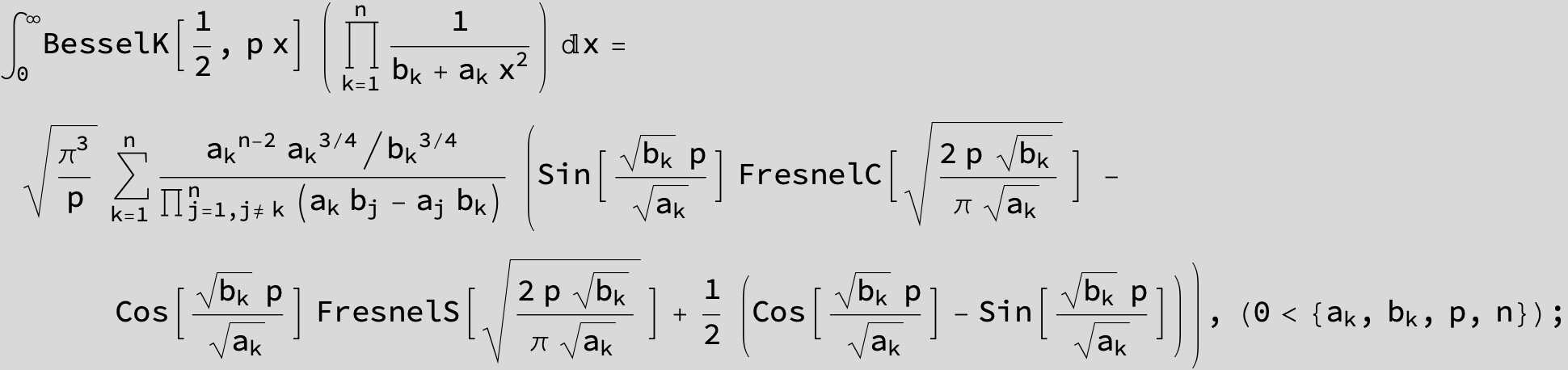
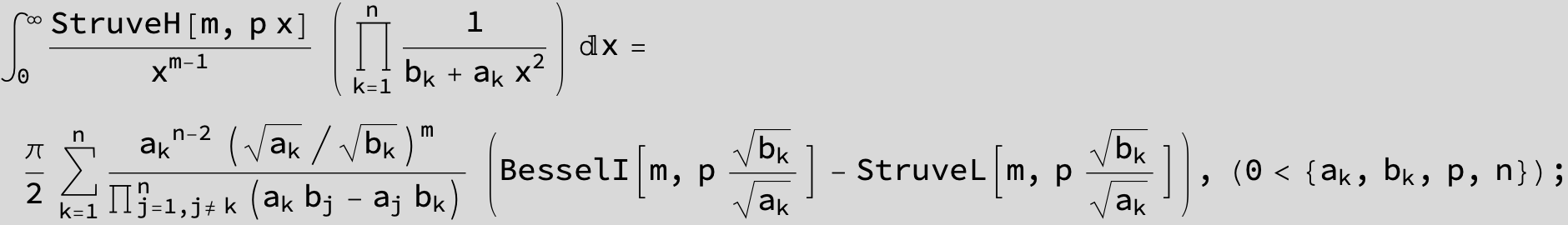

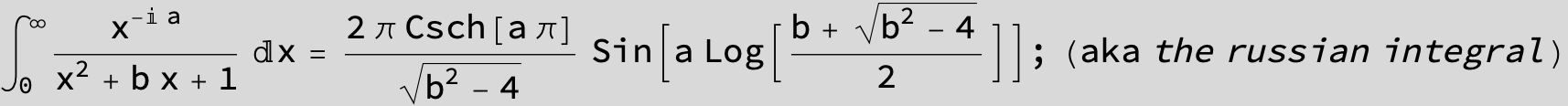
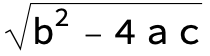
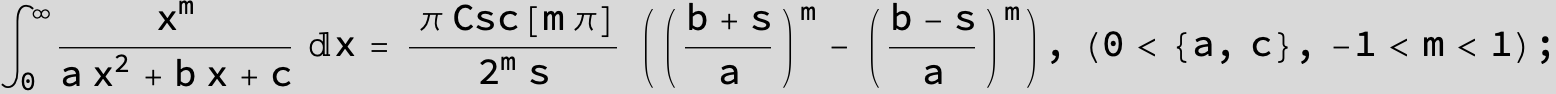
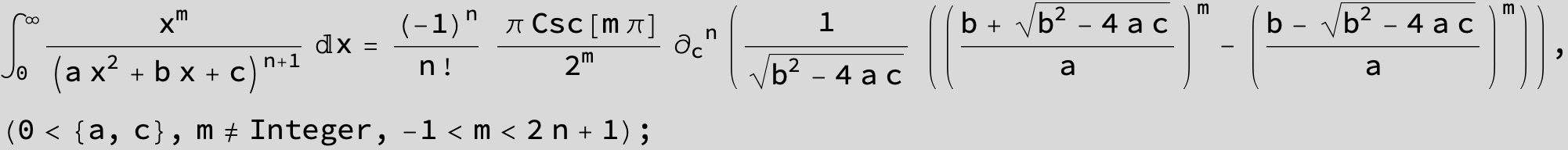

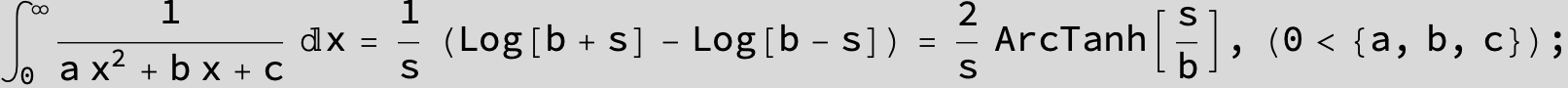
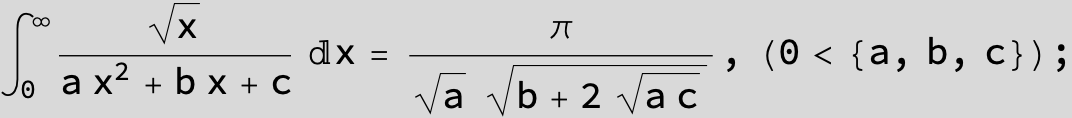
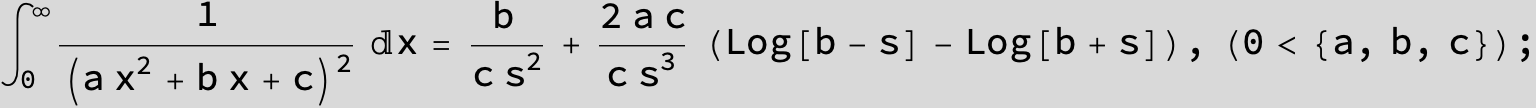
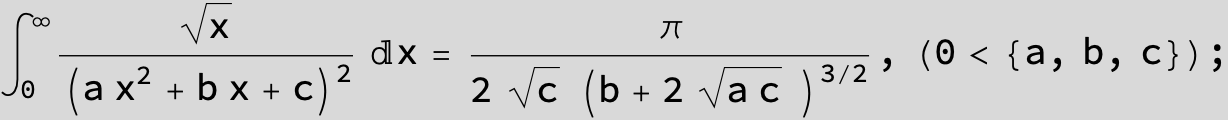
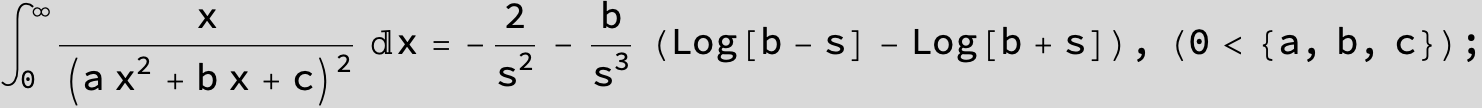
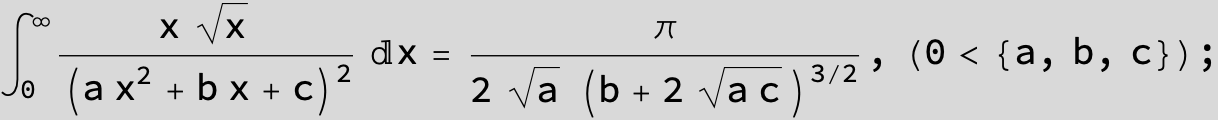
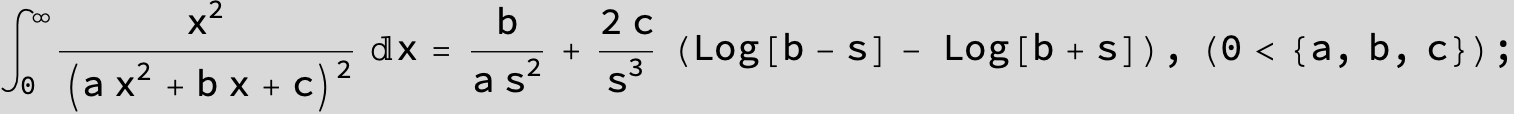
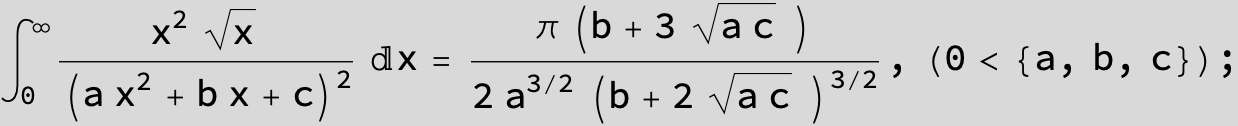
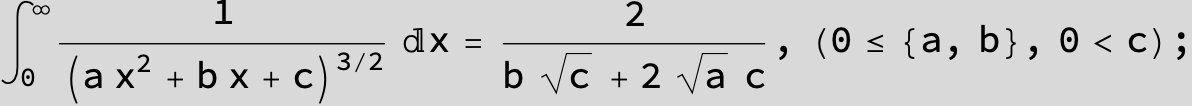
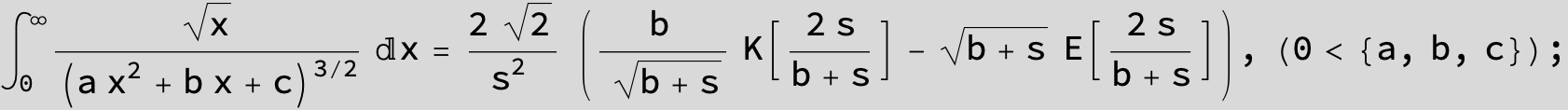
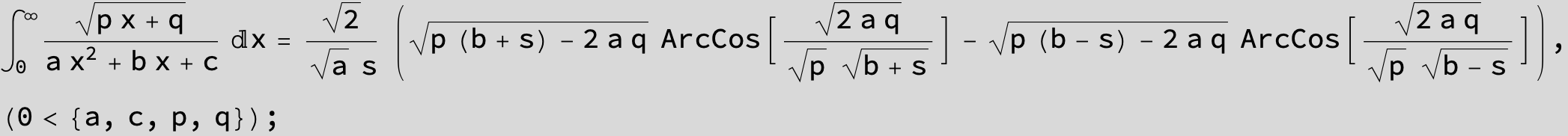
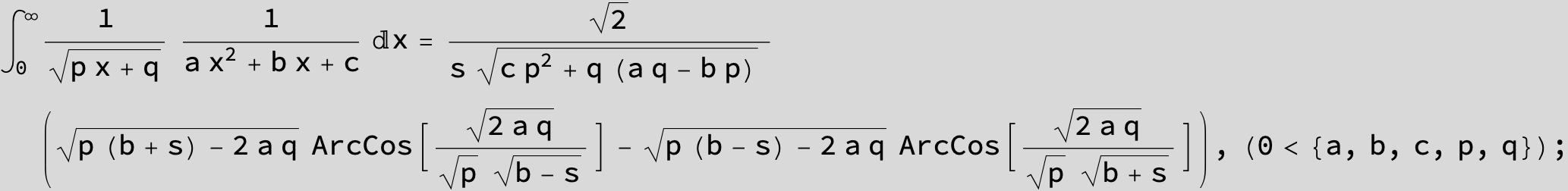
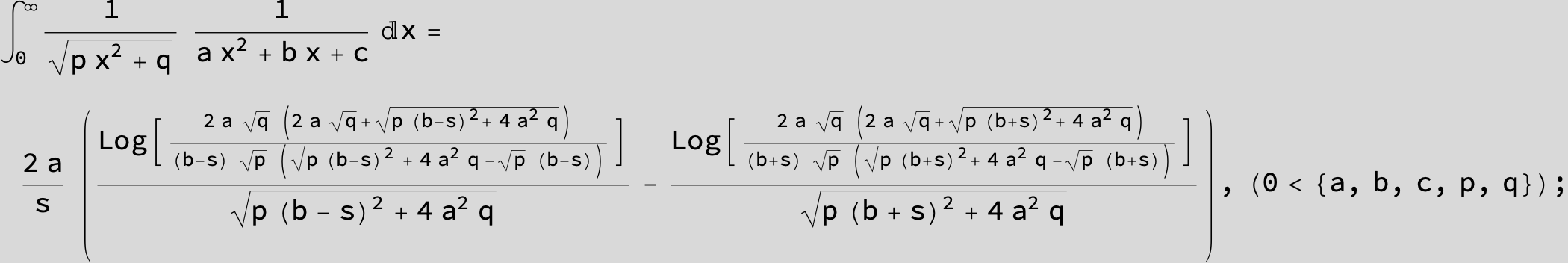
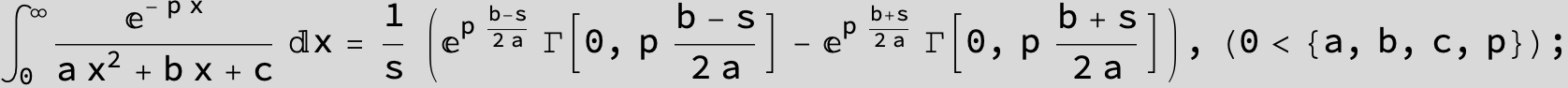
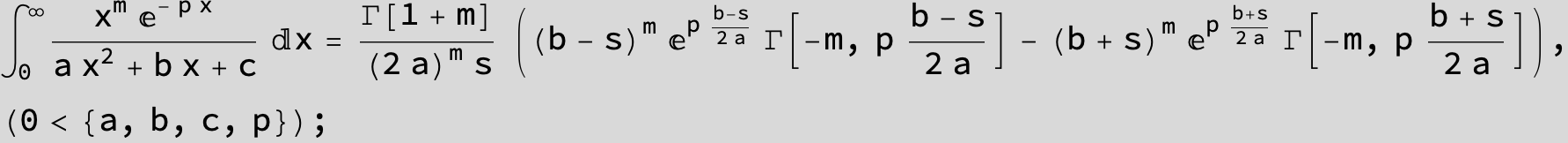


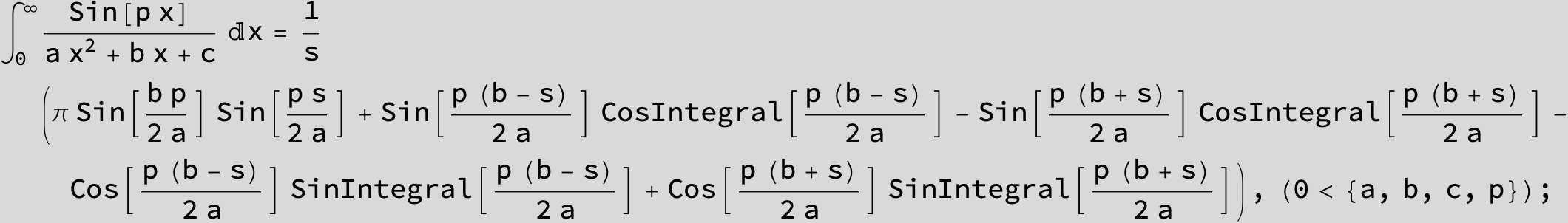
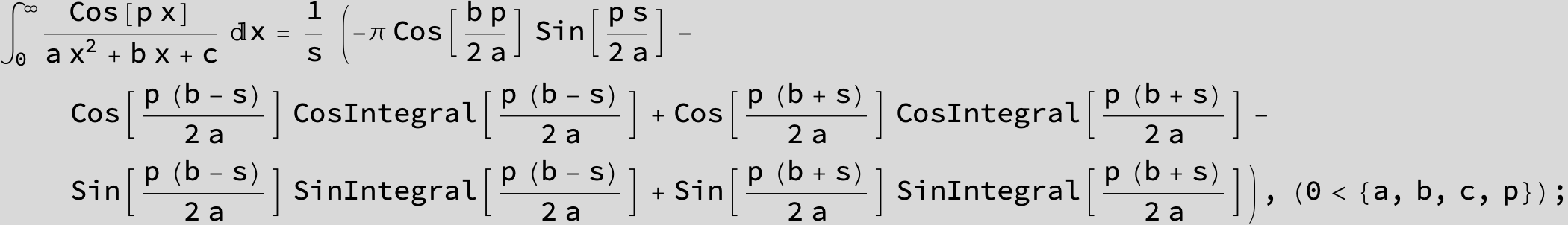
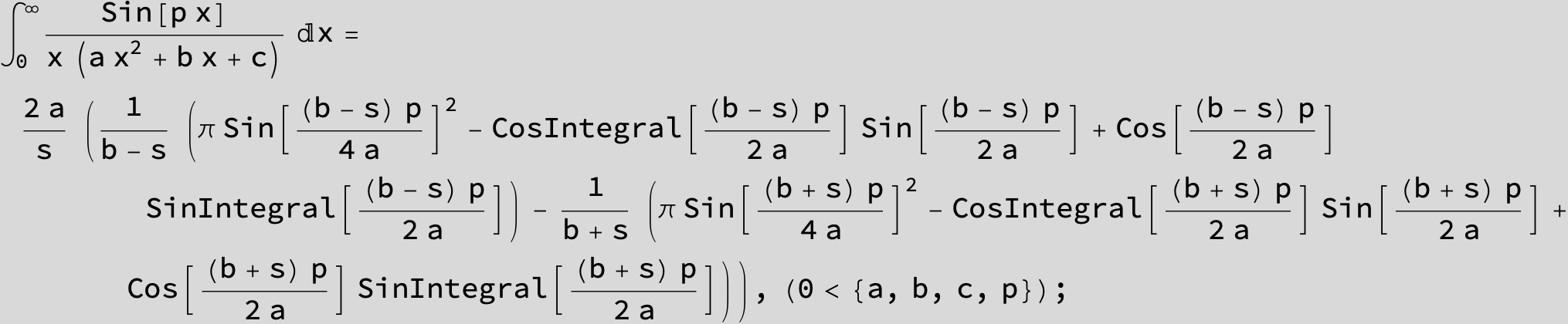

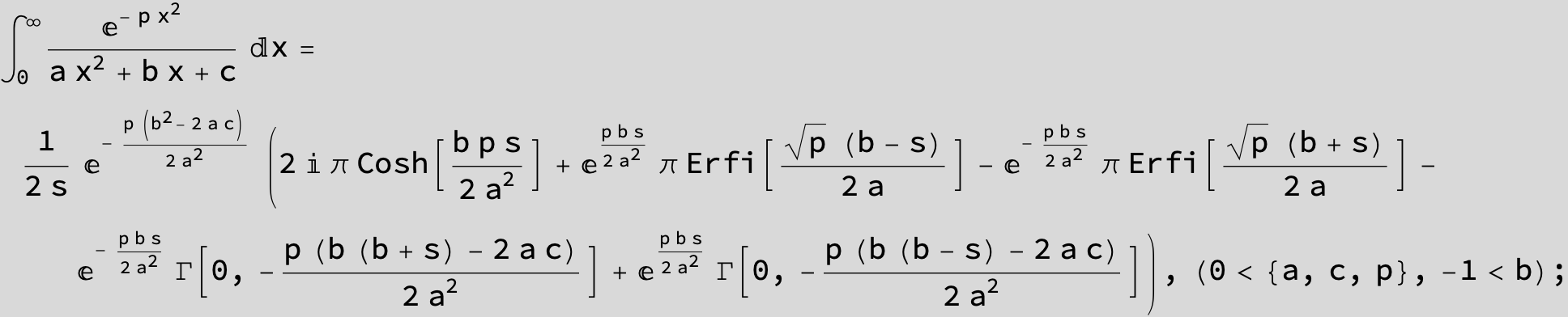
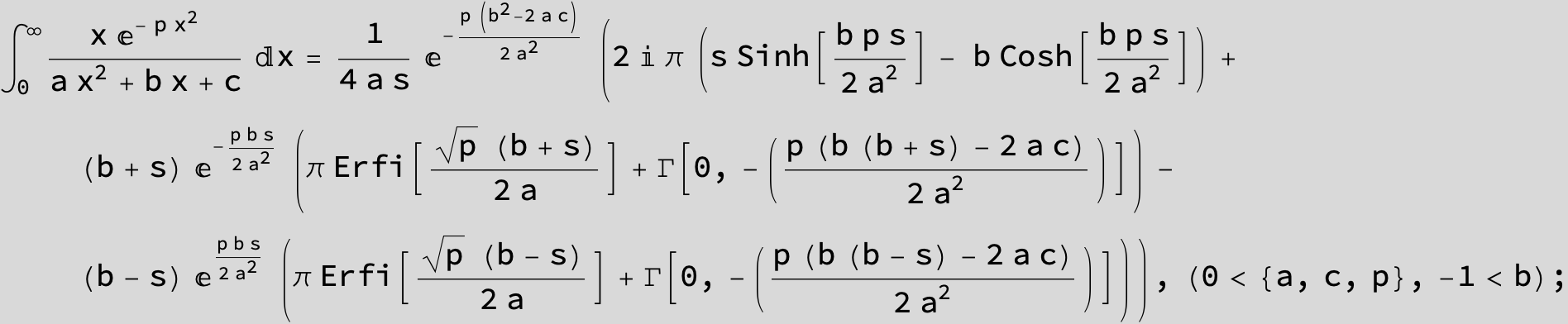
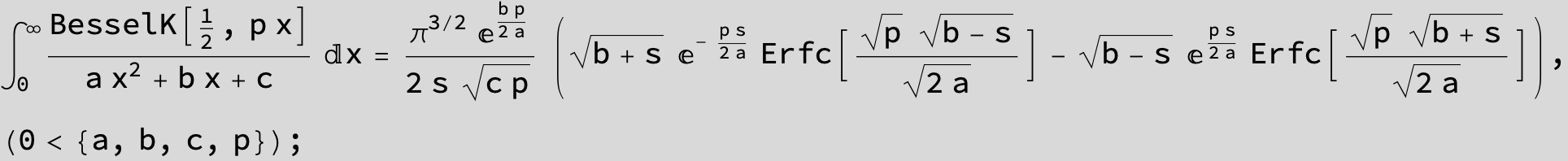
![]()
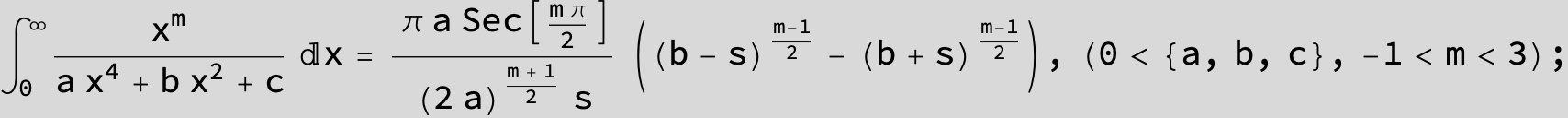
in the following expressions (∫ f(x)/(a x^2 + b x + c ) dx) we abbreviate s = ![]() :
:
![]()
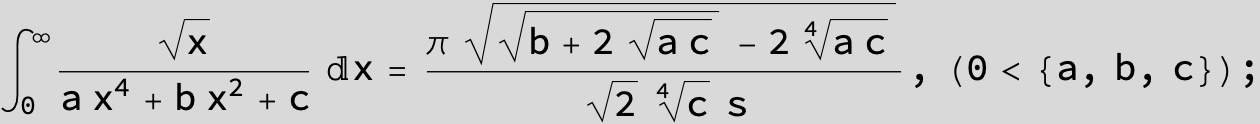
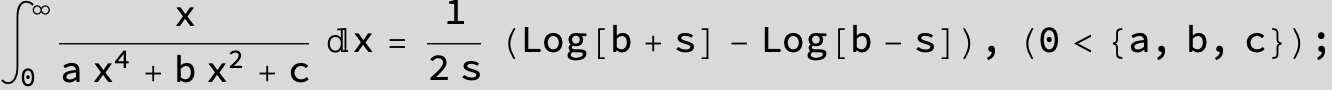
the values at integer n can be found approximately by setting n near to an integer ![]() .
.
![]()
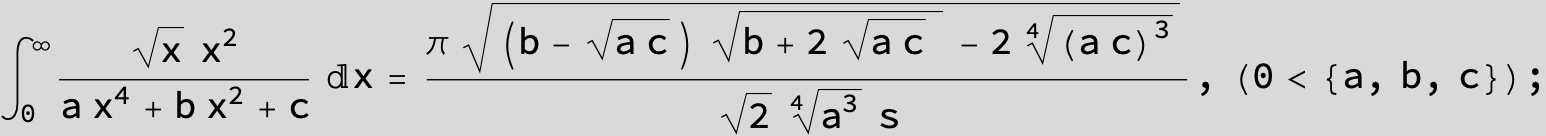
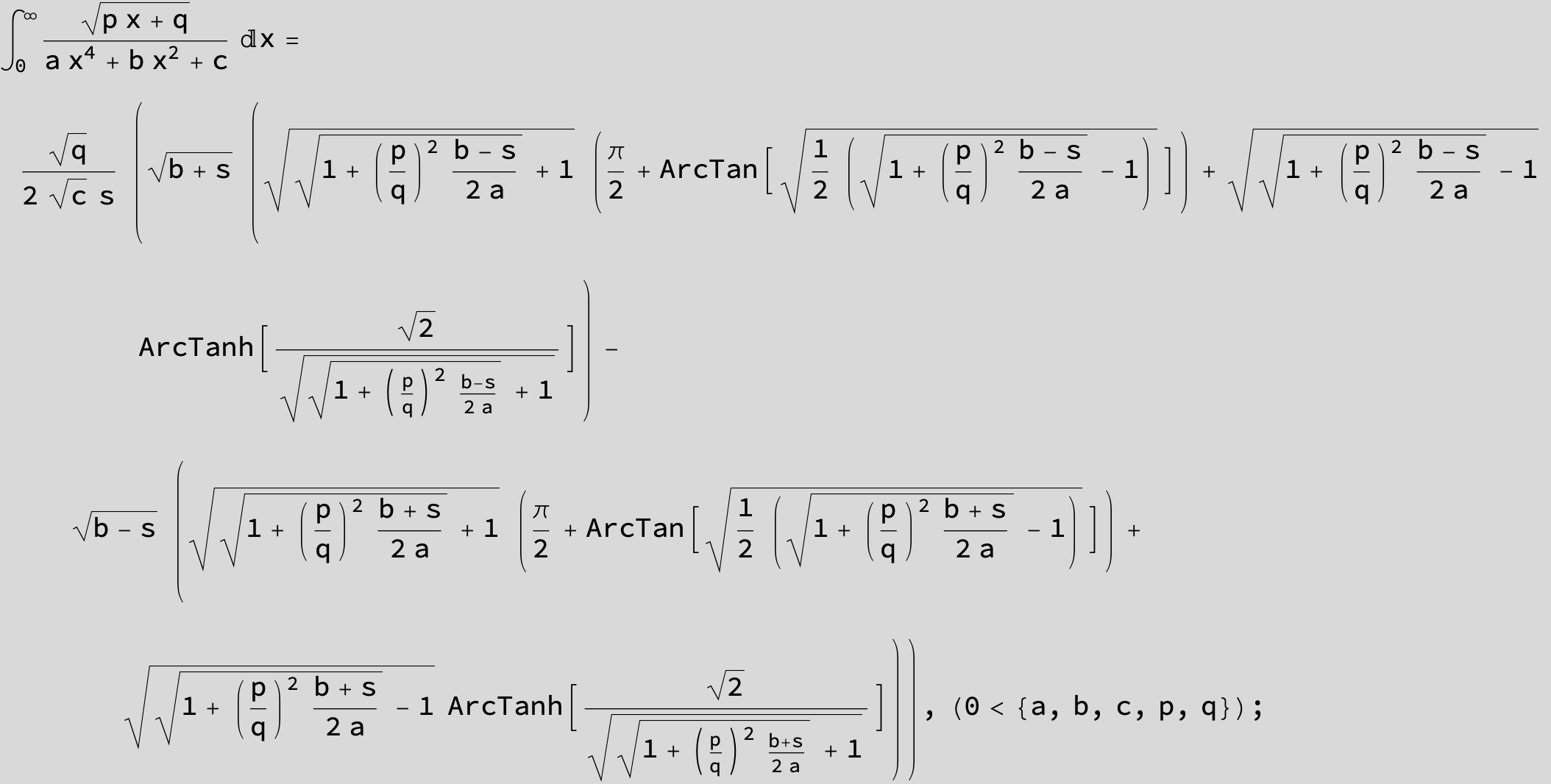
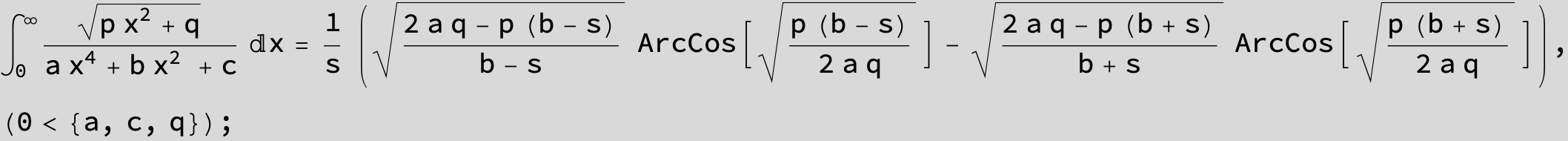
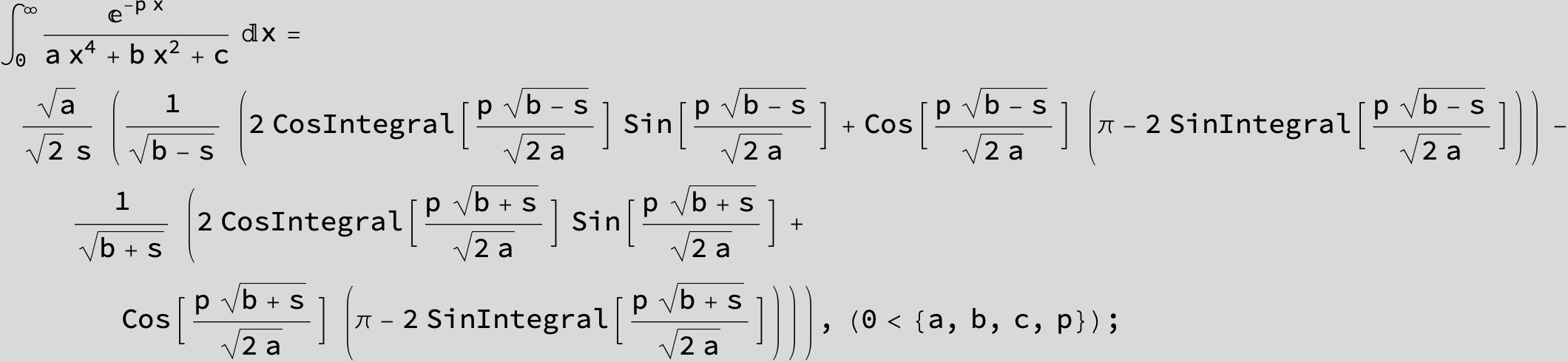
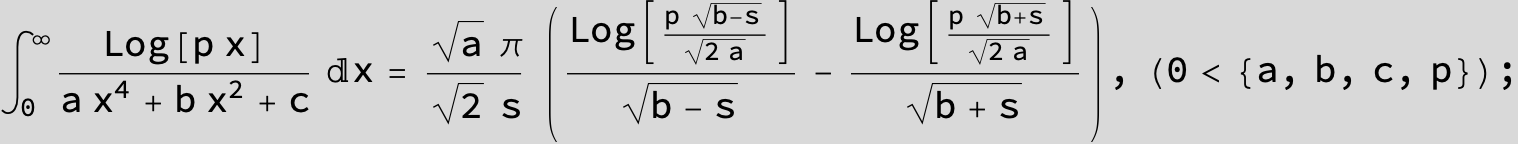

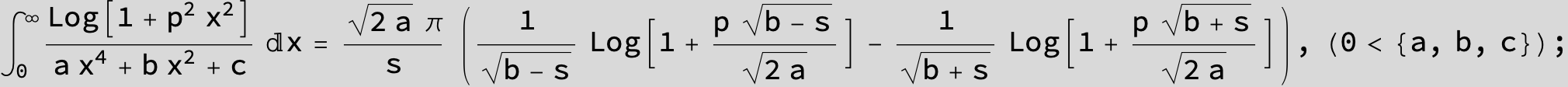
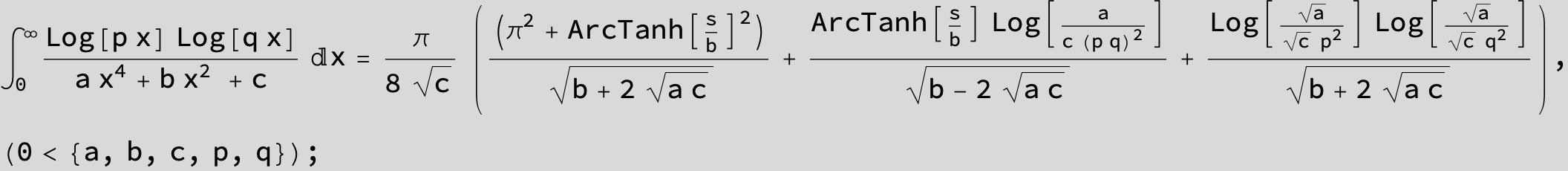
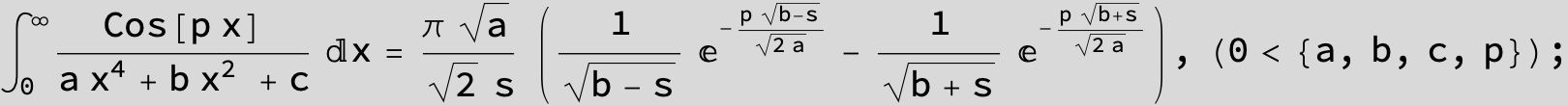
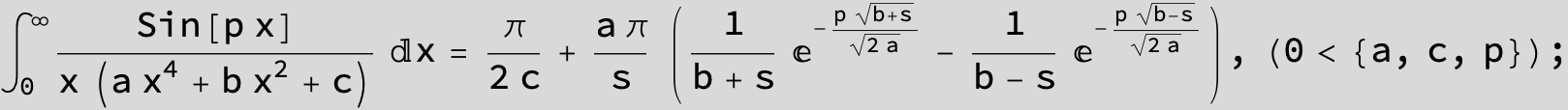
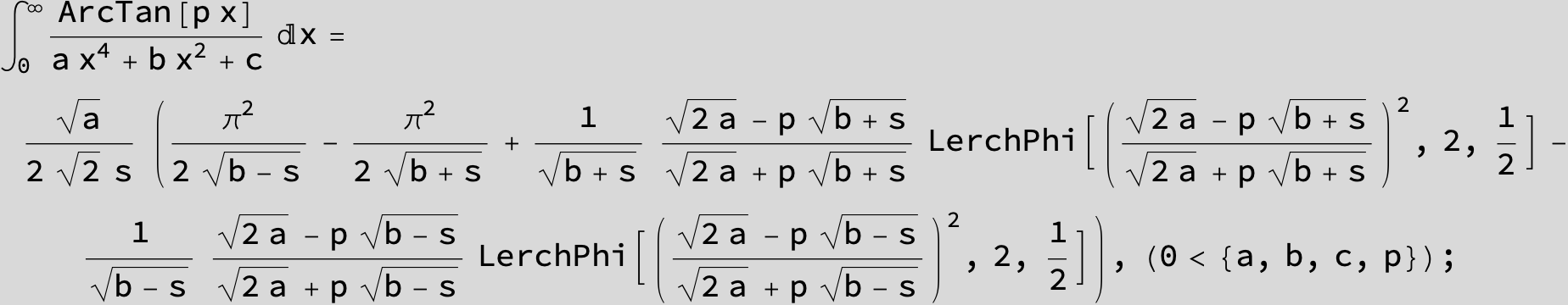
![]()
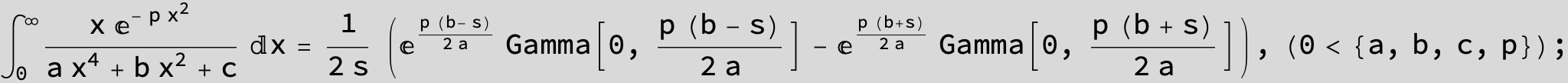
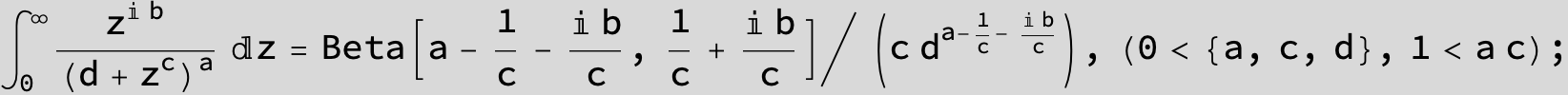
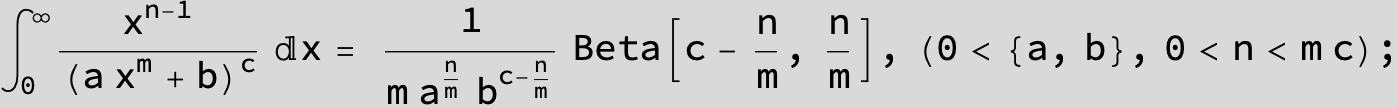
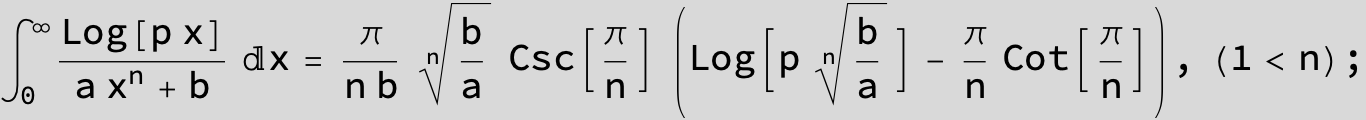
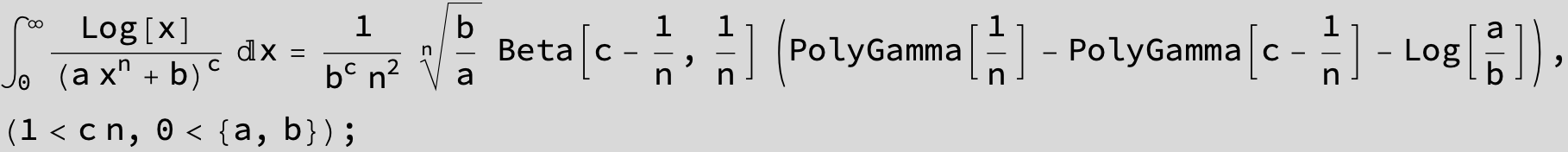
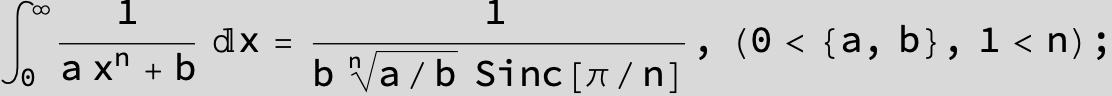
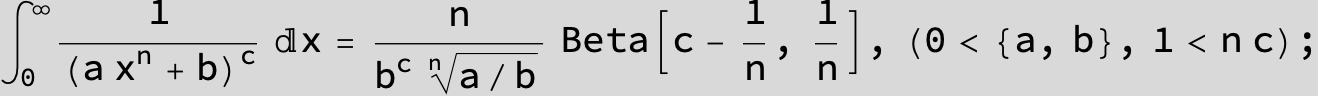
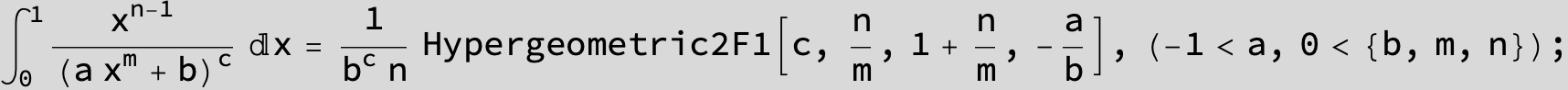
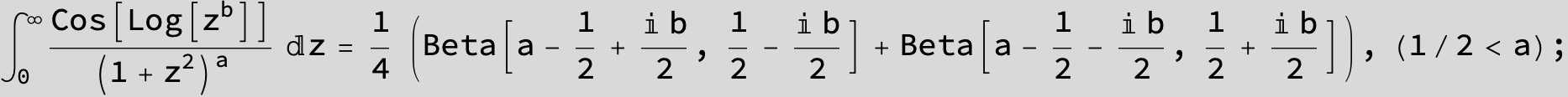
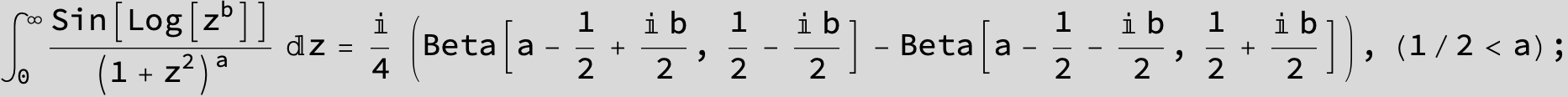
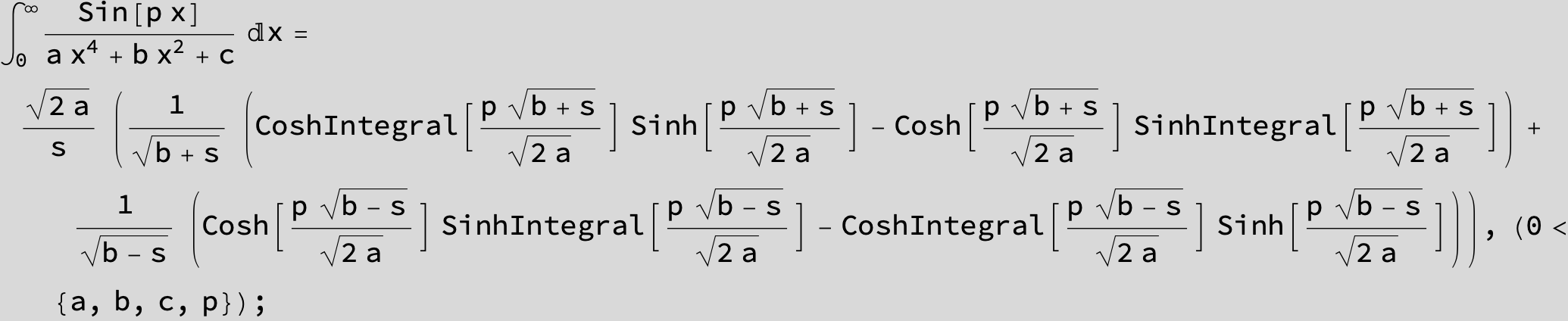
in the following expressions (∫ f(x)/(a x^4 + b x^2 + c ) dx) we abbreviate s = ![]() :
:
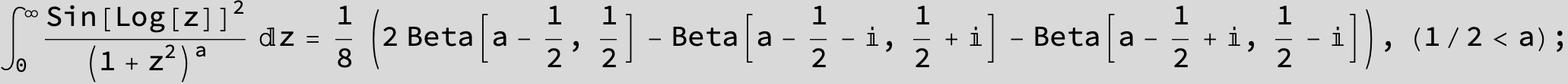
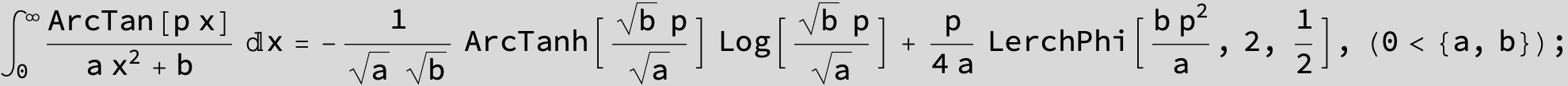

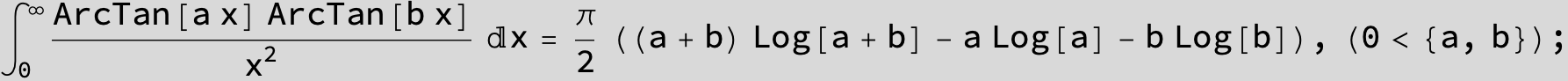
![]()
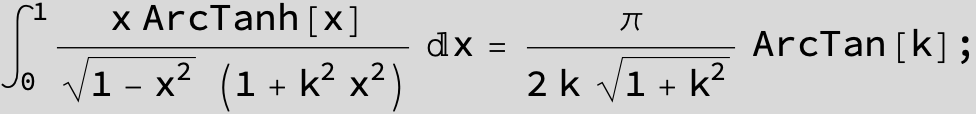
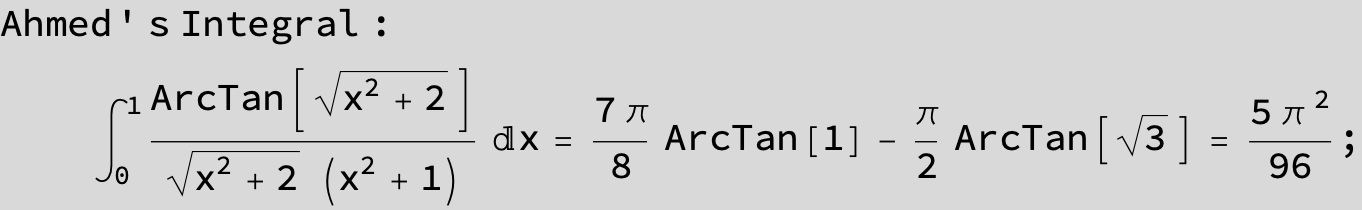
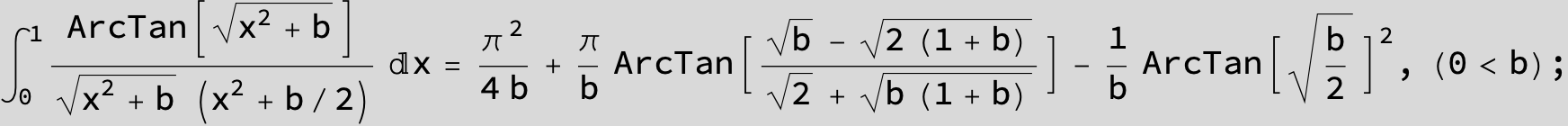
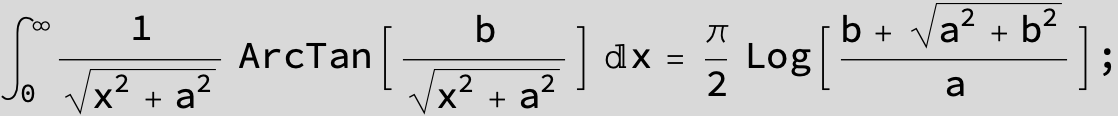
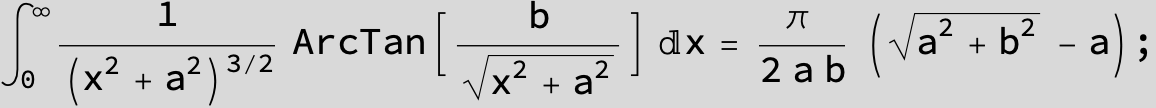

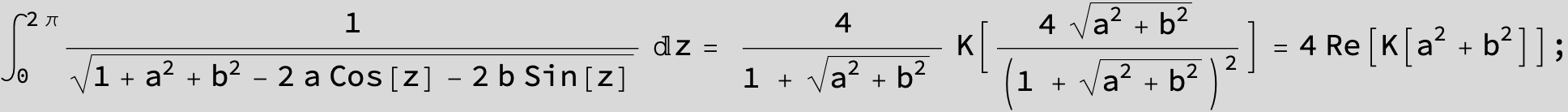
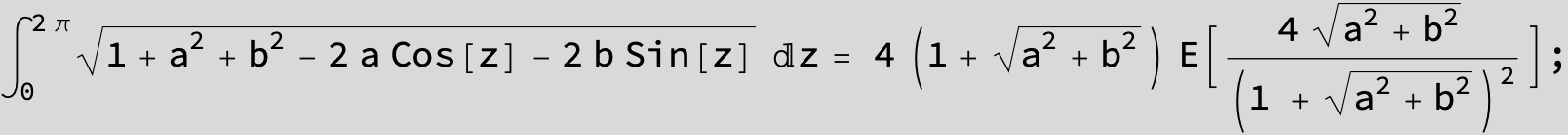

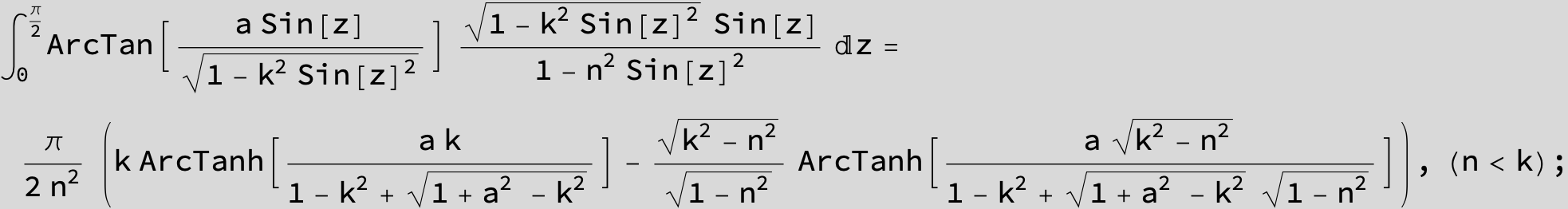
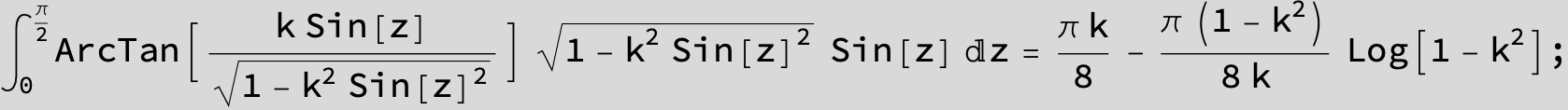
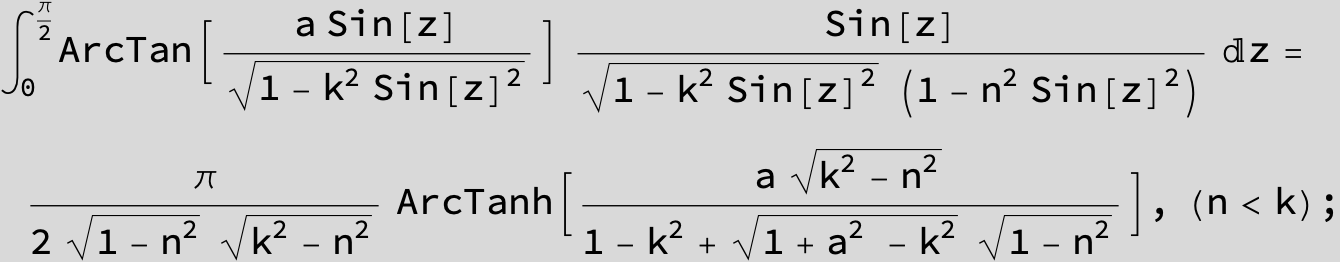
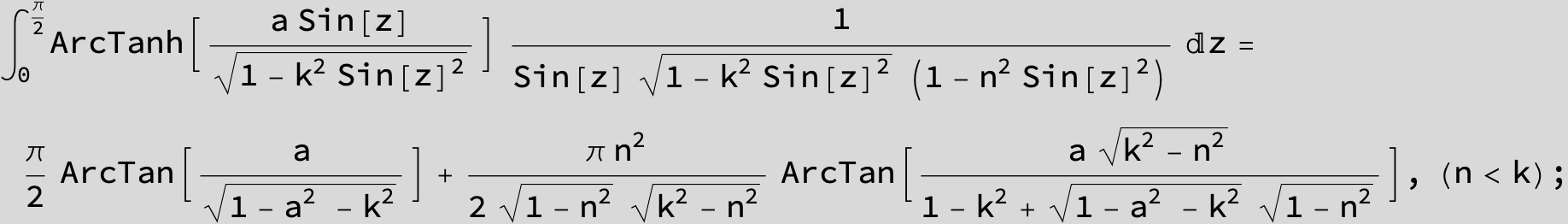
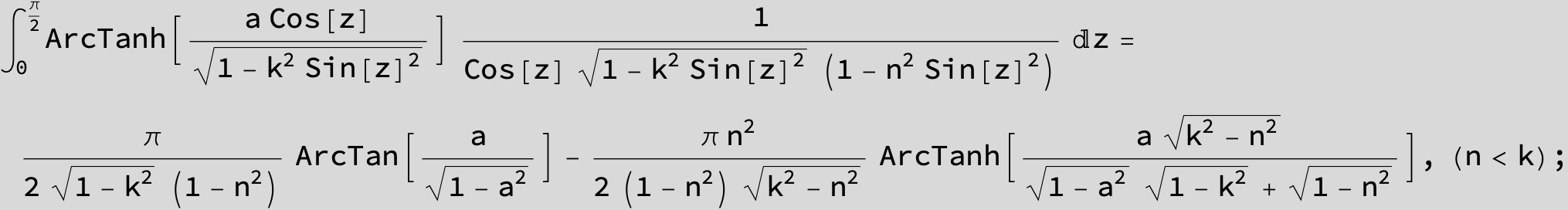
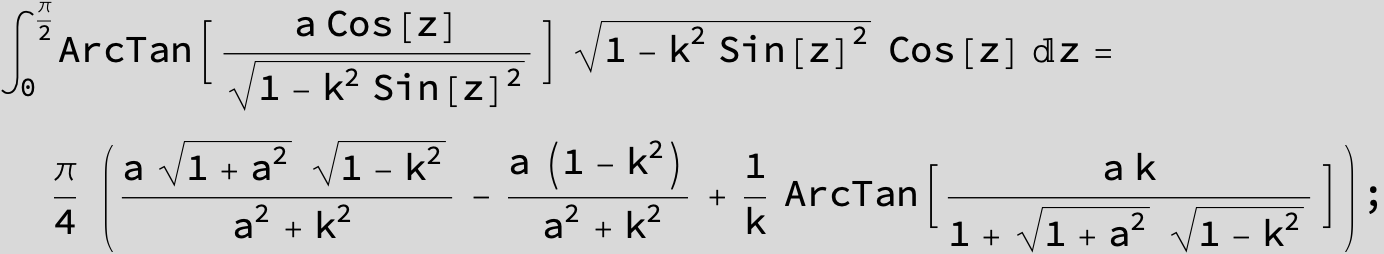
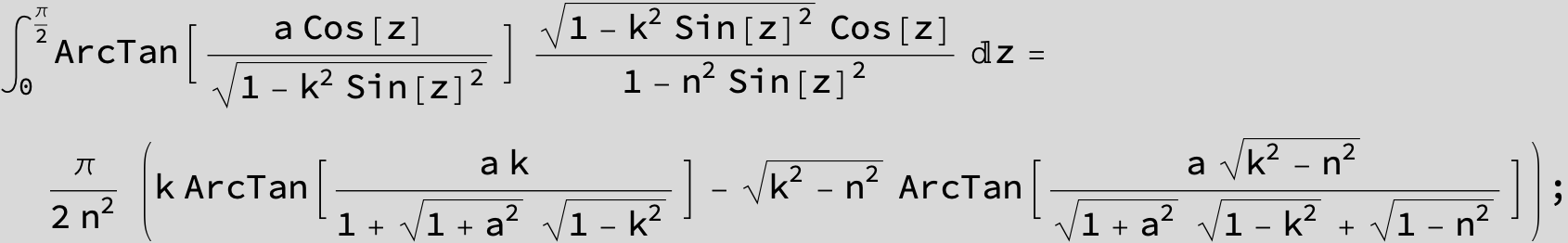
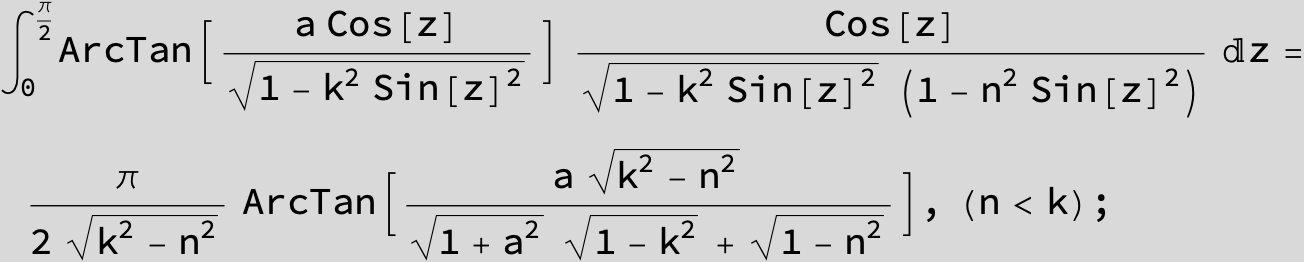
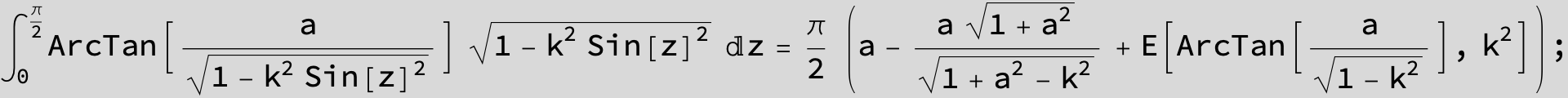
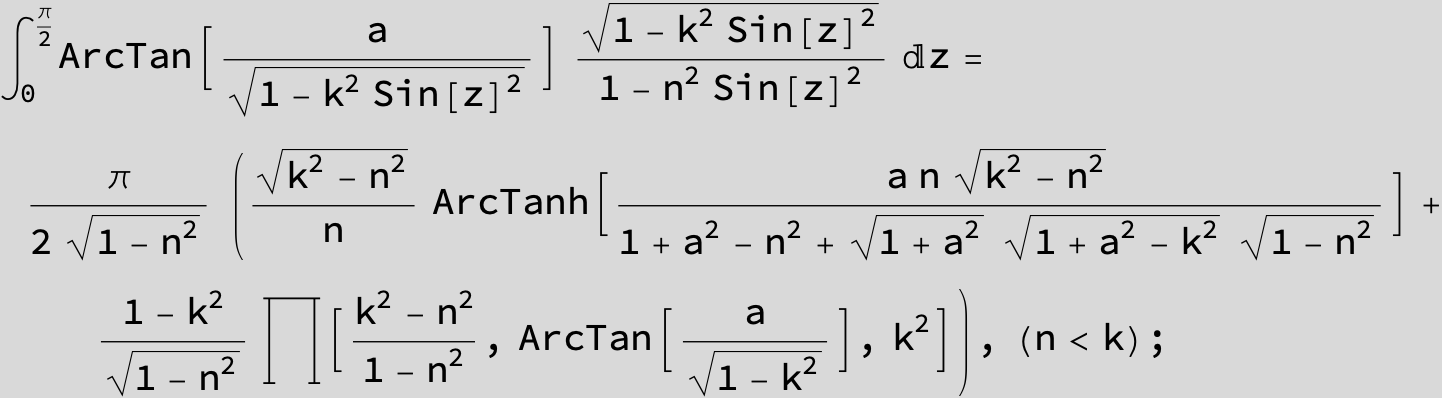
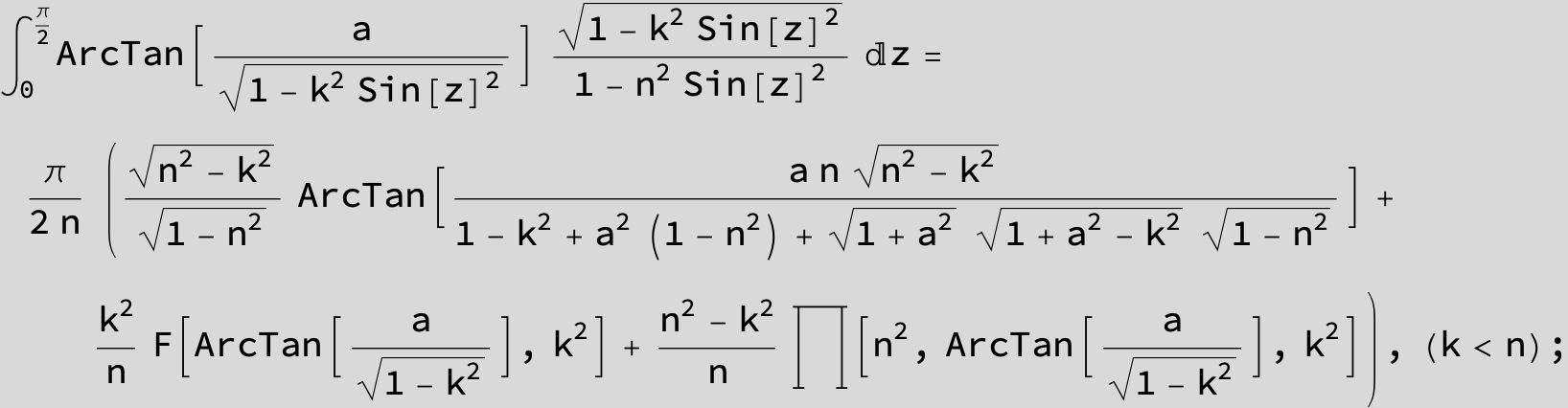
![]()
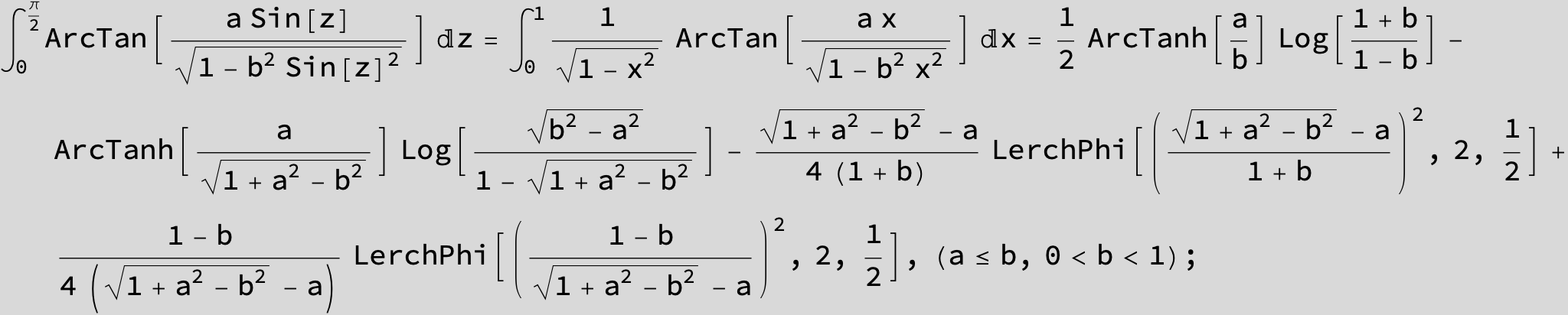
![]()

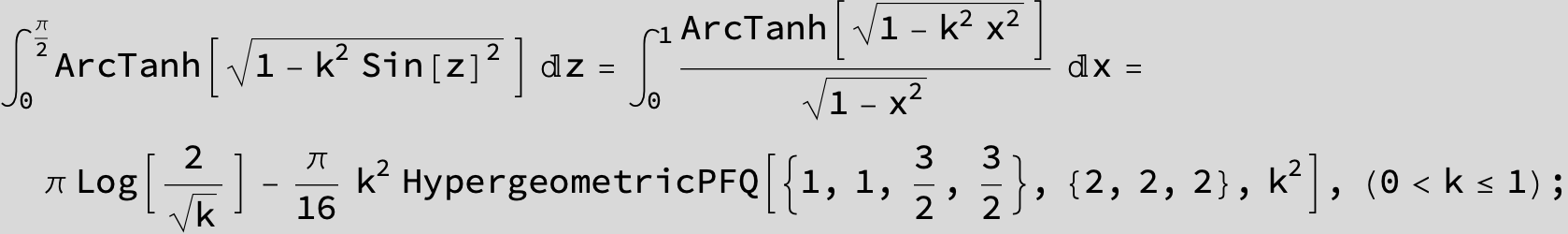


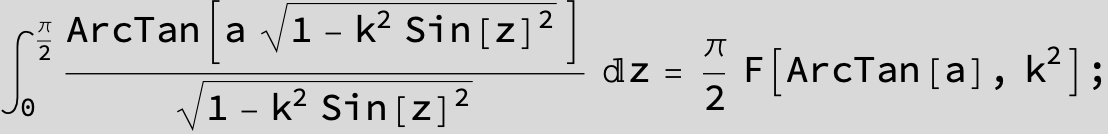

![]()
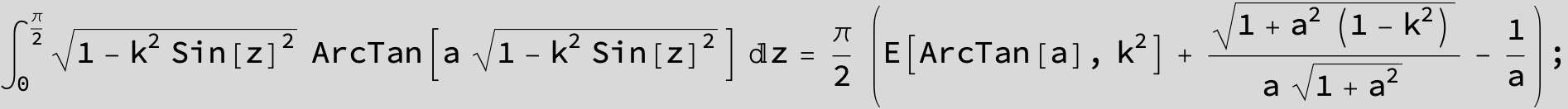

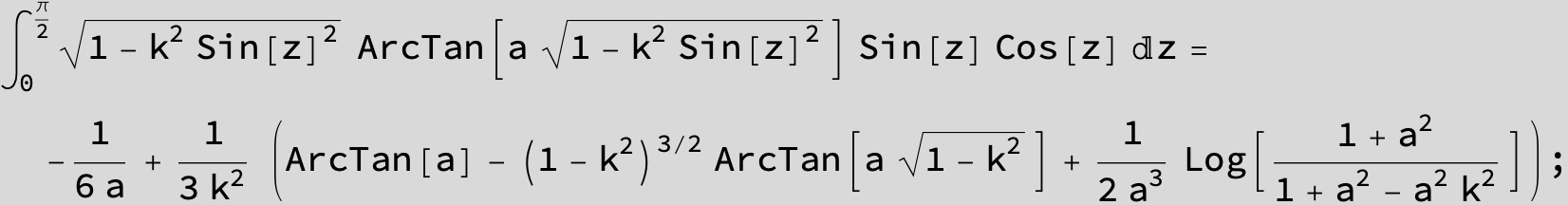
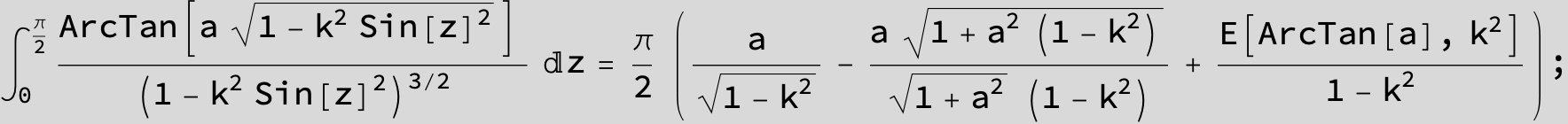
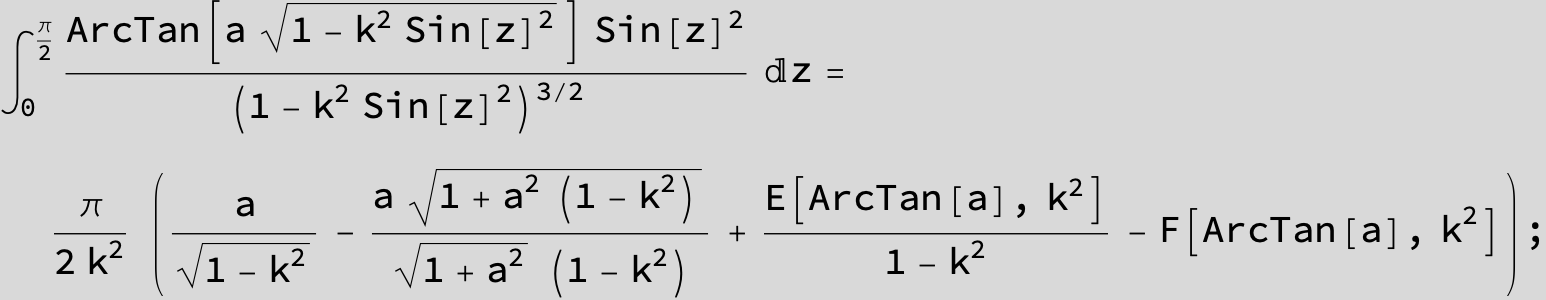


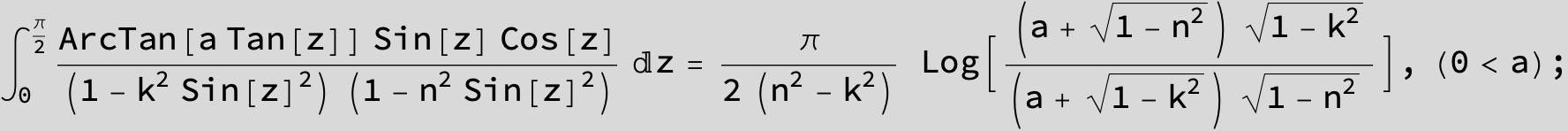
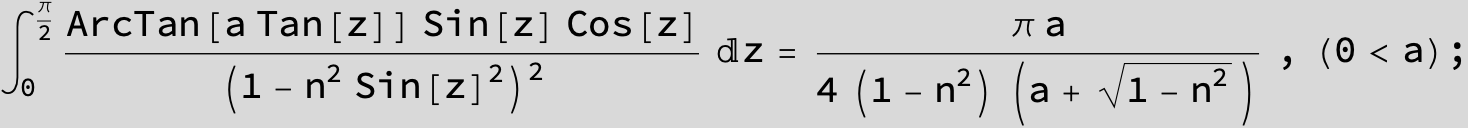
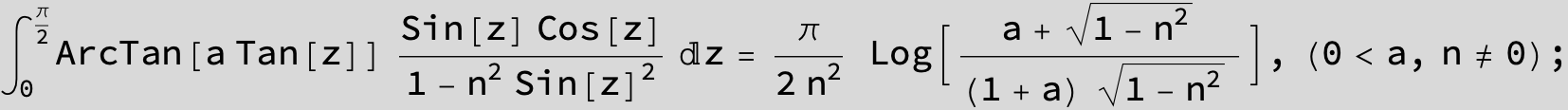

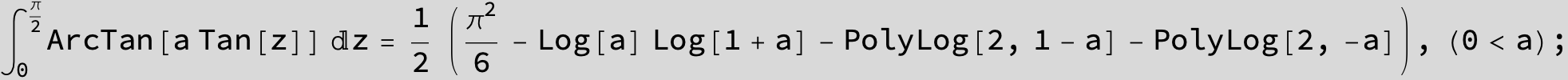

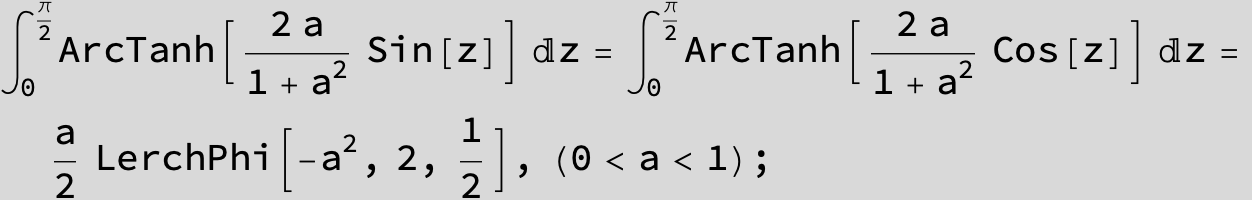


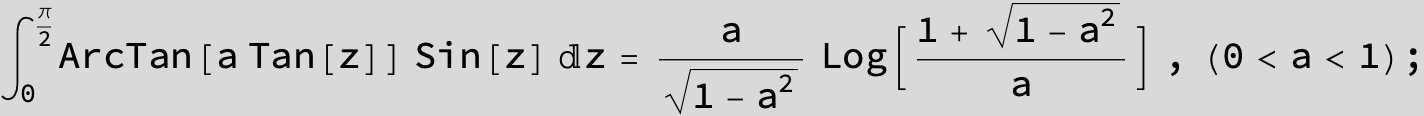
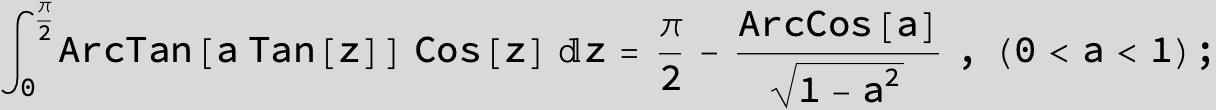
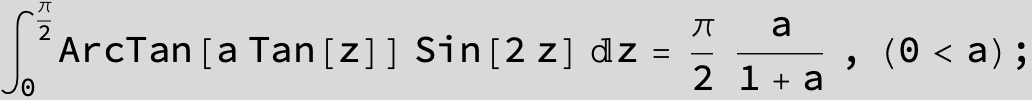
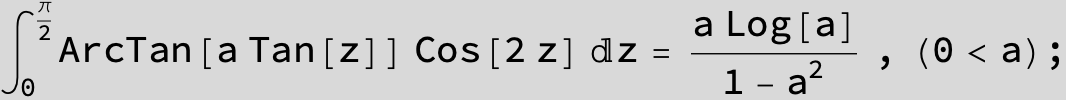
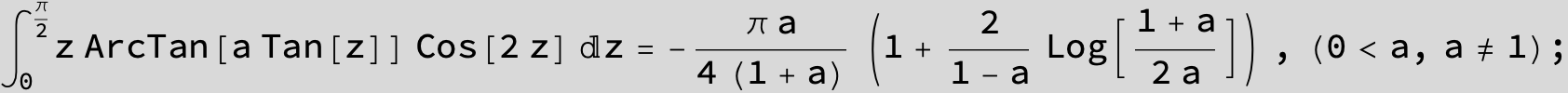
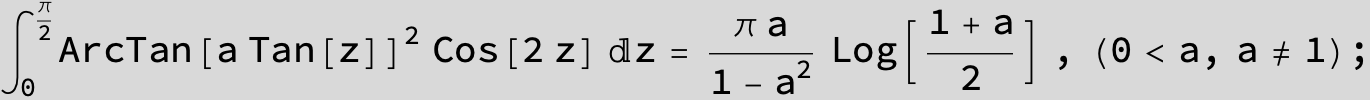
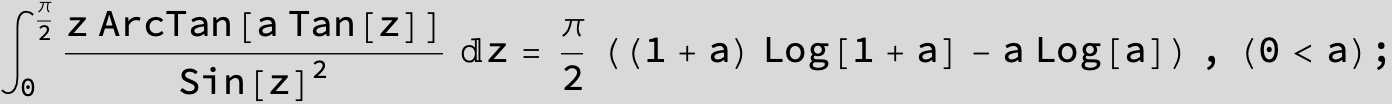

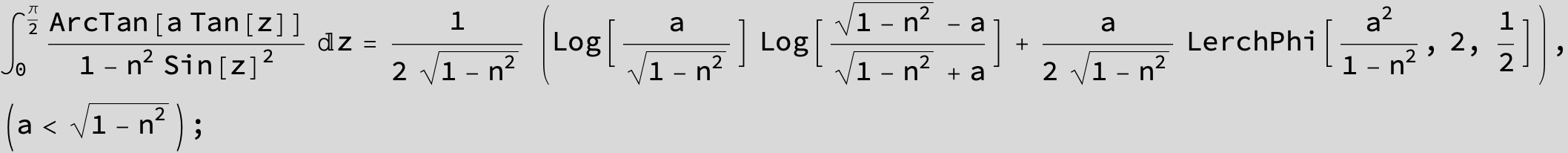
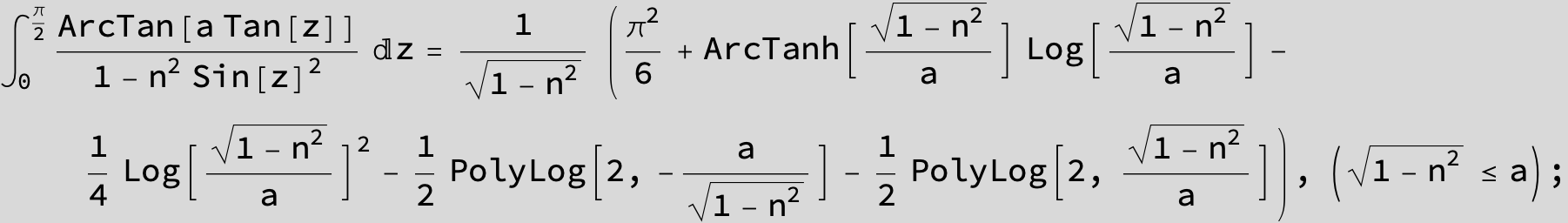
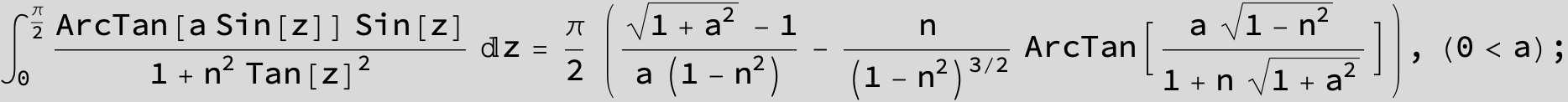
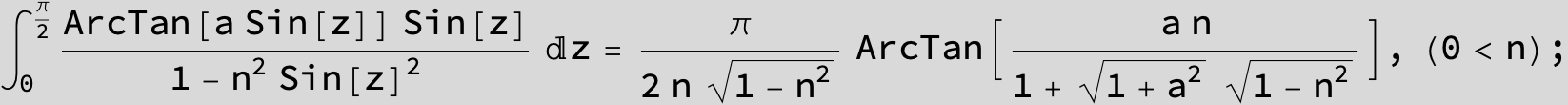

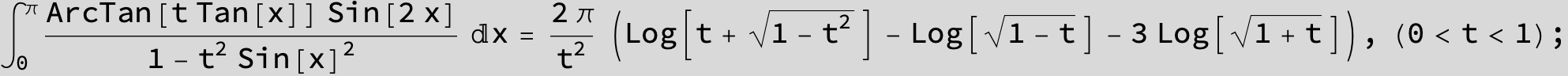
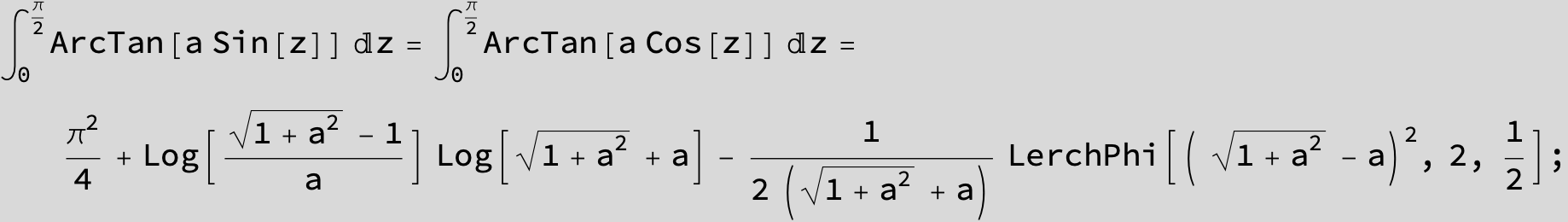



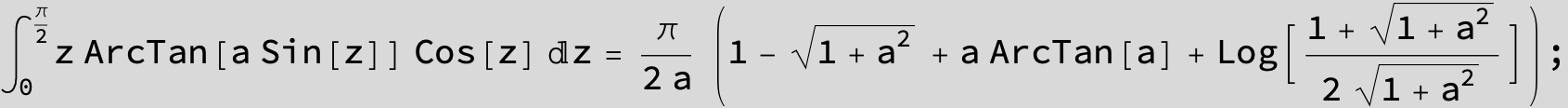
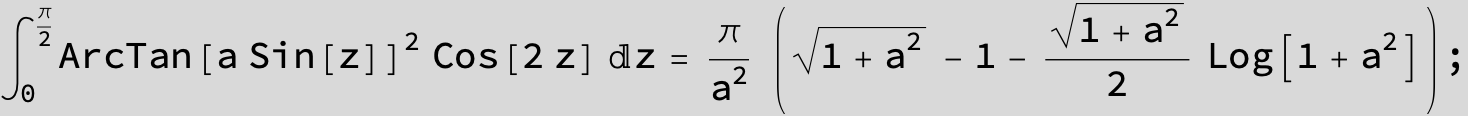
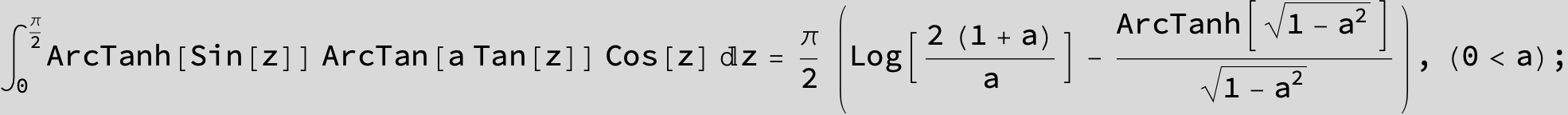


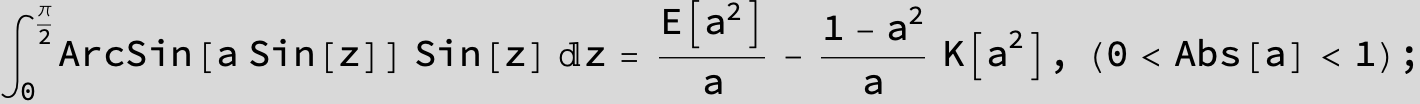
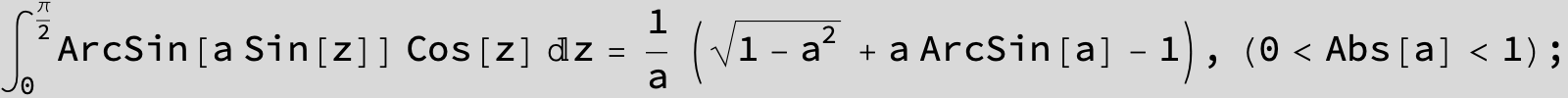
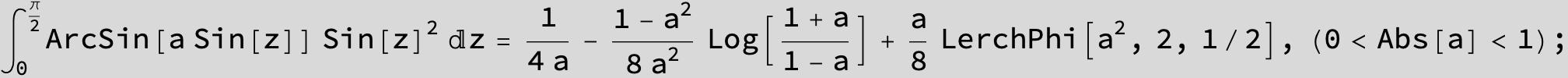
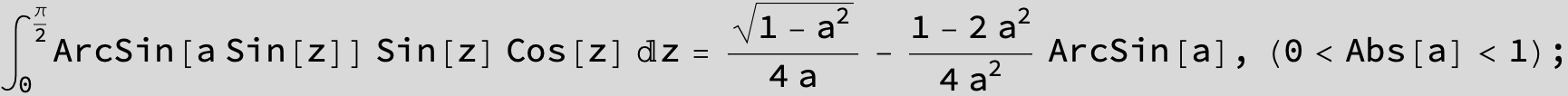

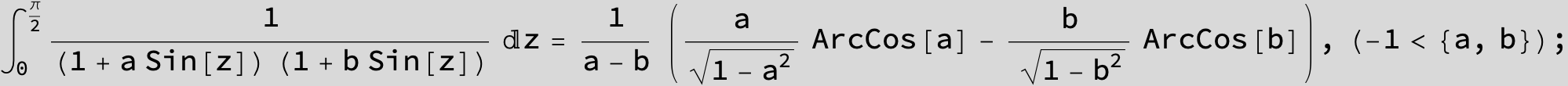
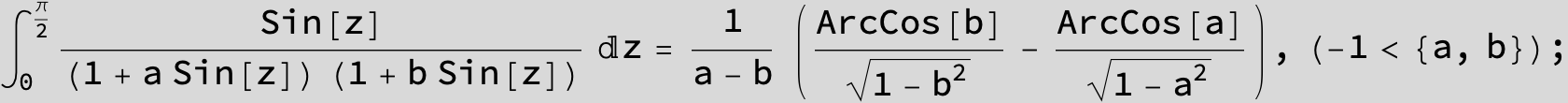
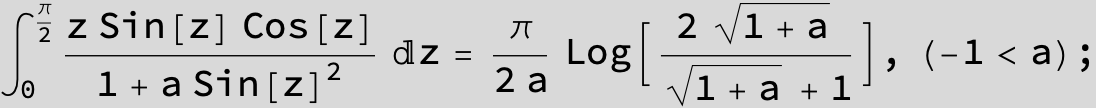
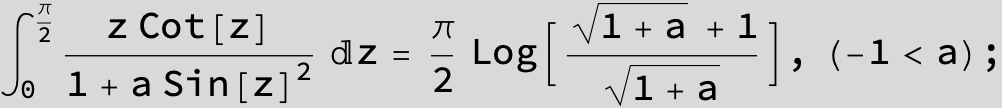
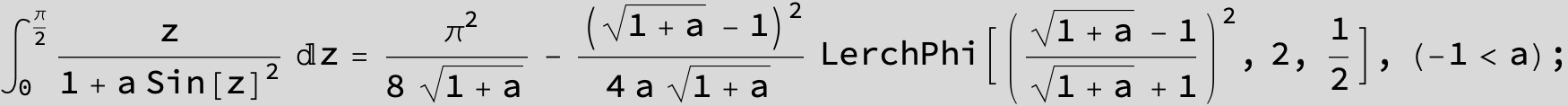
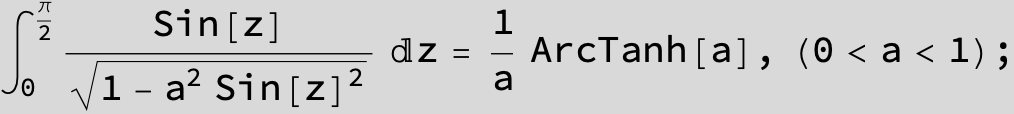
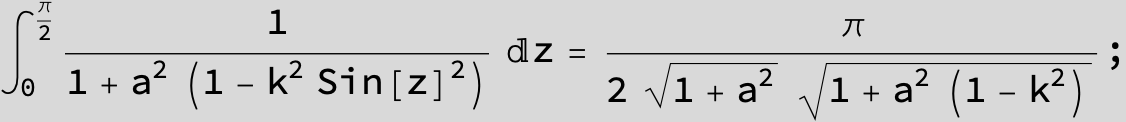
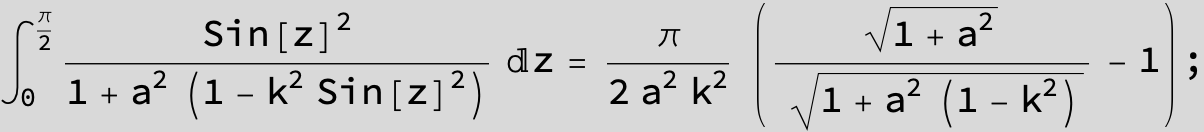
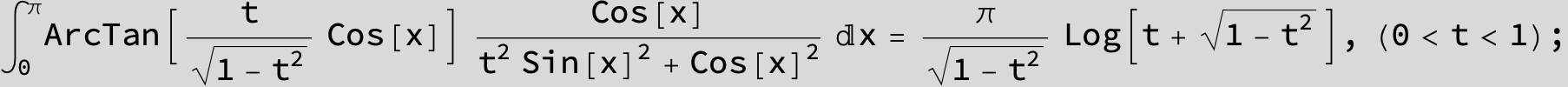
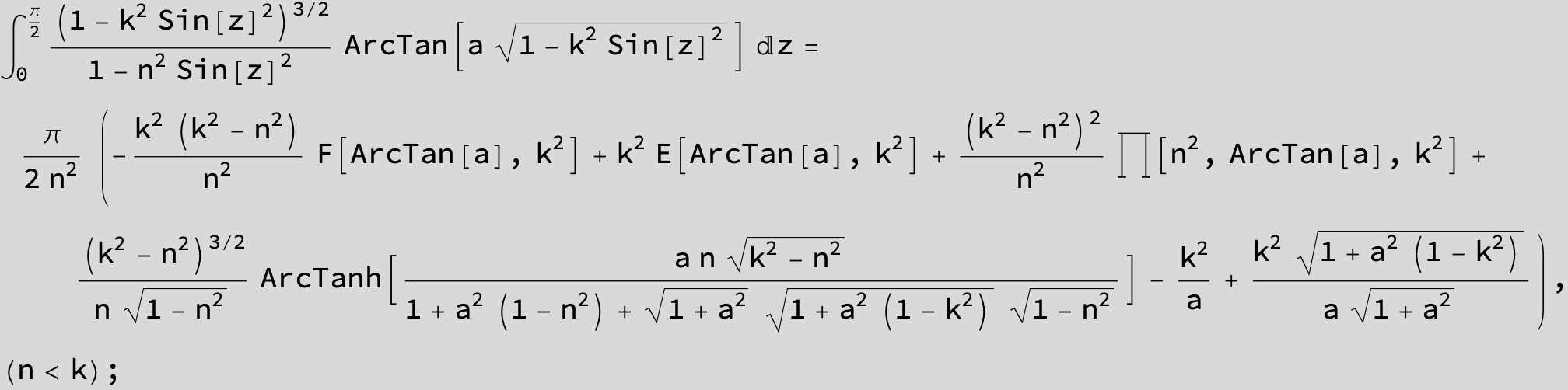
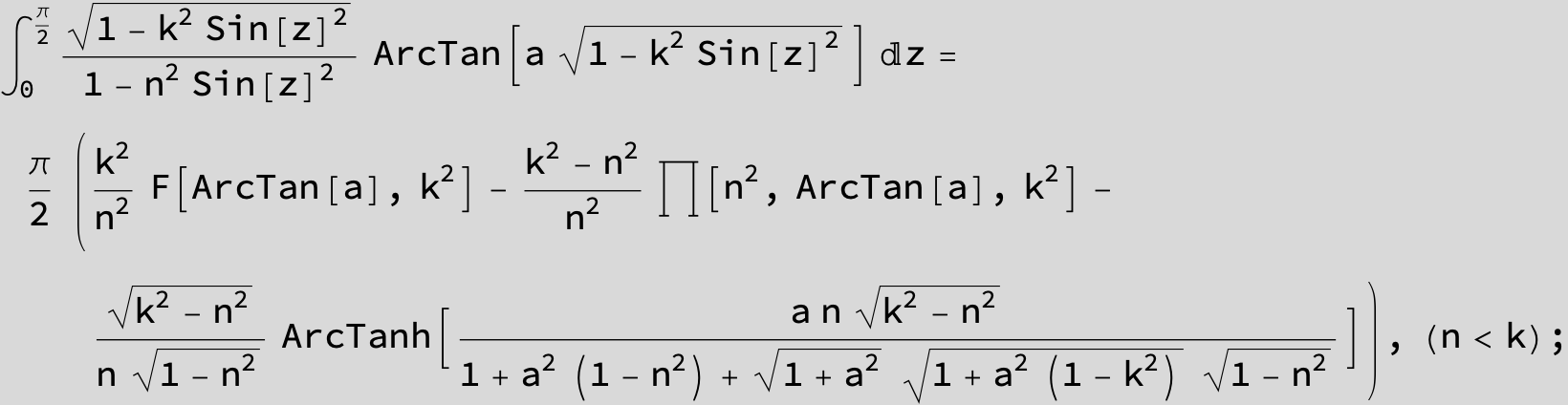
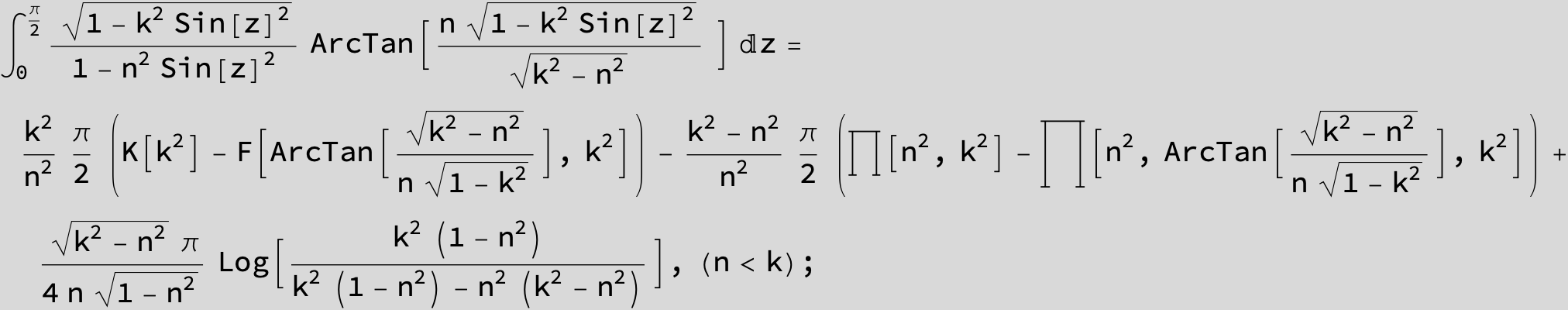
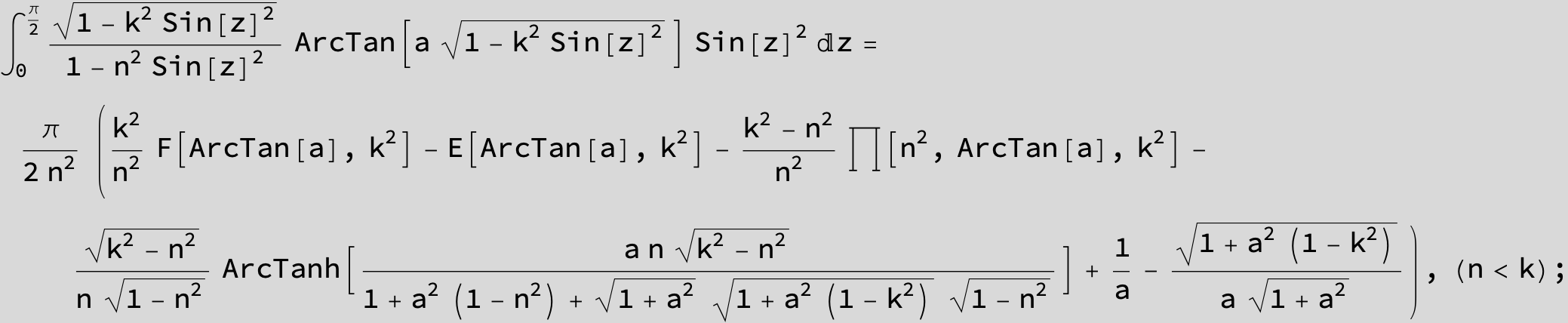
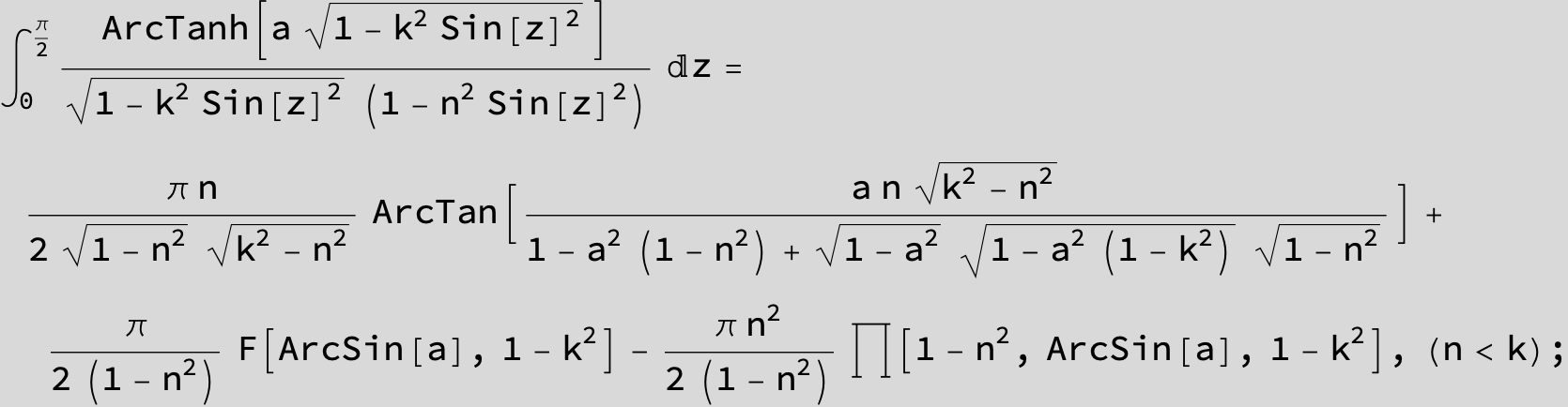
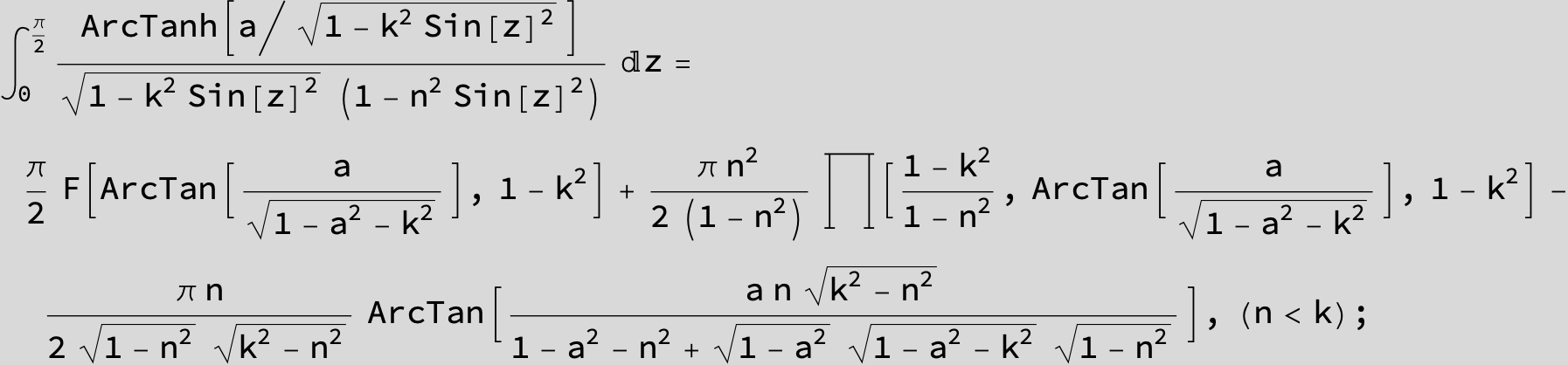
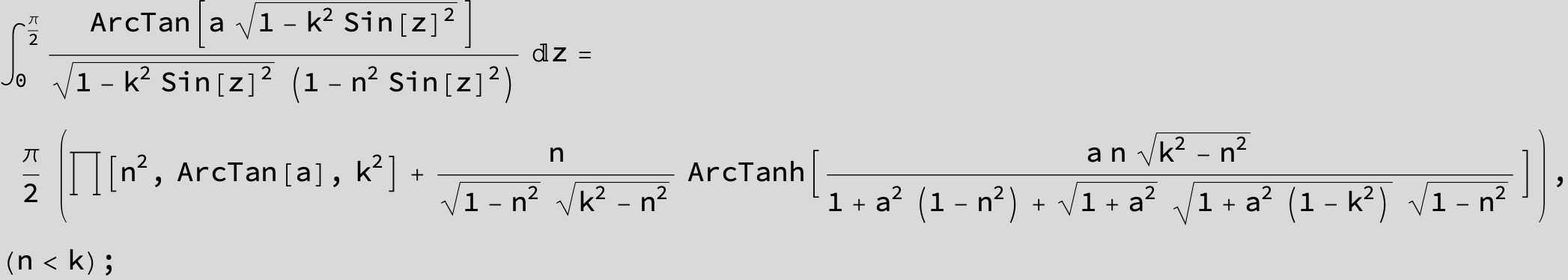
![]()
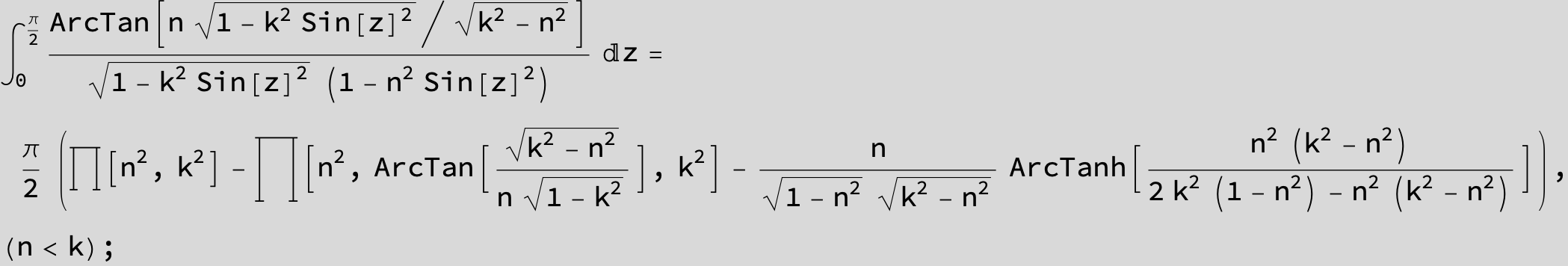
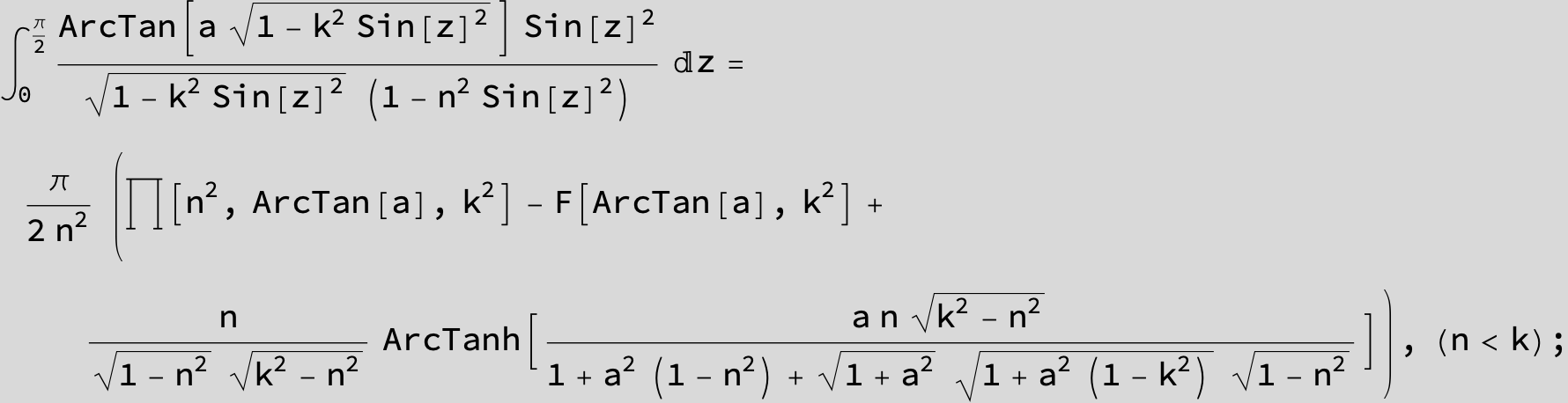


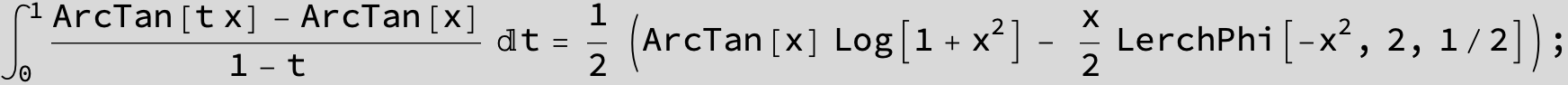

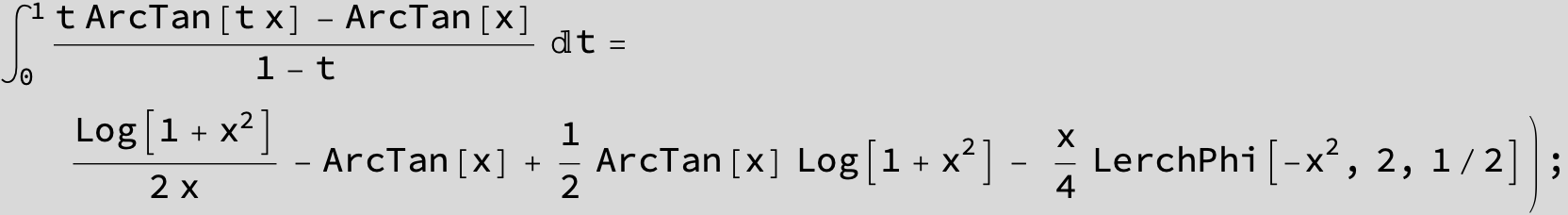
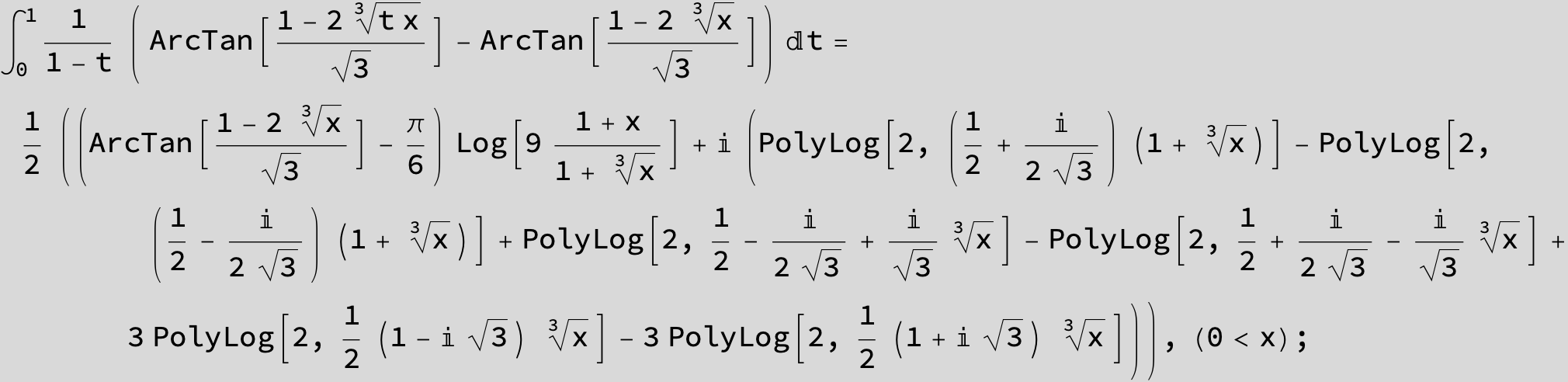


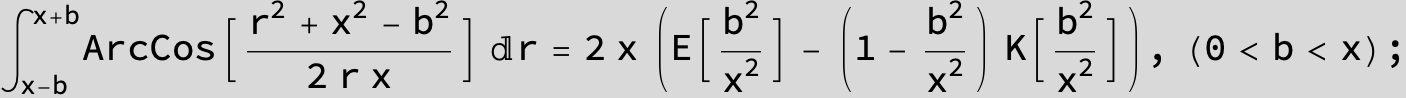
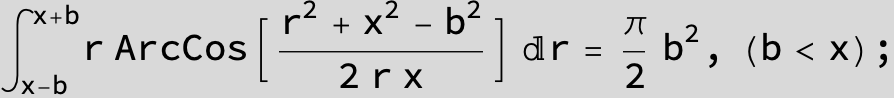
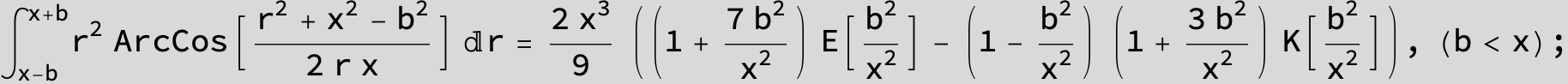


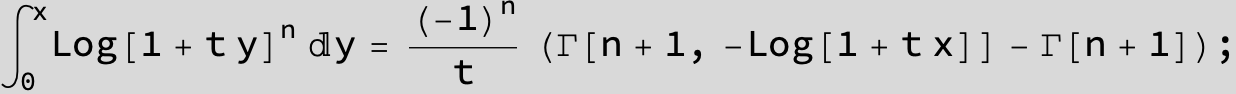

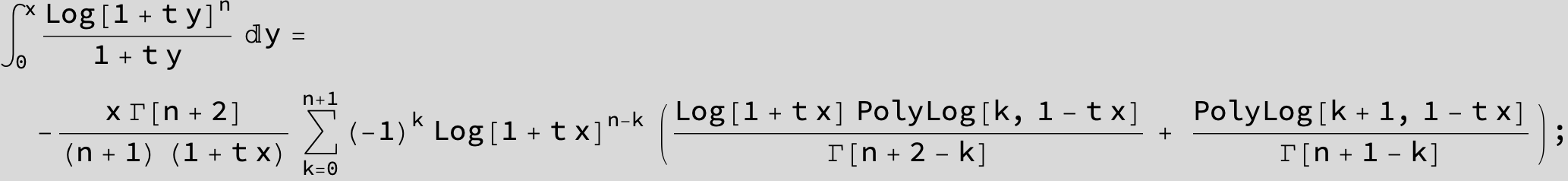
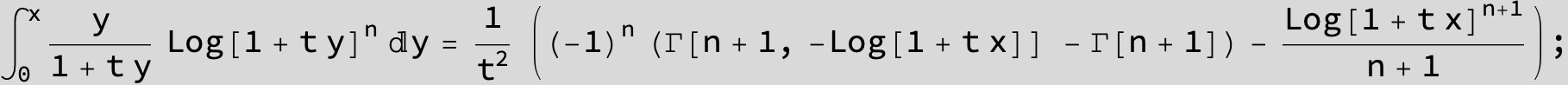
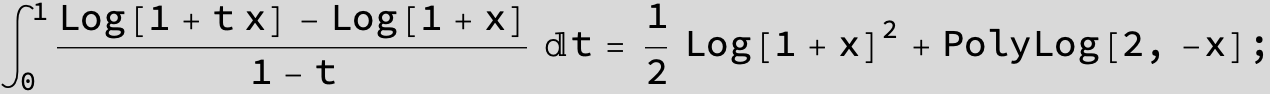
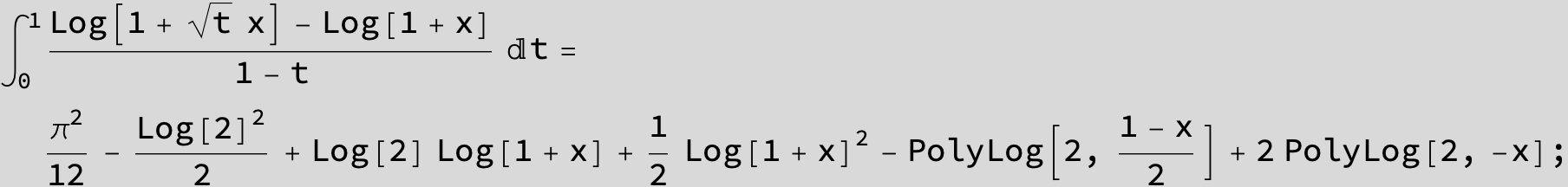
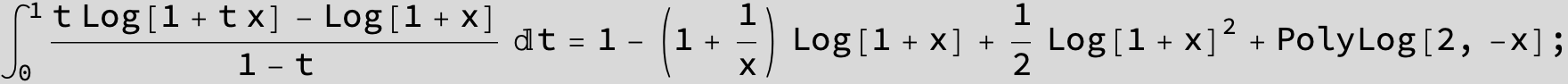

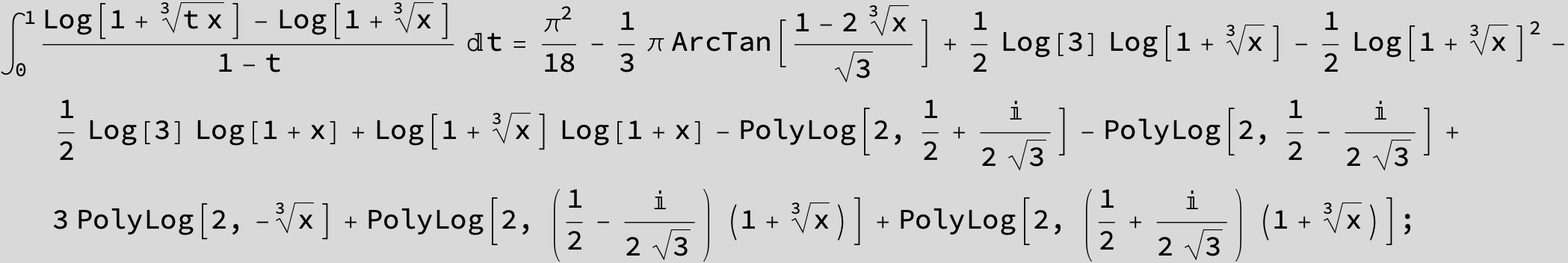
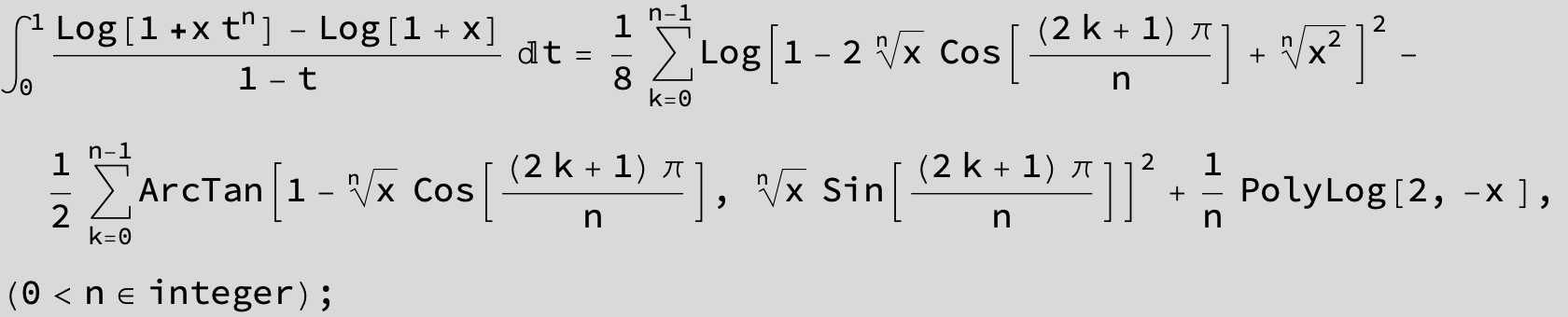
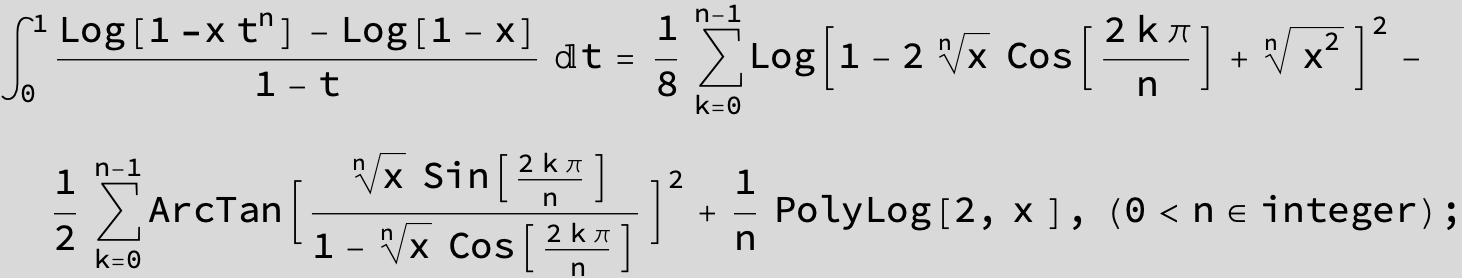


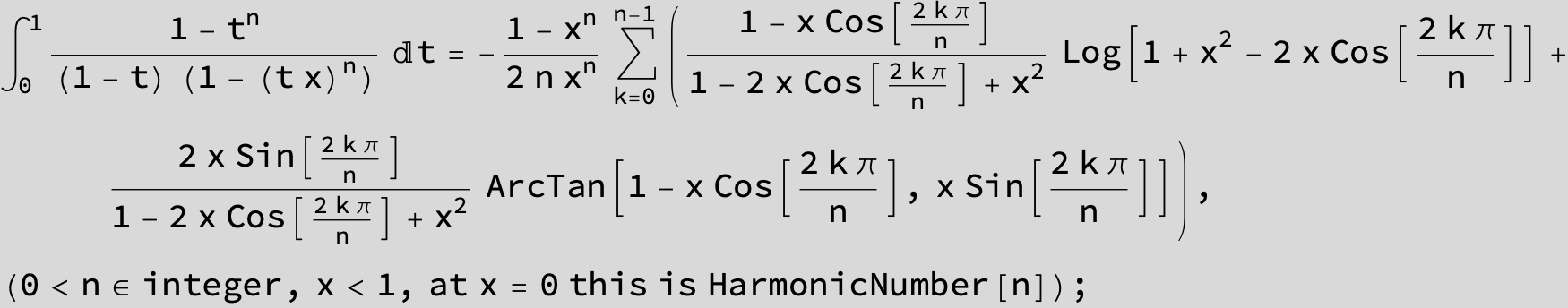
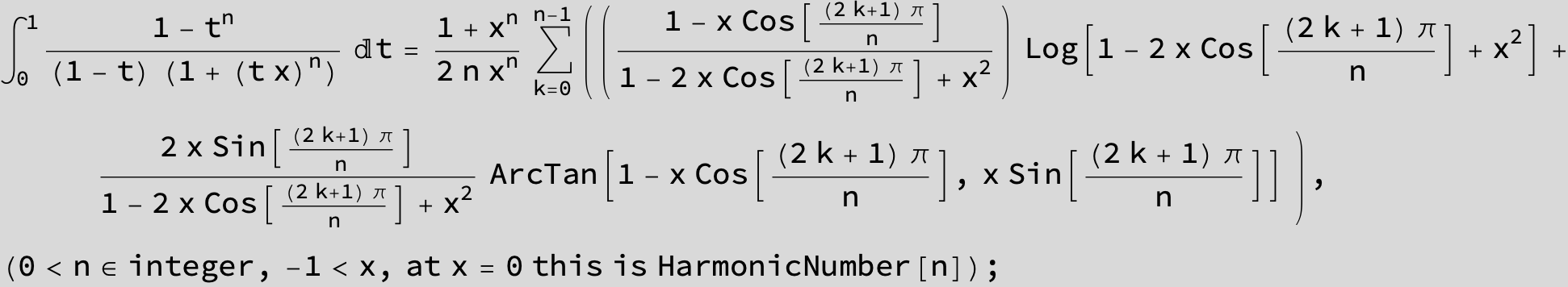

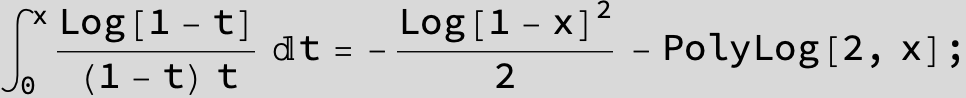
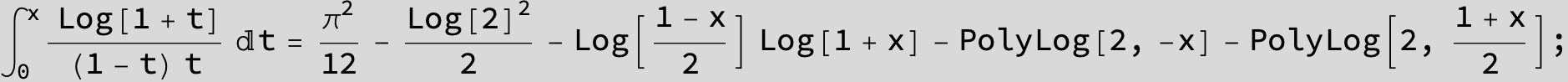
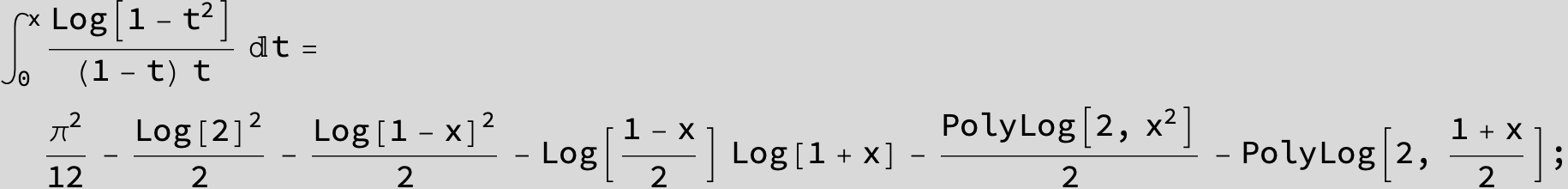
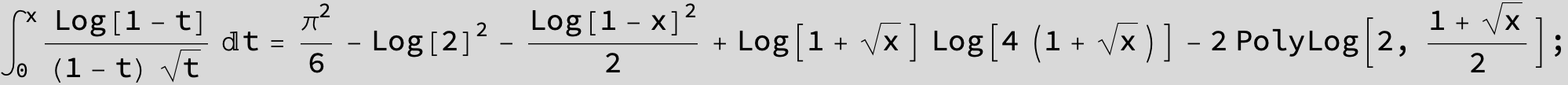
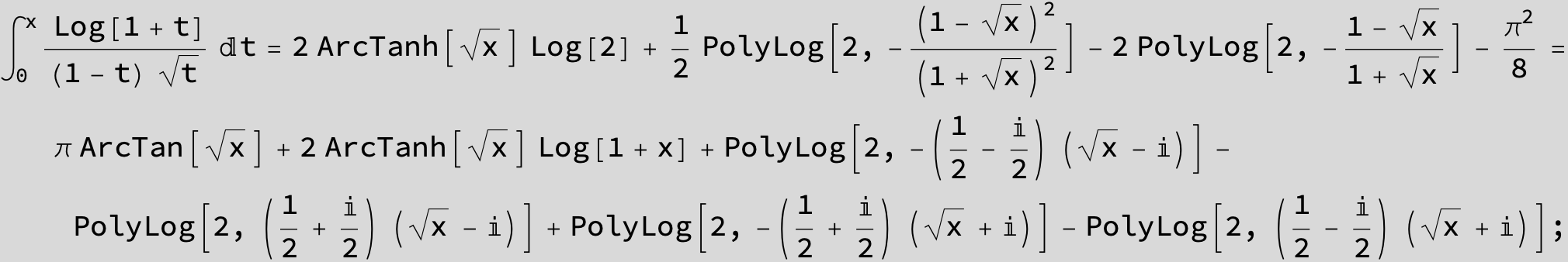
![]()
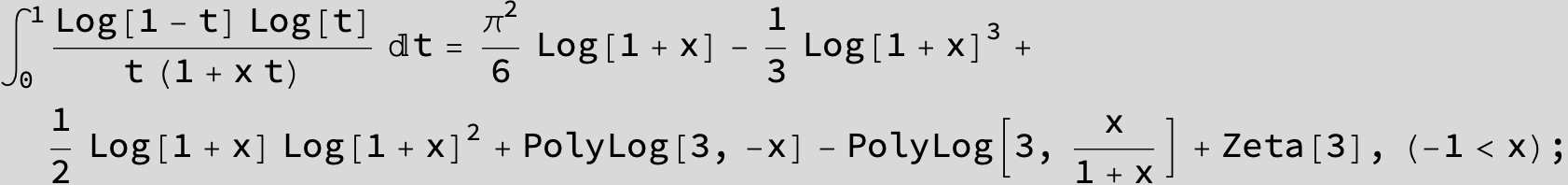
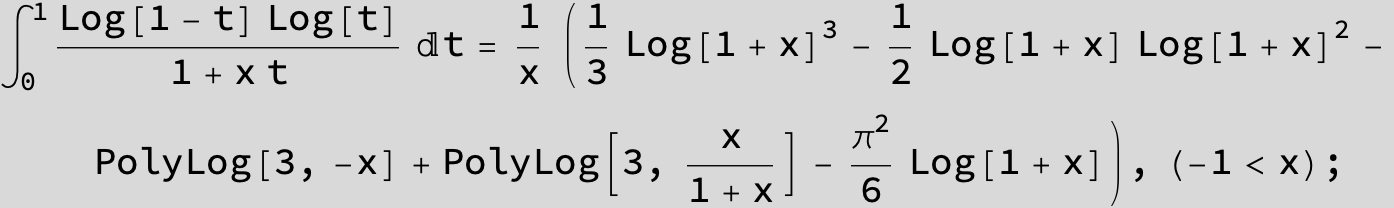
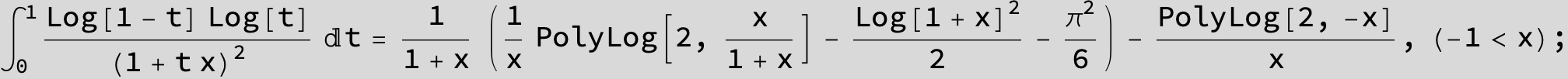
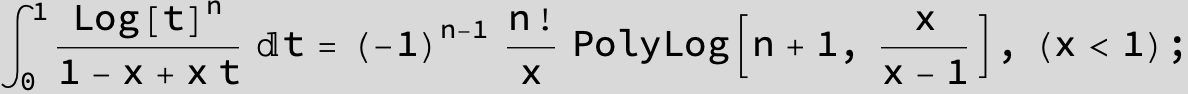

![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
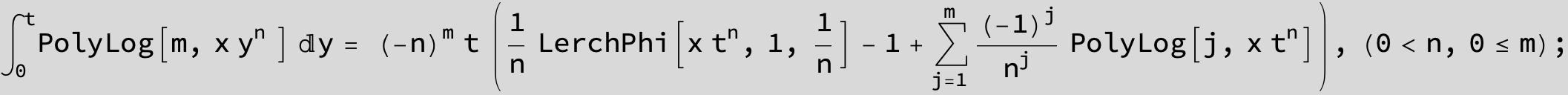
![]()
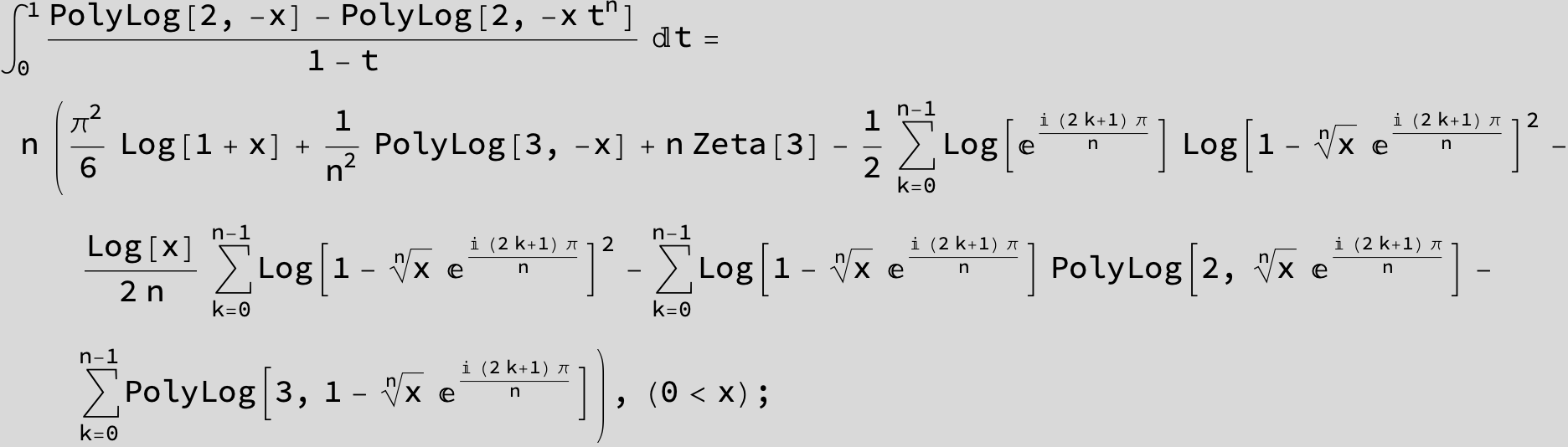
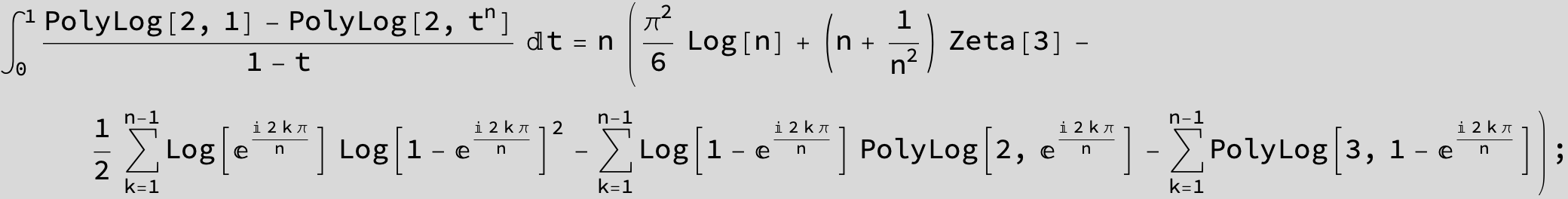
![]()
![]()
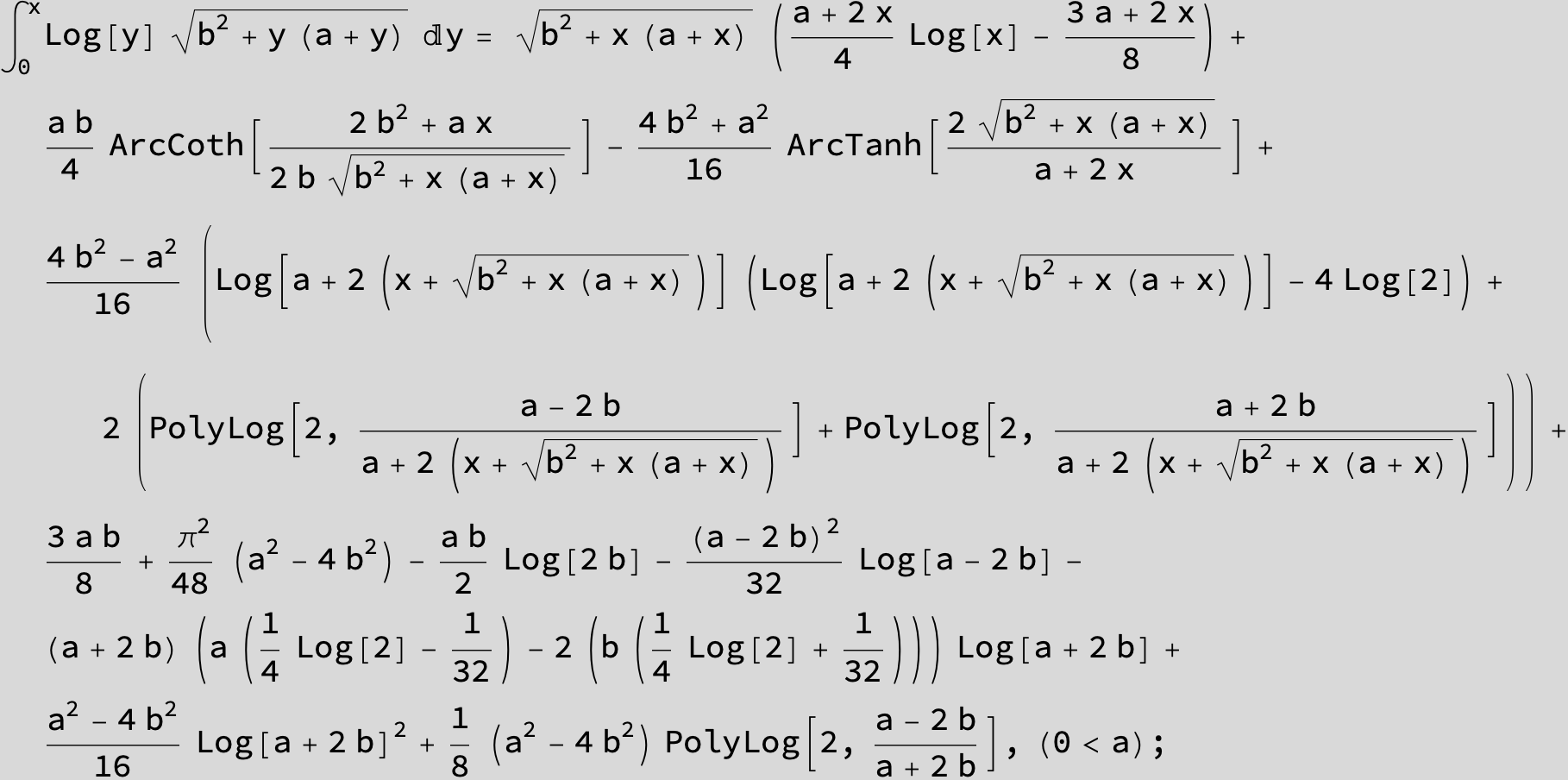
![]()


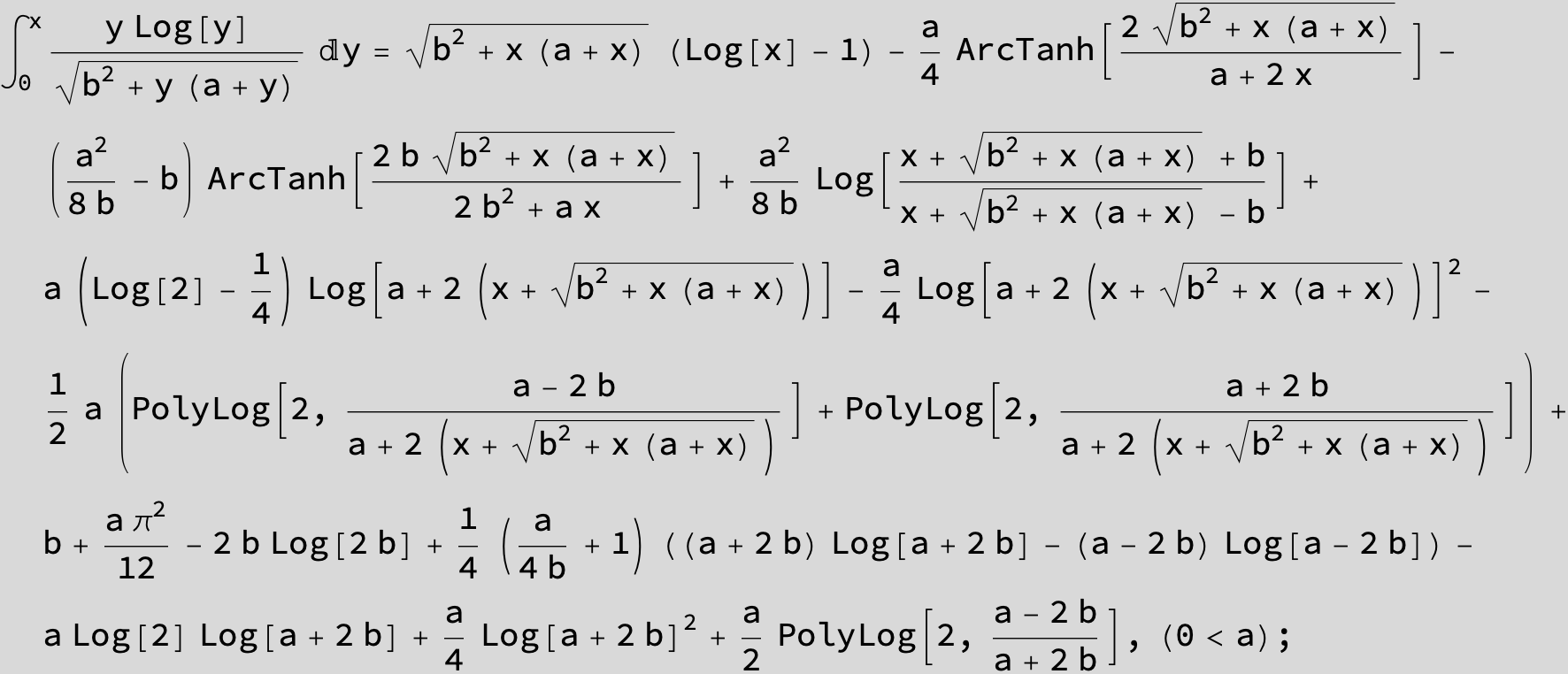

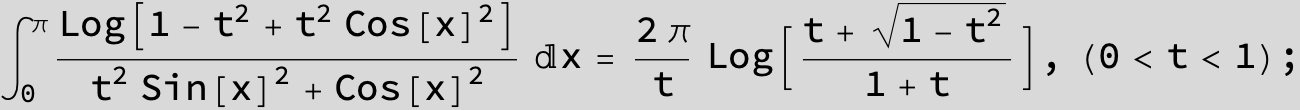

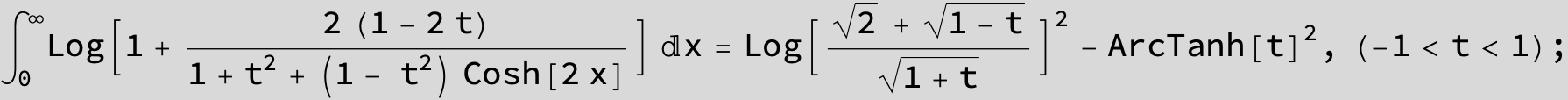
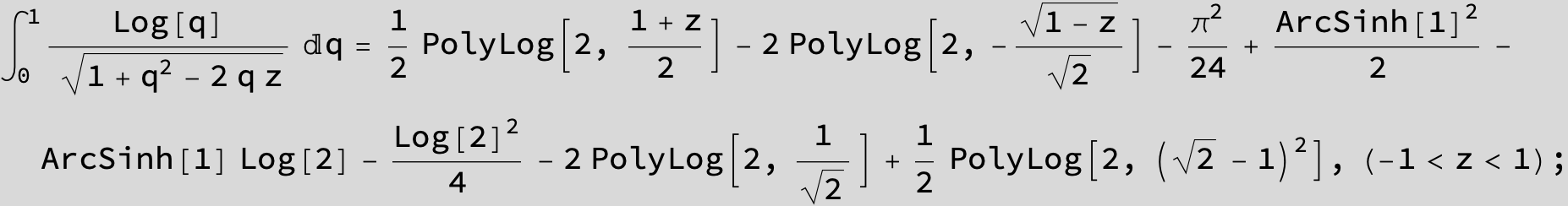
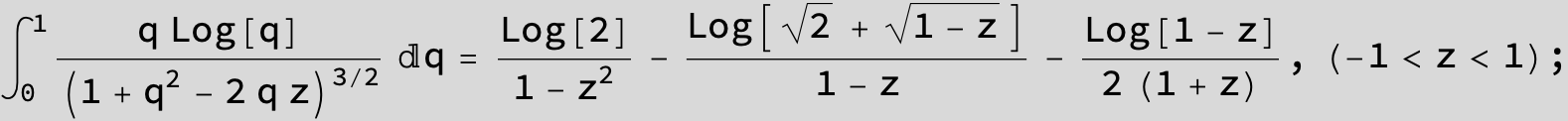
![]()
![]()
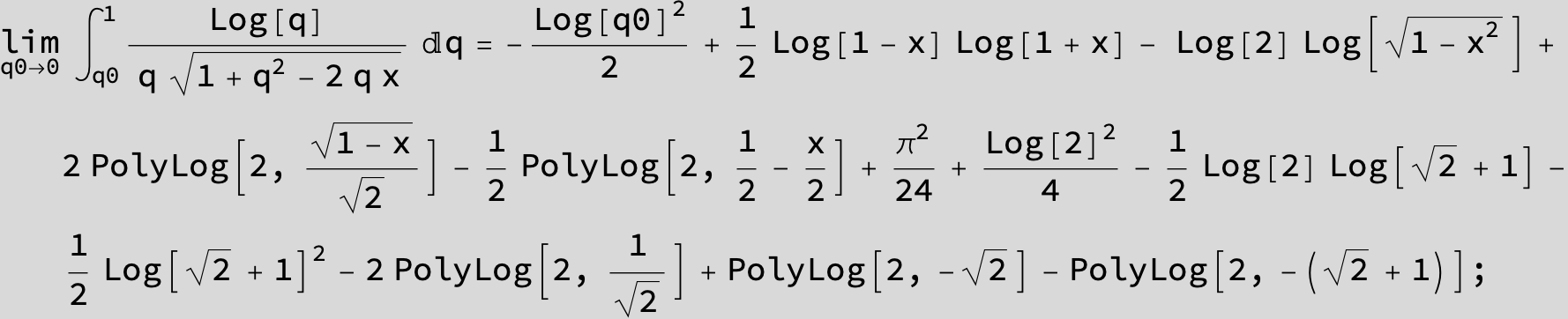
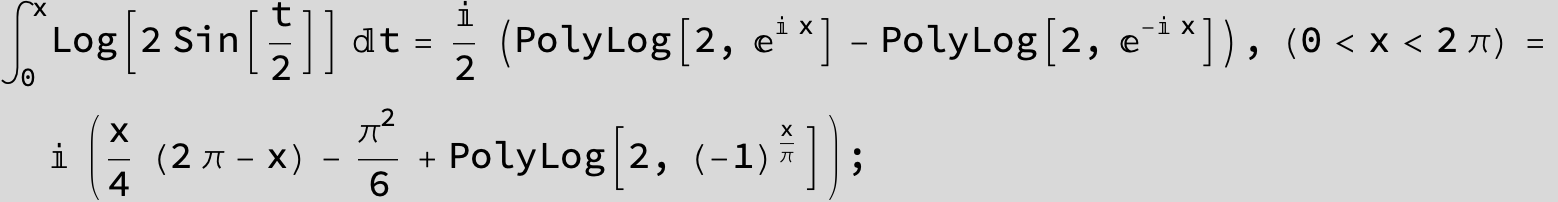
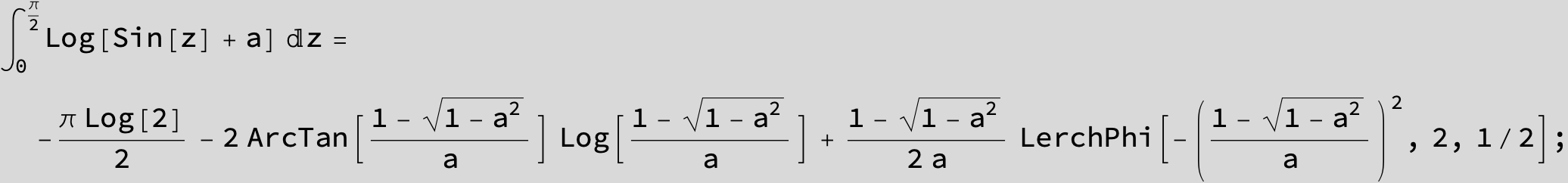

![]()
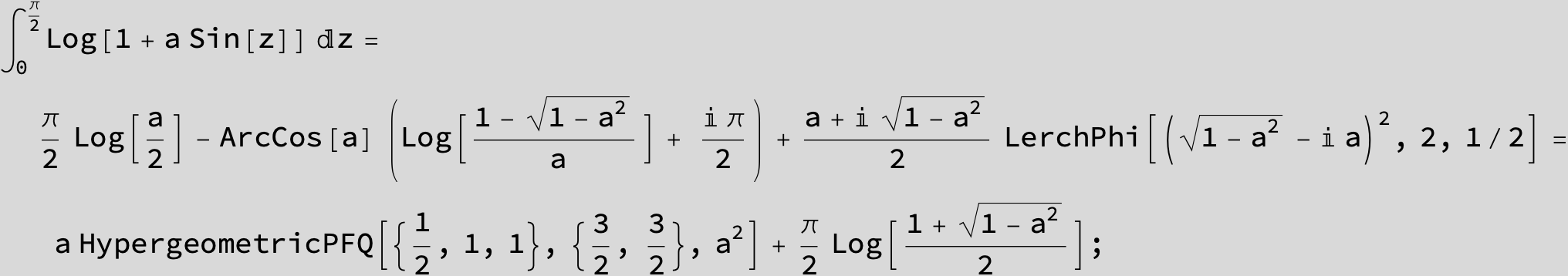
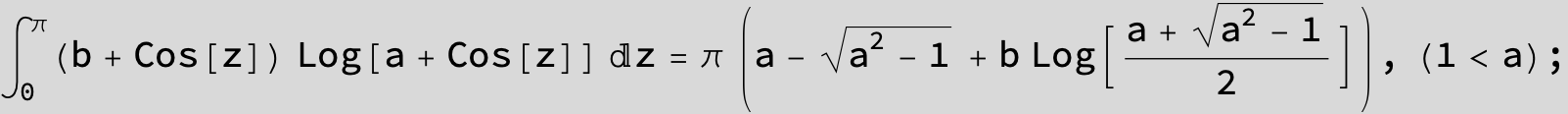

![]()
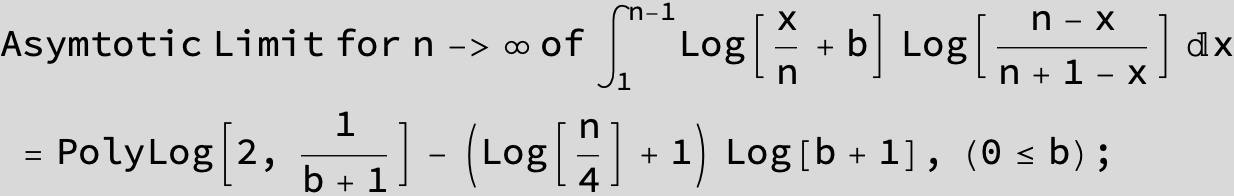
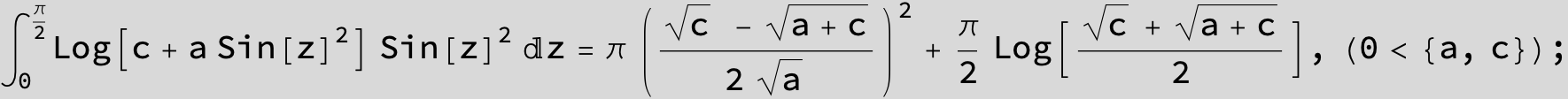
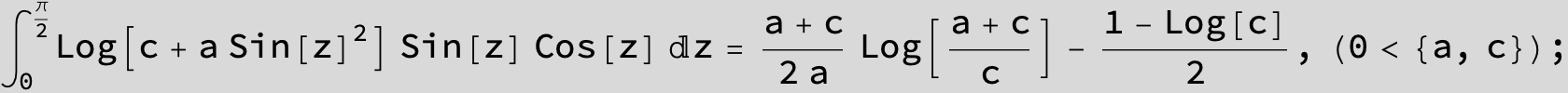

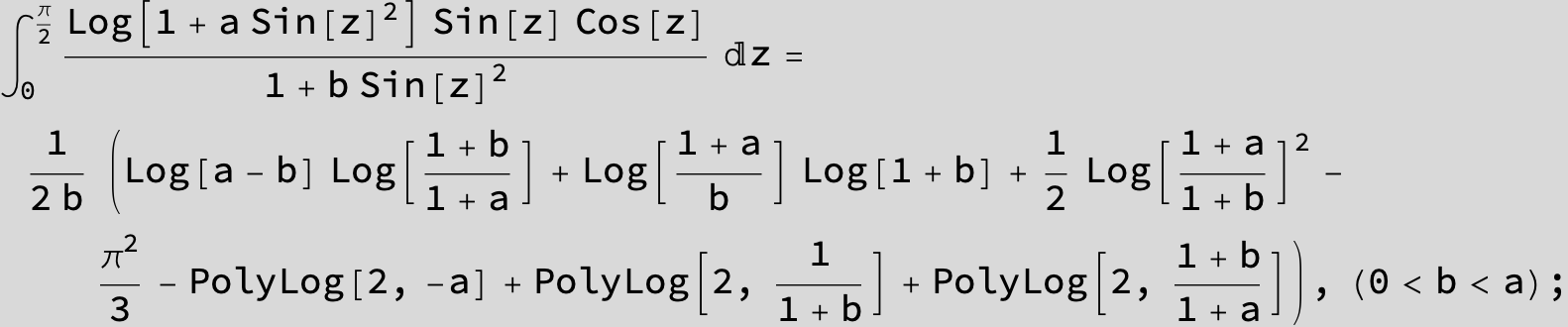
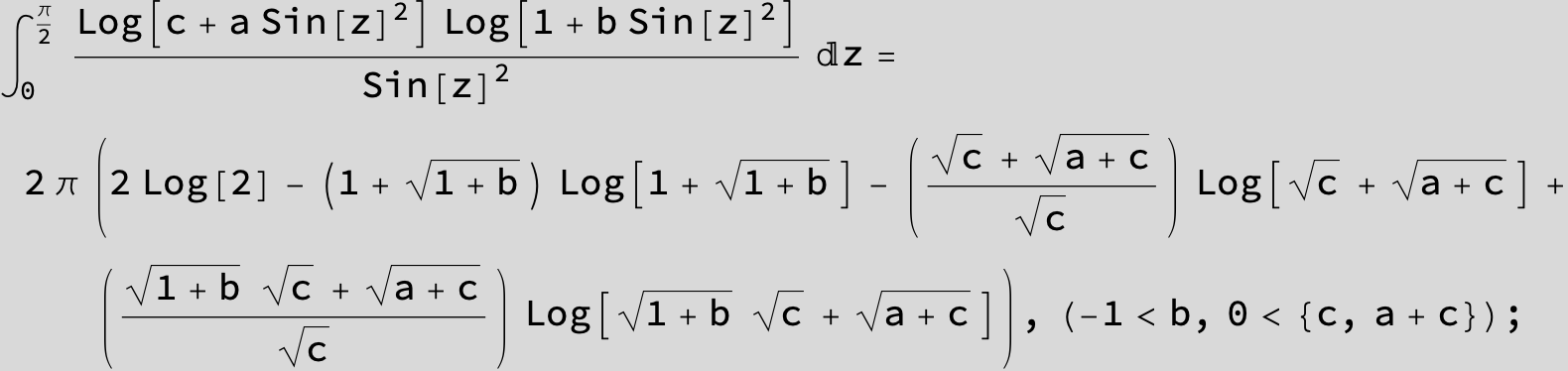

![]()

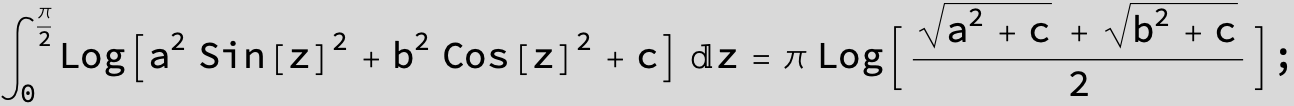
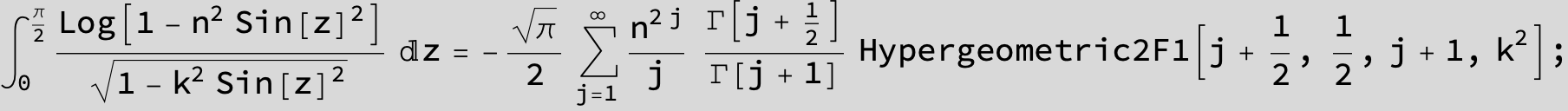



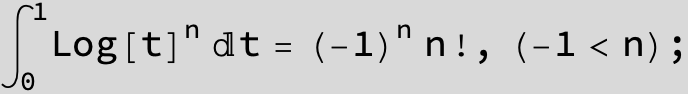
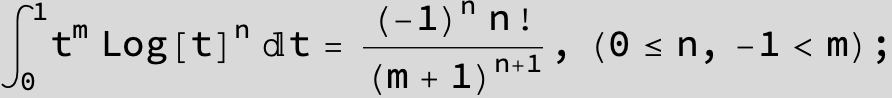
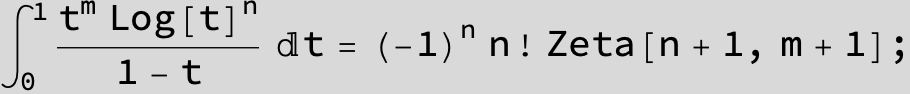

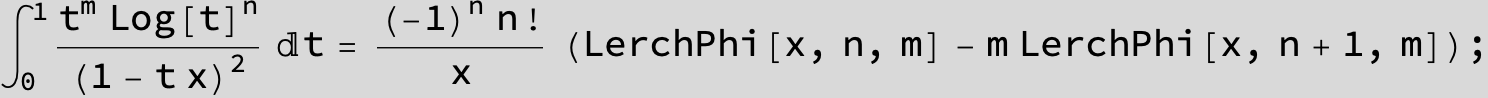

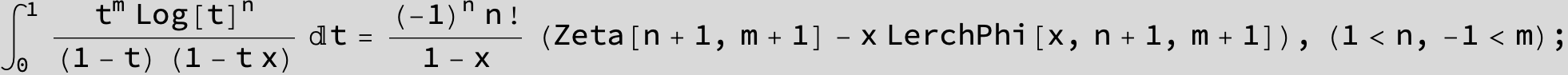
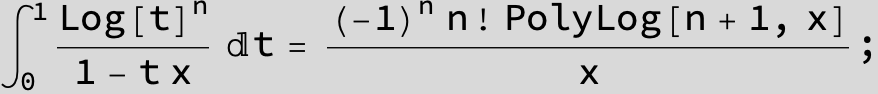
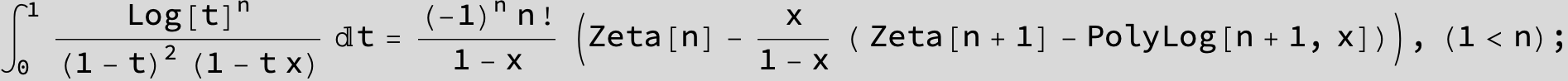

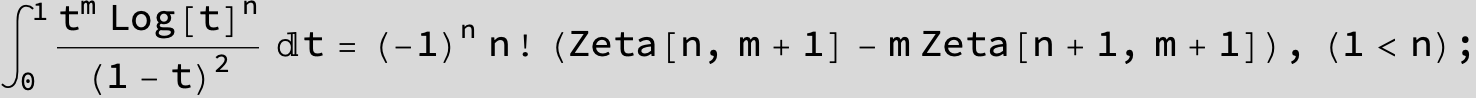
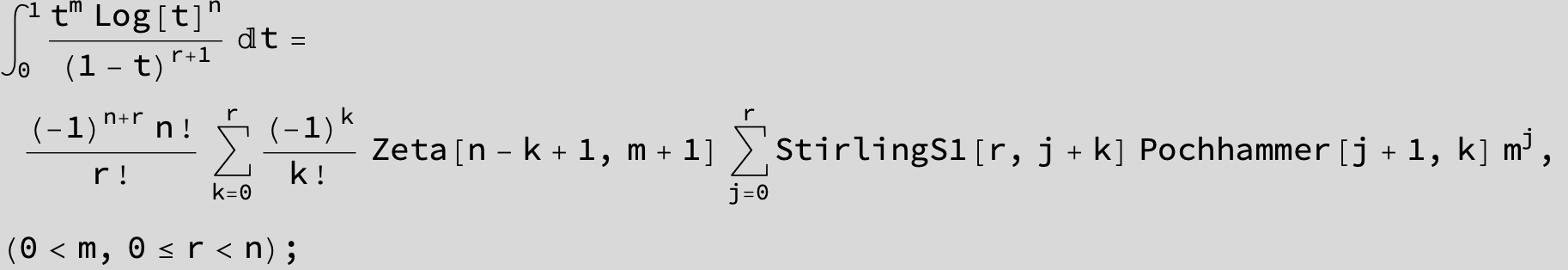

![]()
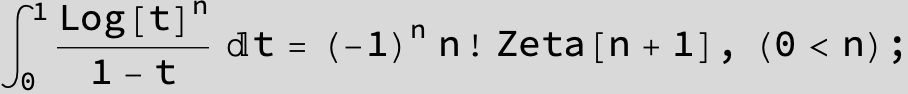

![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()

![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
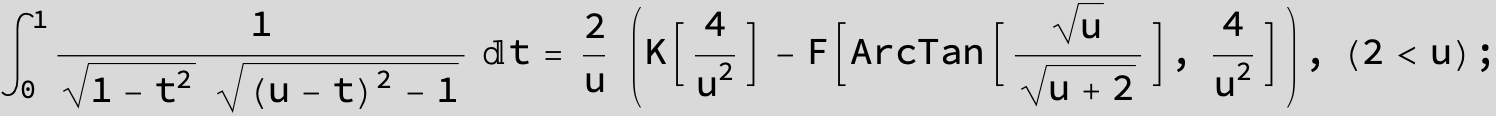
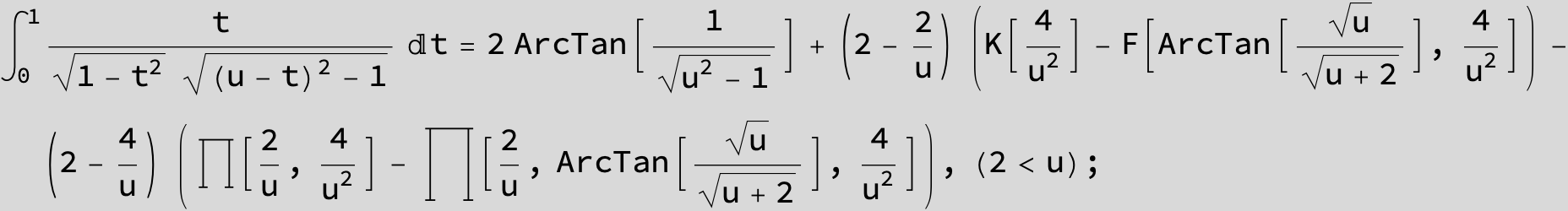
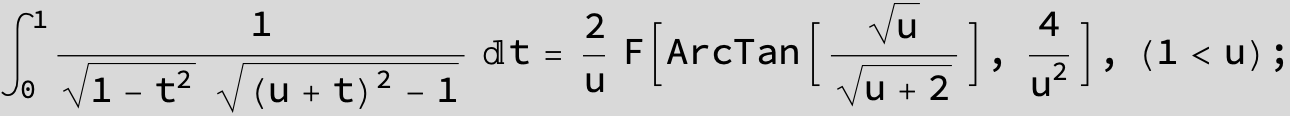
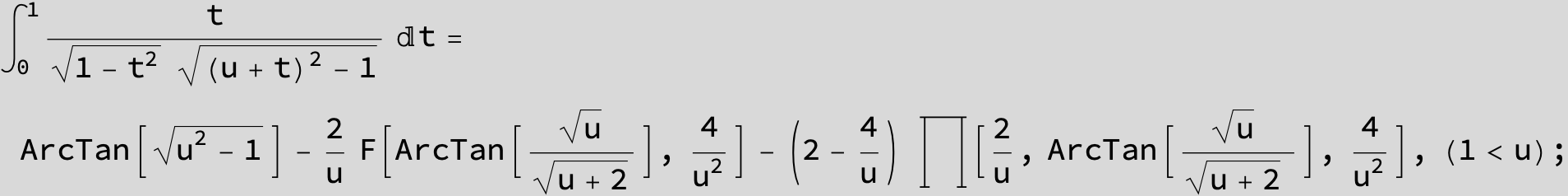
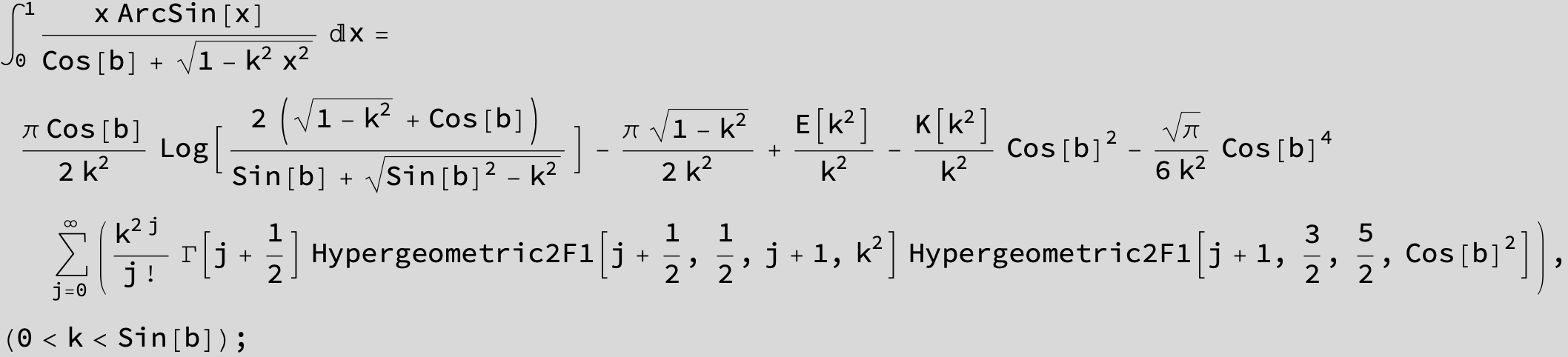
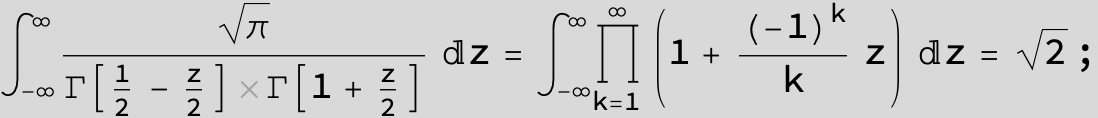
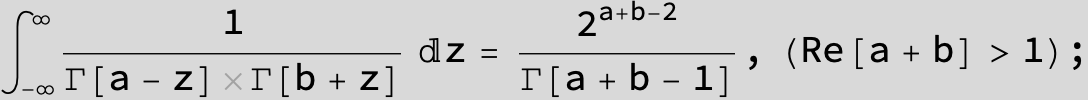
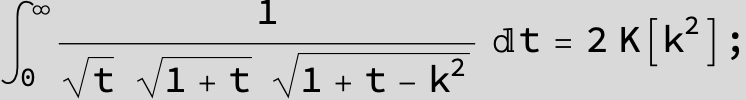
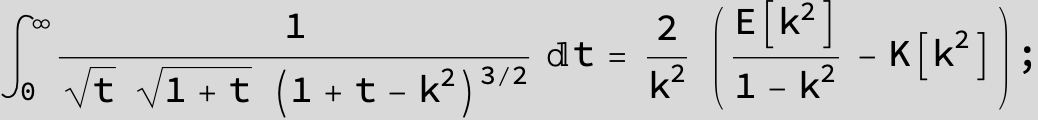
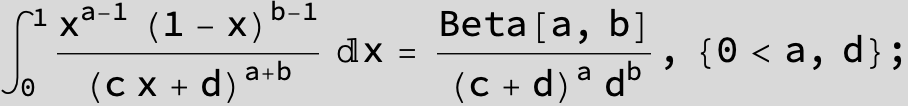
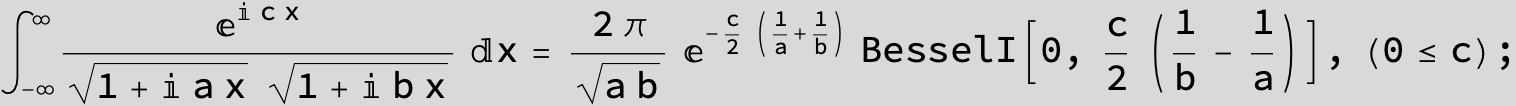
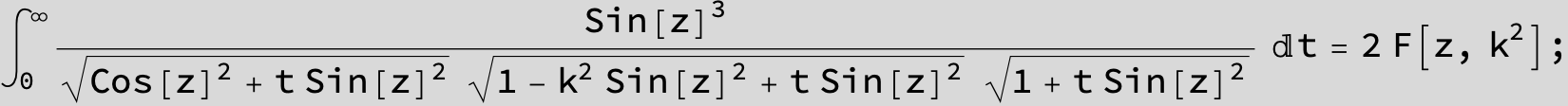
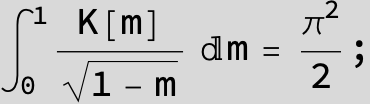
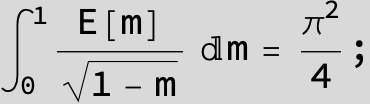
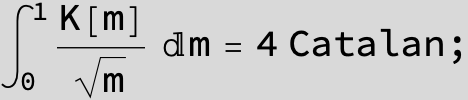
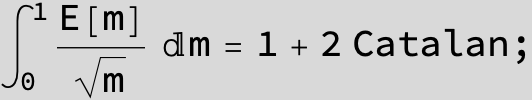
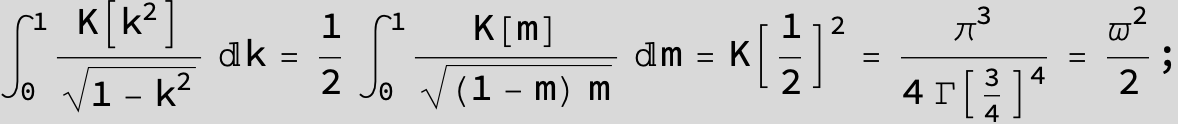
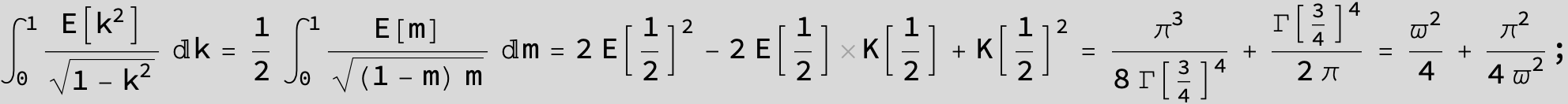
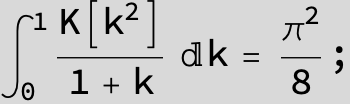
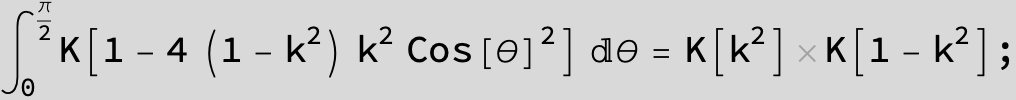
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
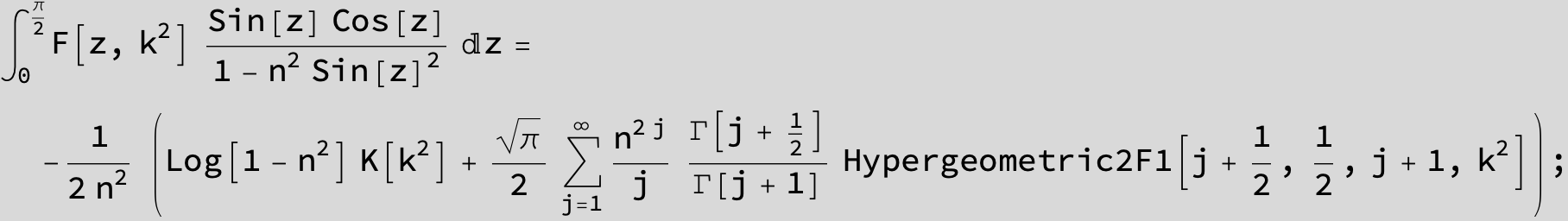
![]()
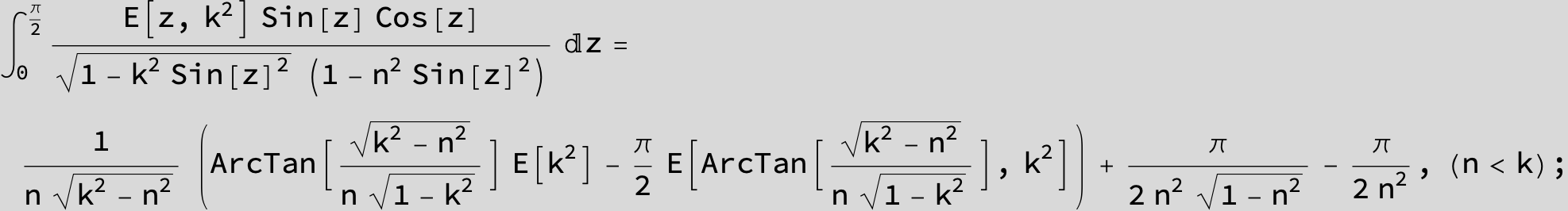
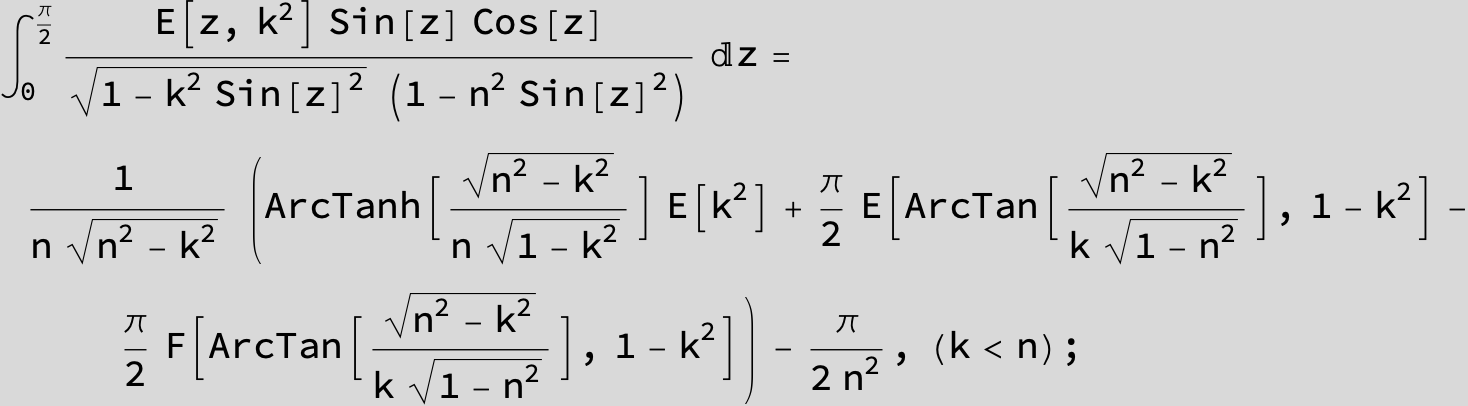
![]()
![]()
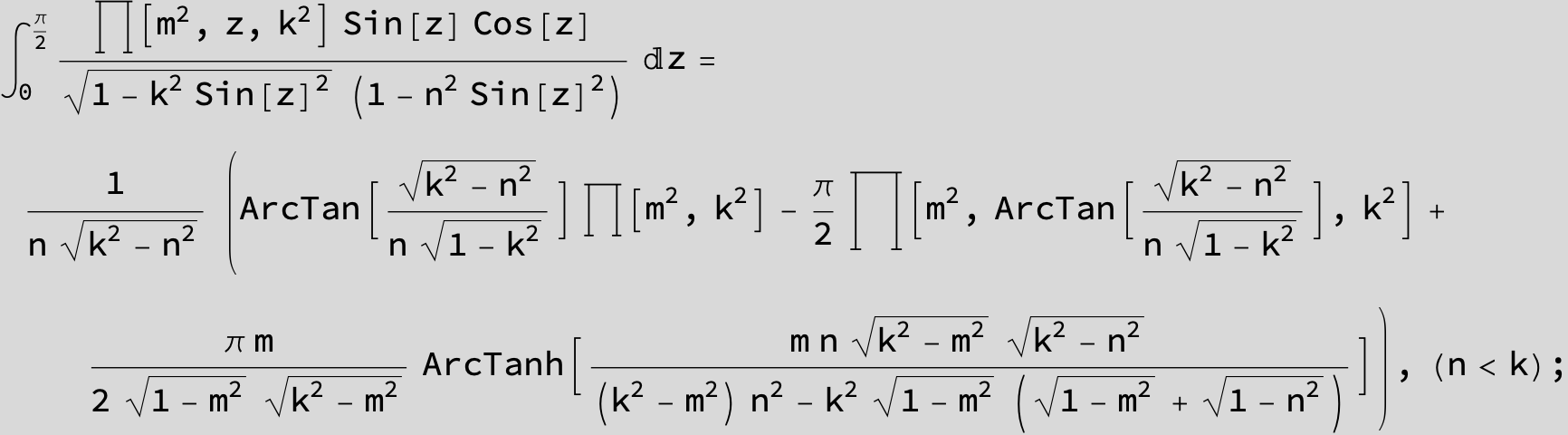
![]()
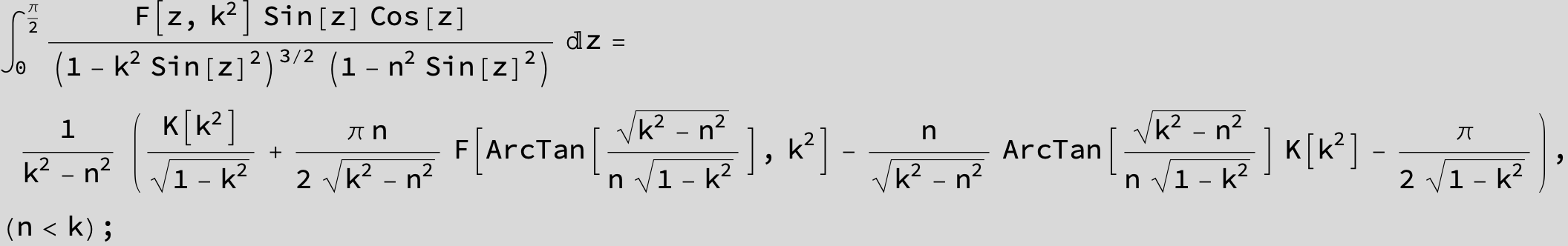
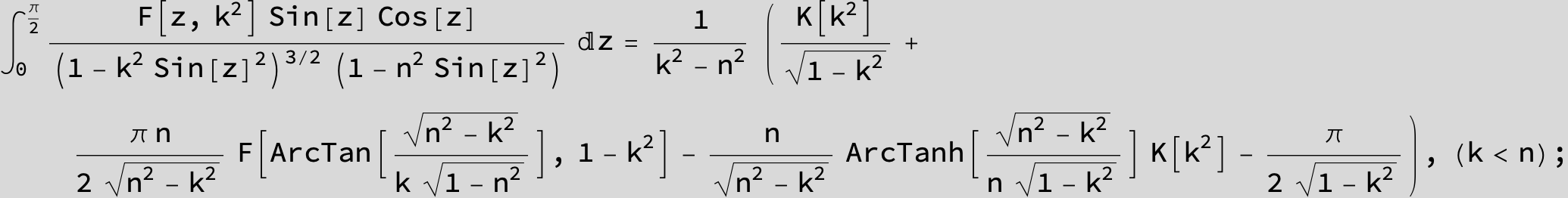
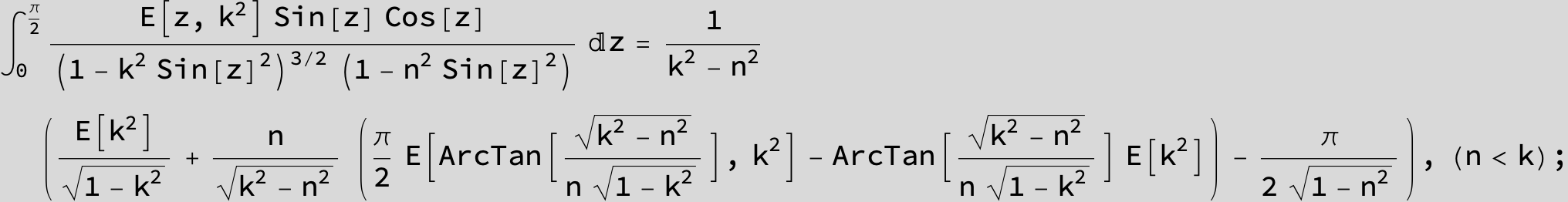
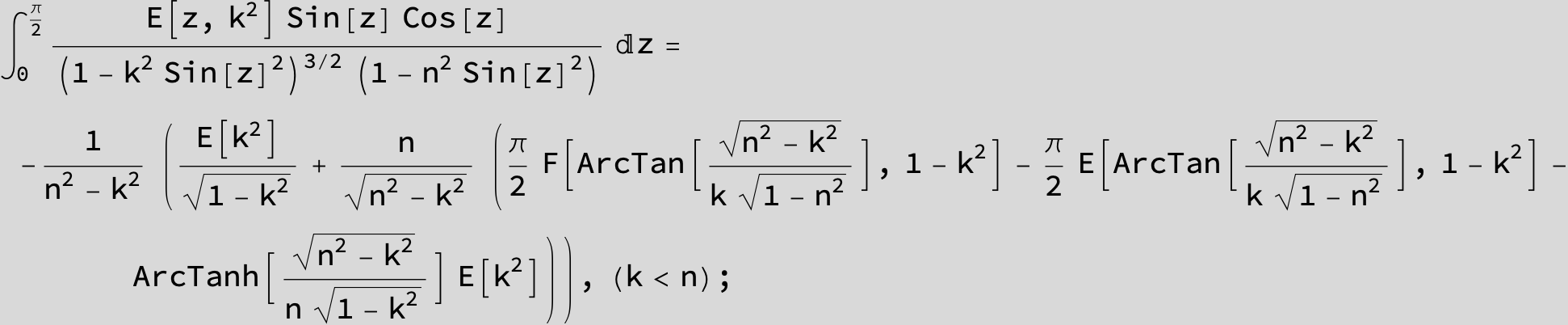
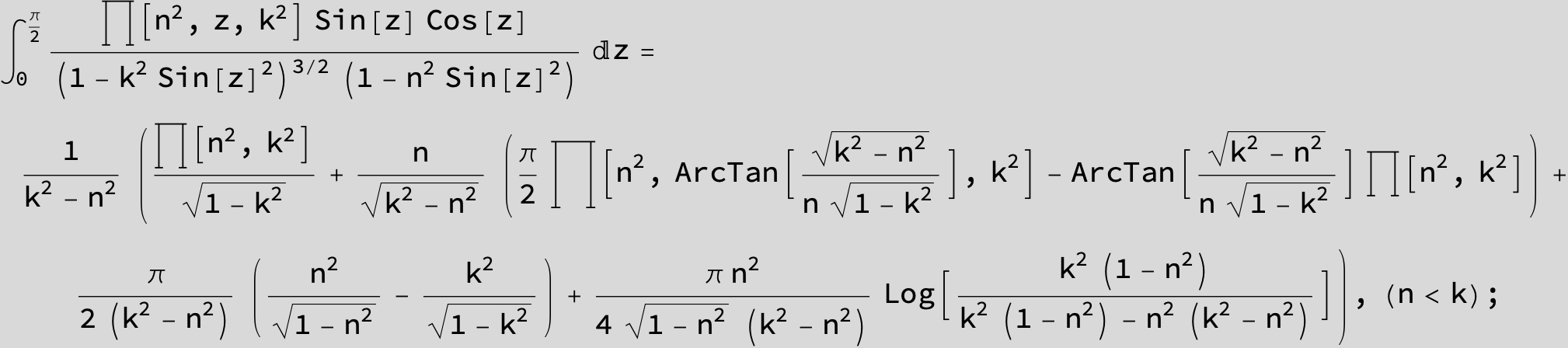
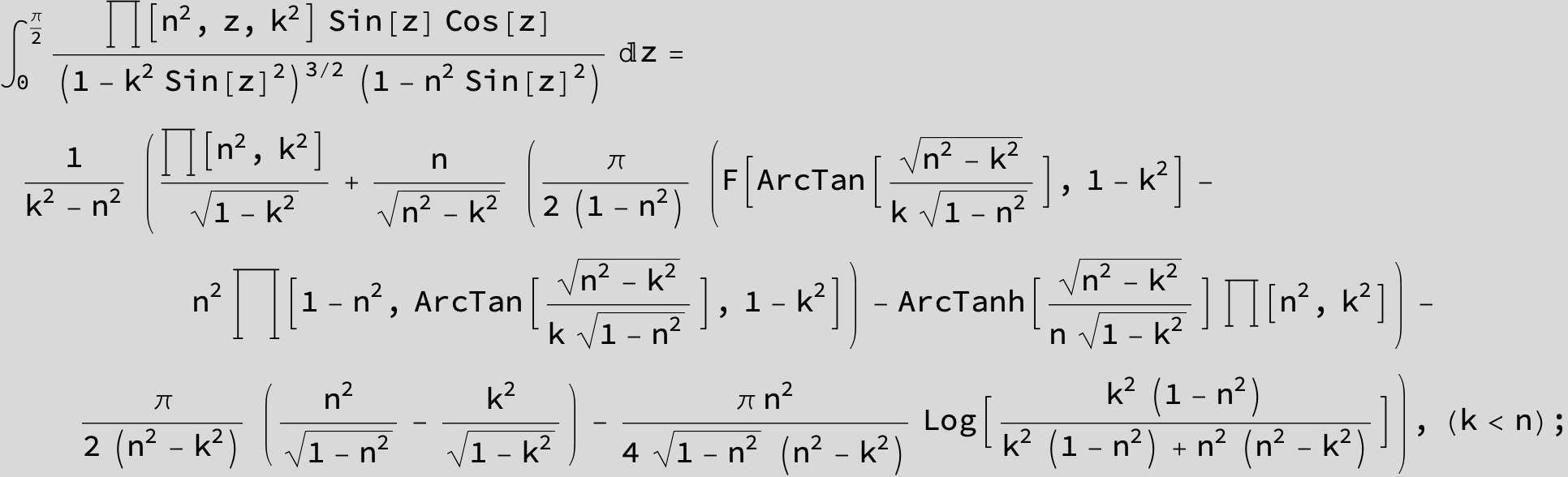
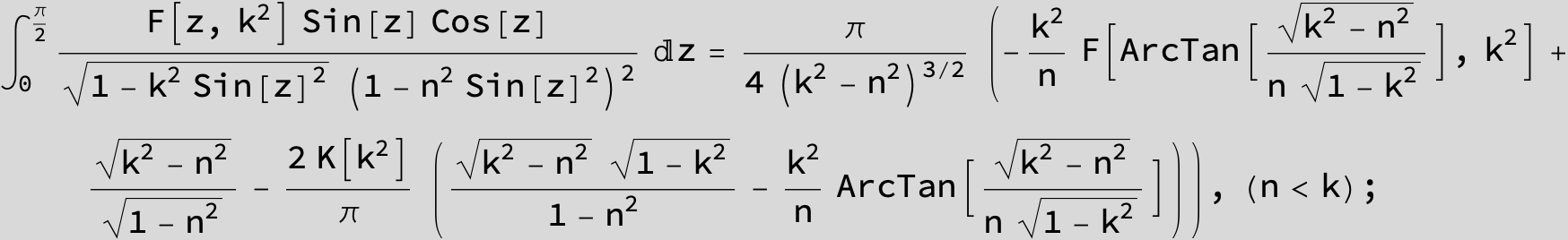
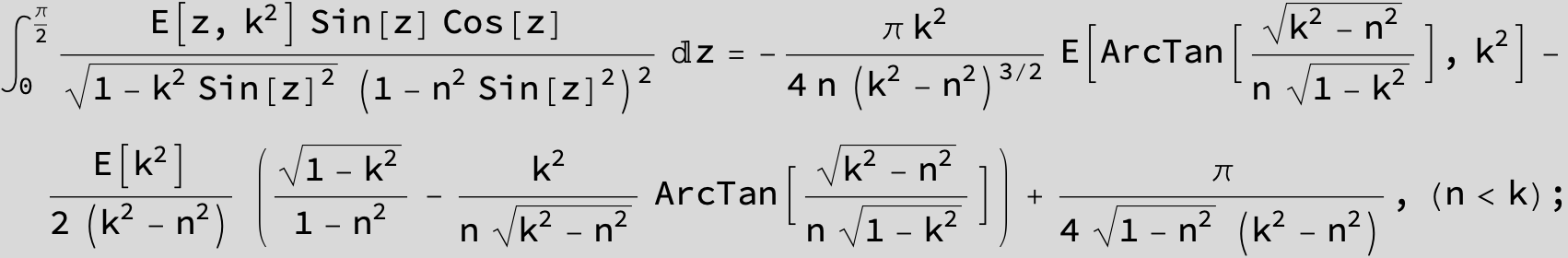
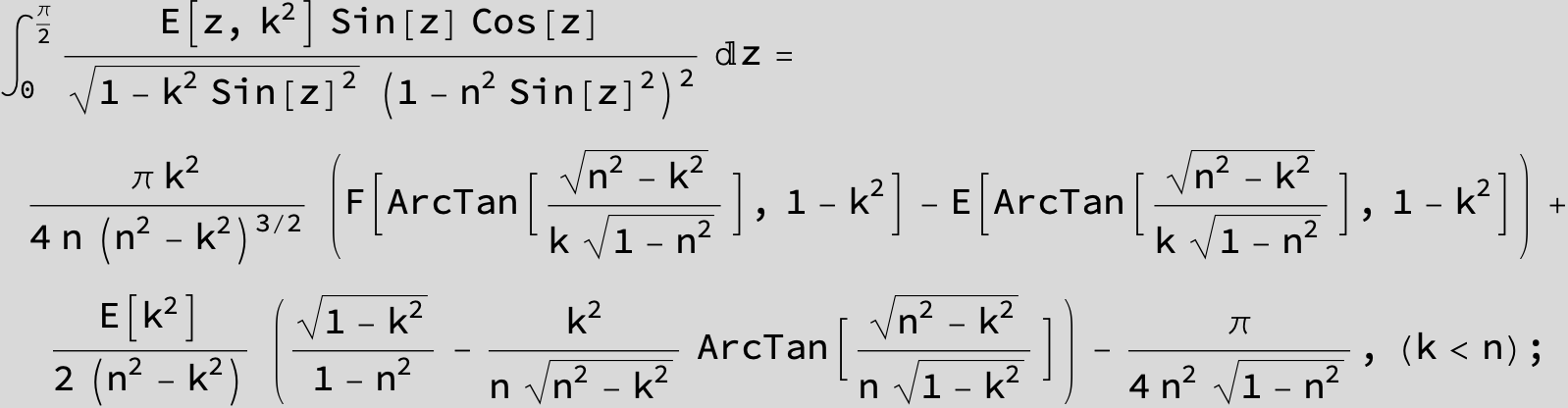
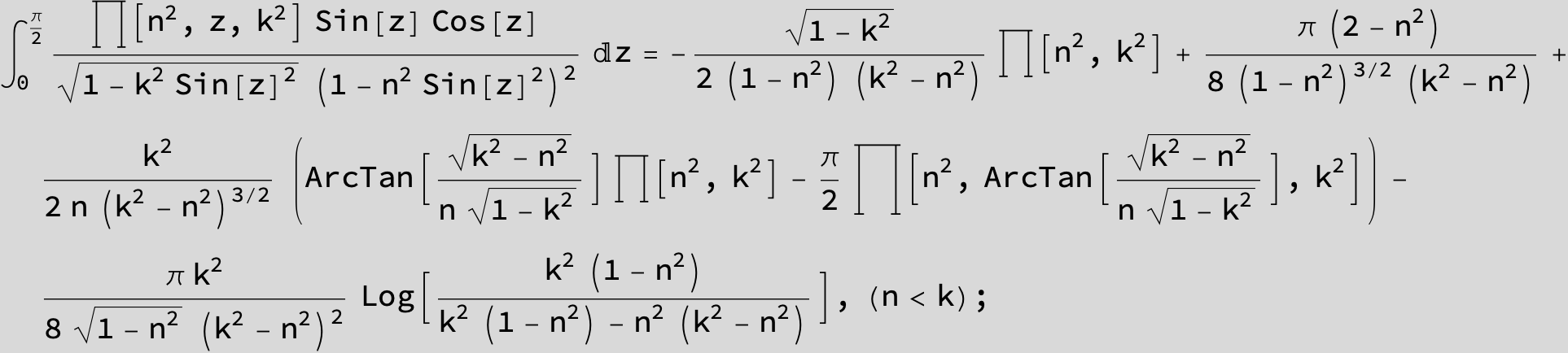
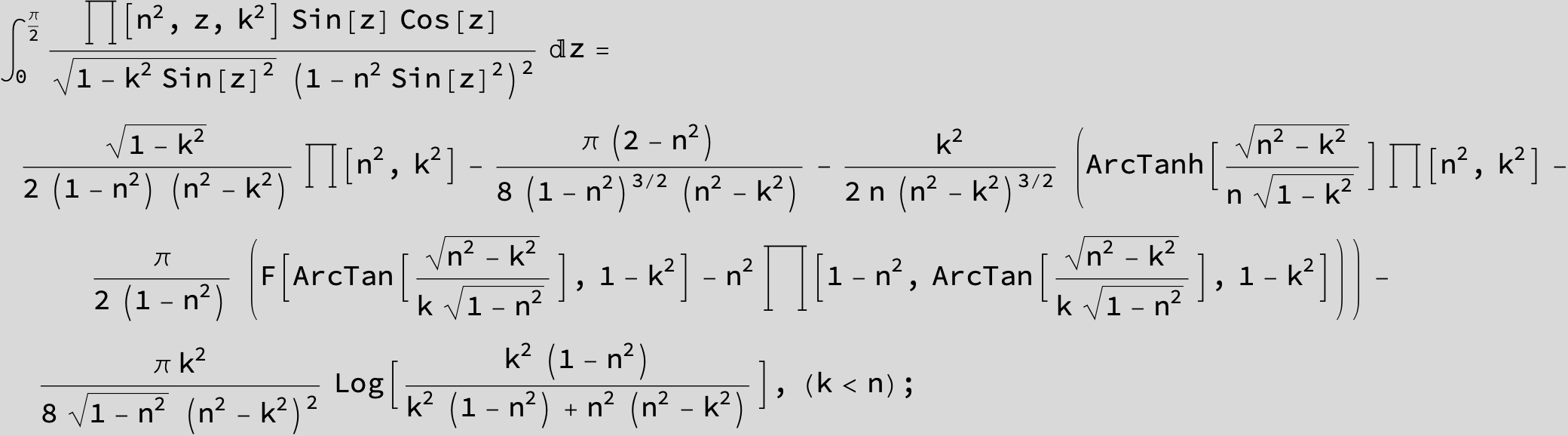
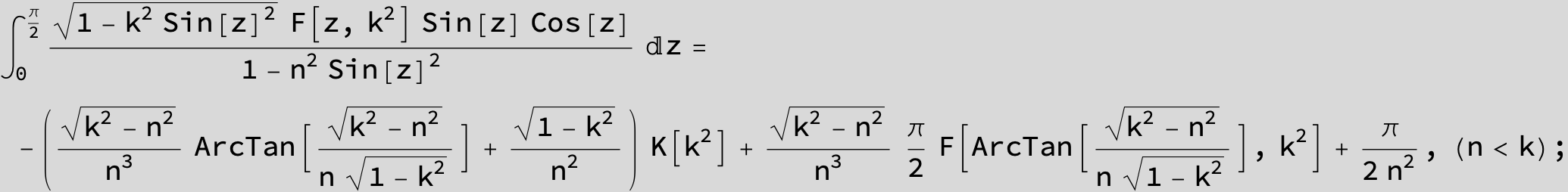
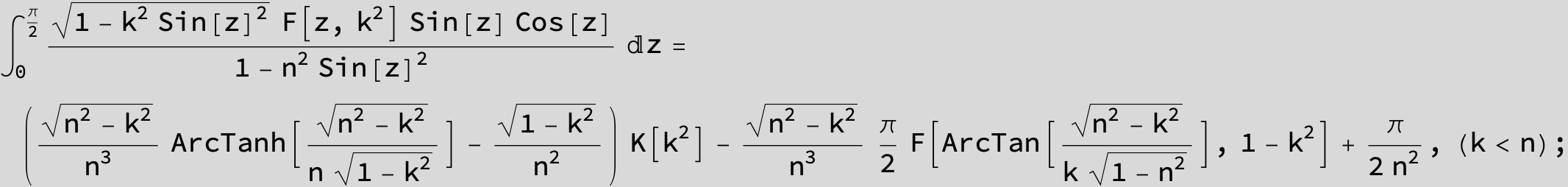
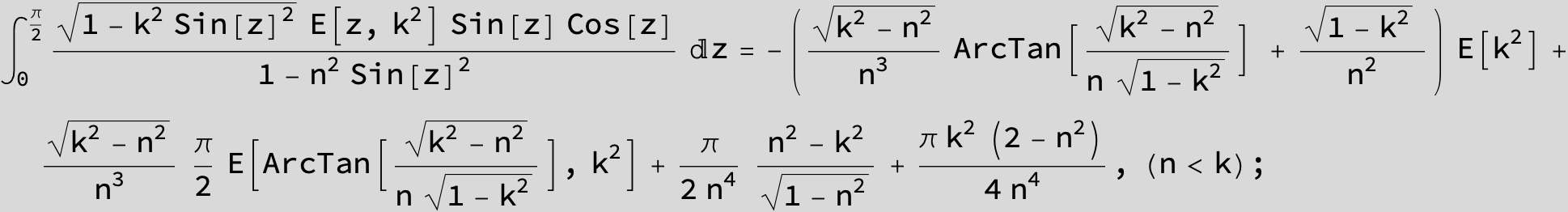
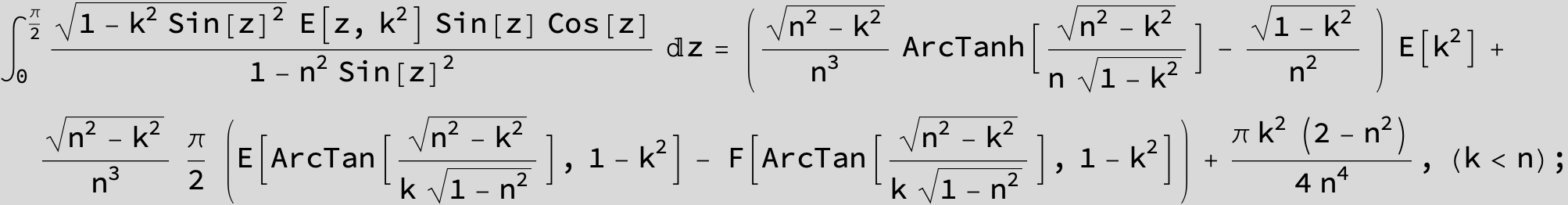
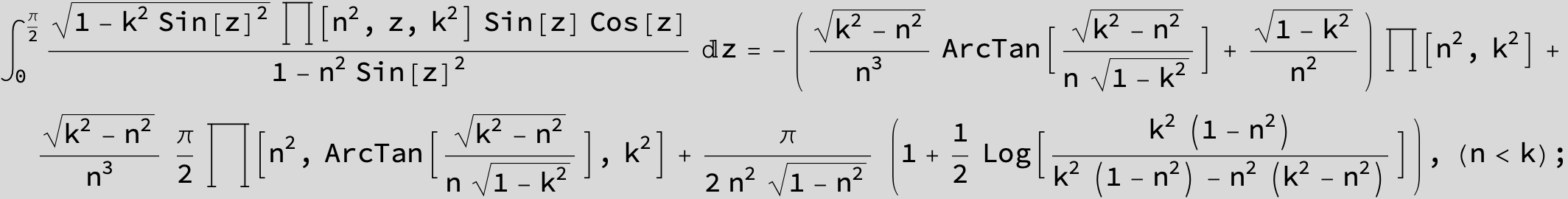
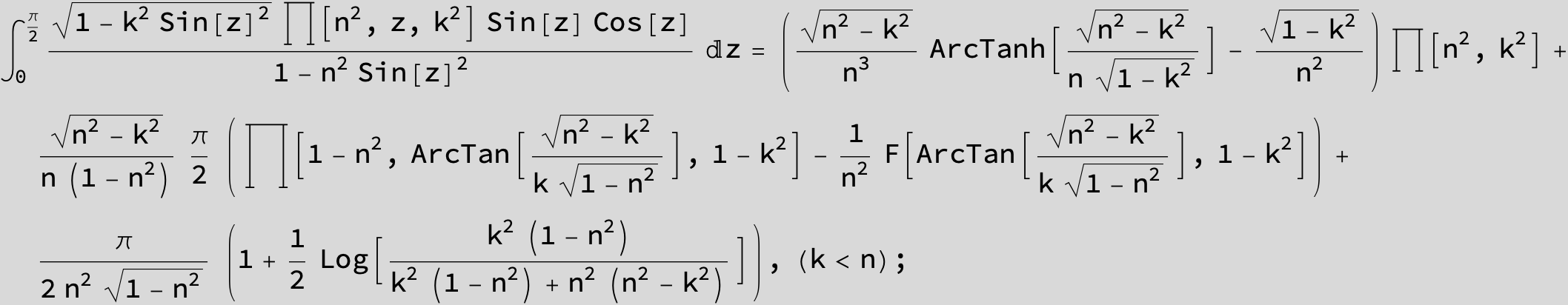
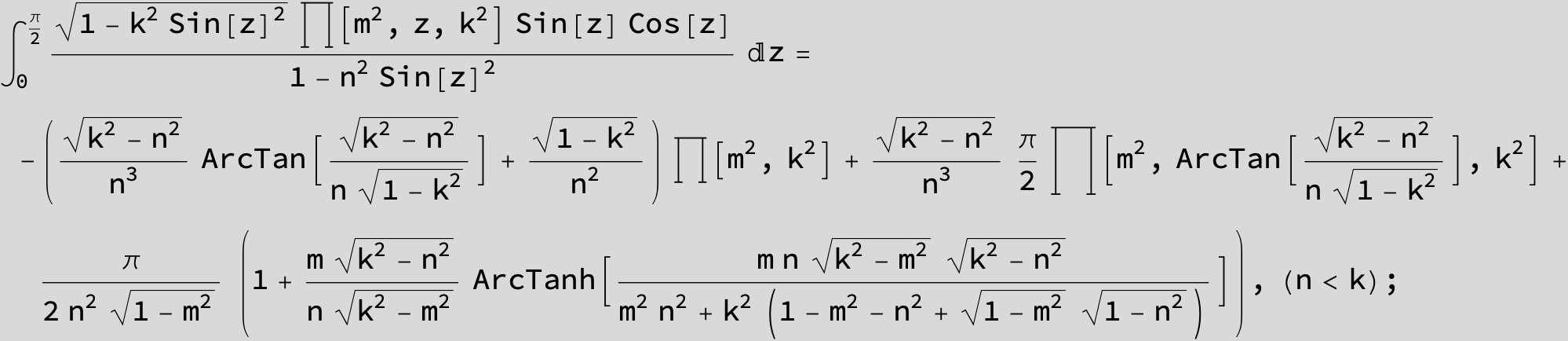
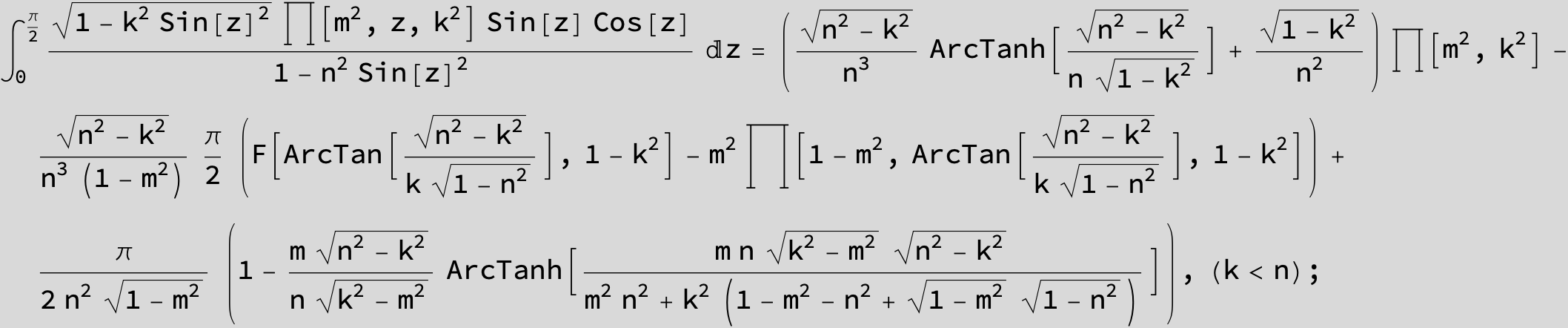
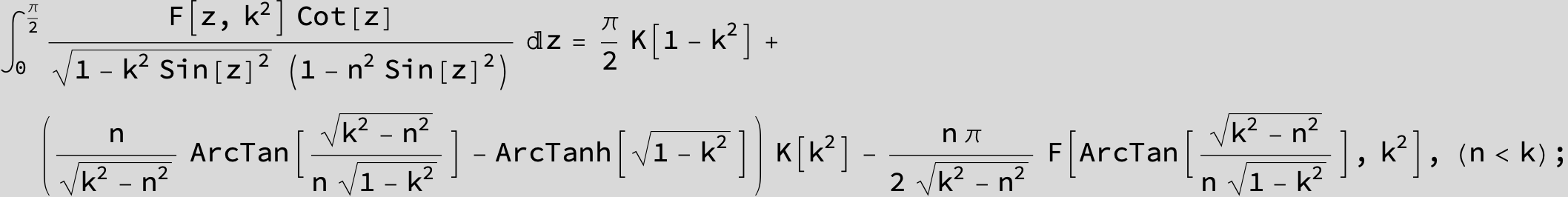
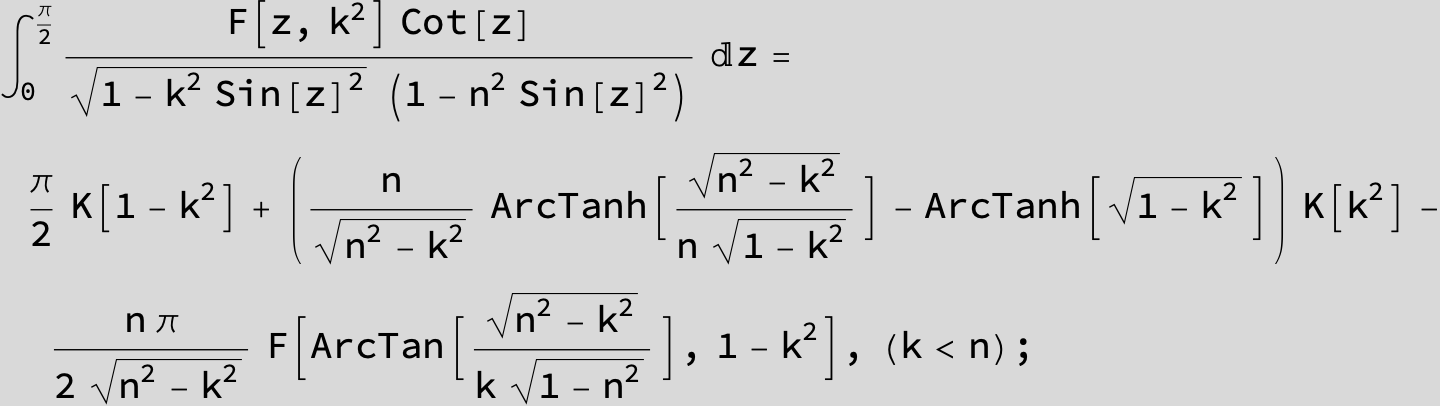


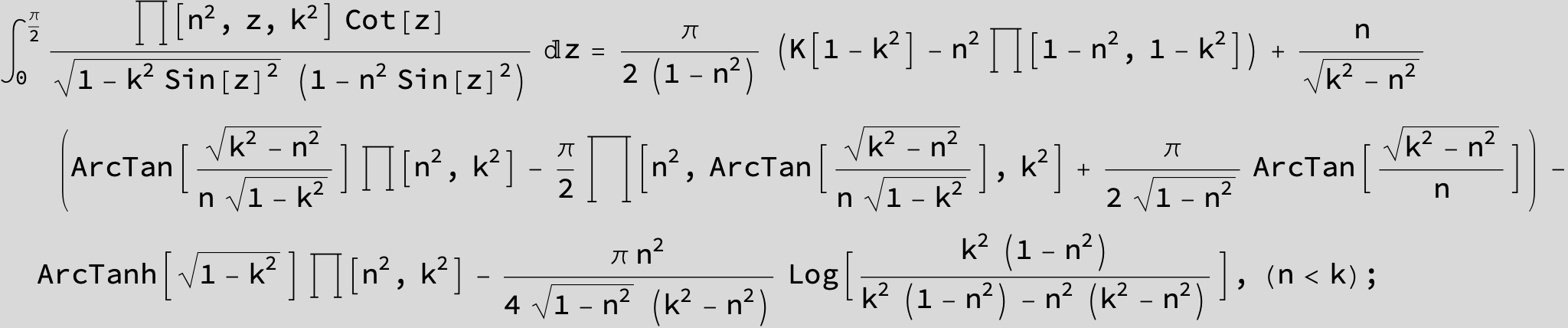
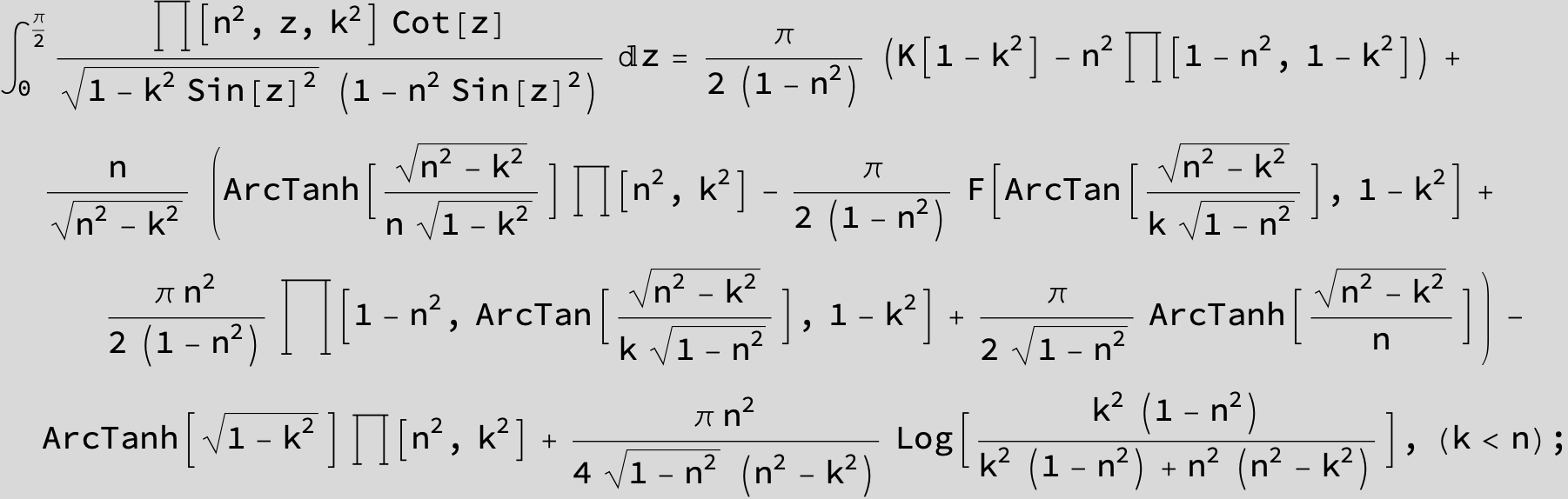
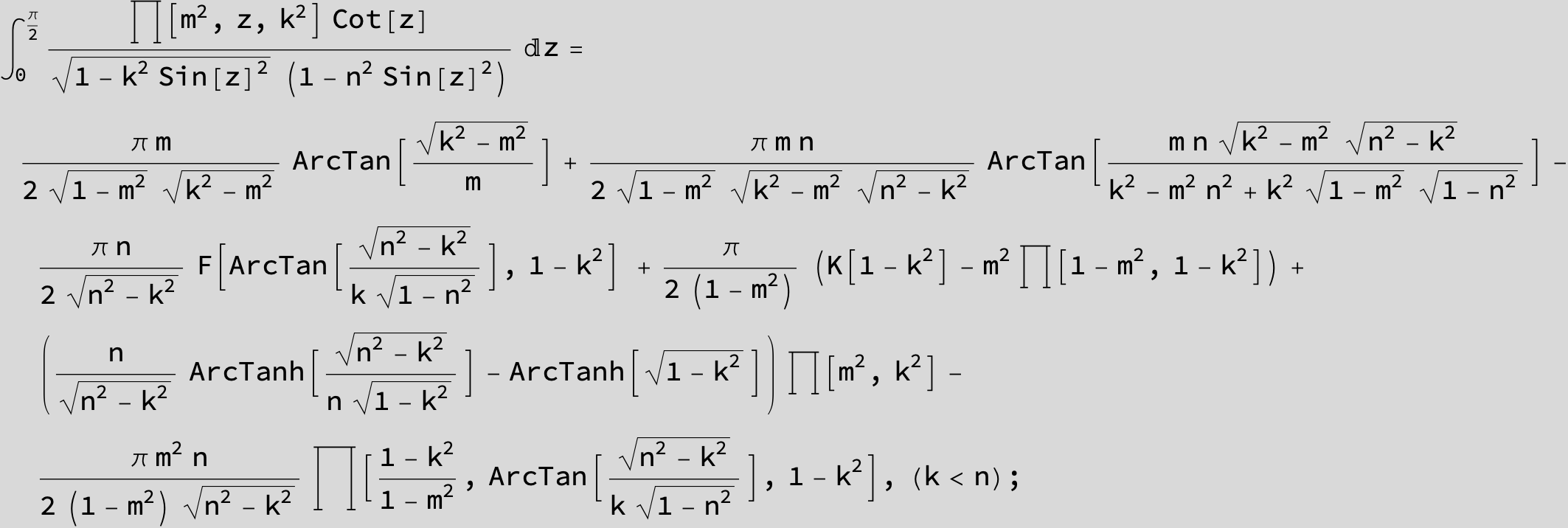
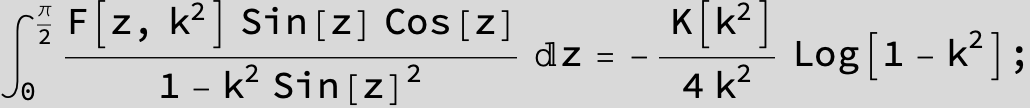
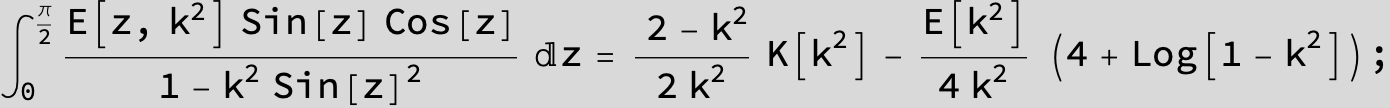
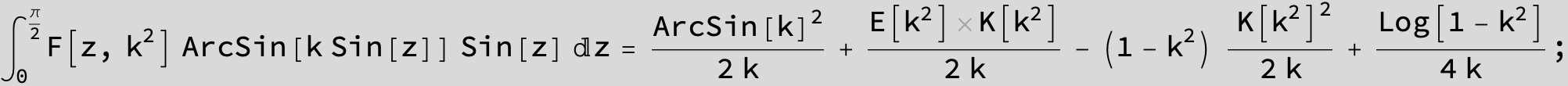
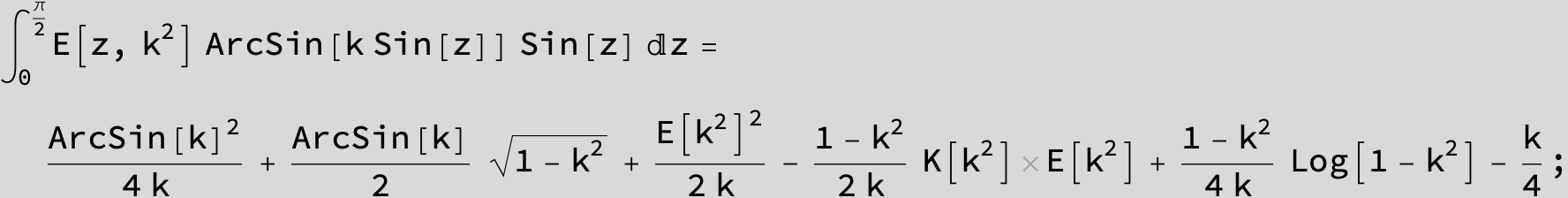
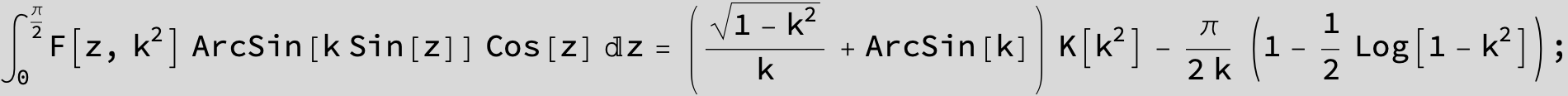
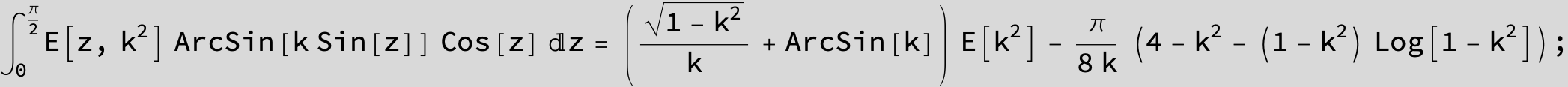
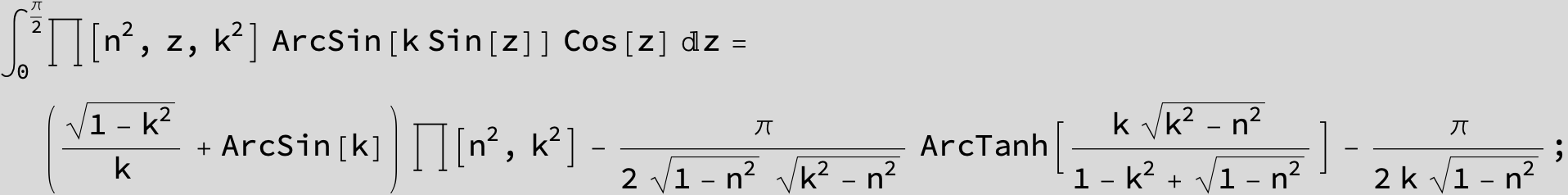
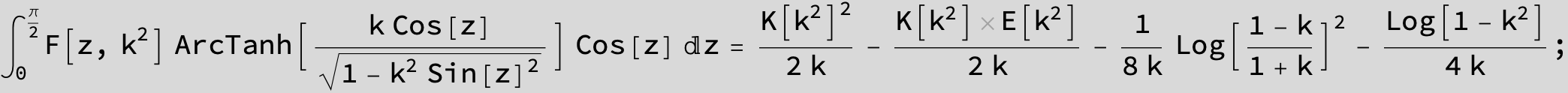
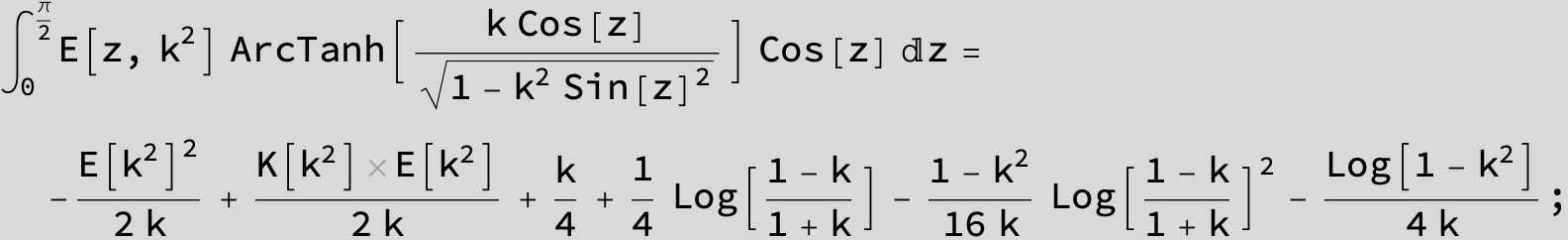
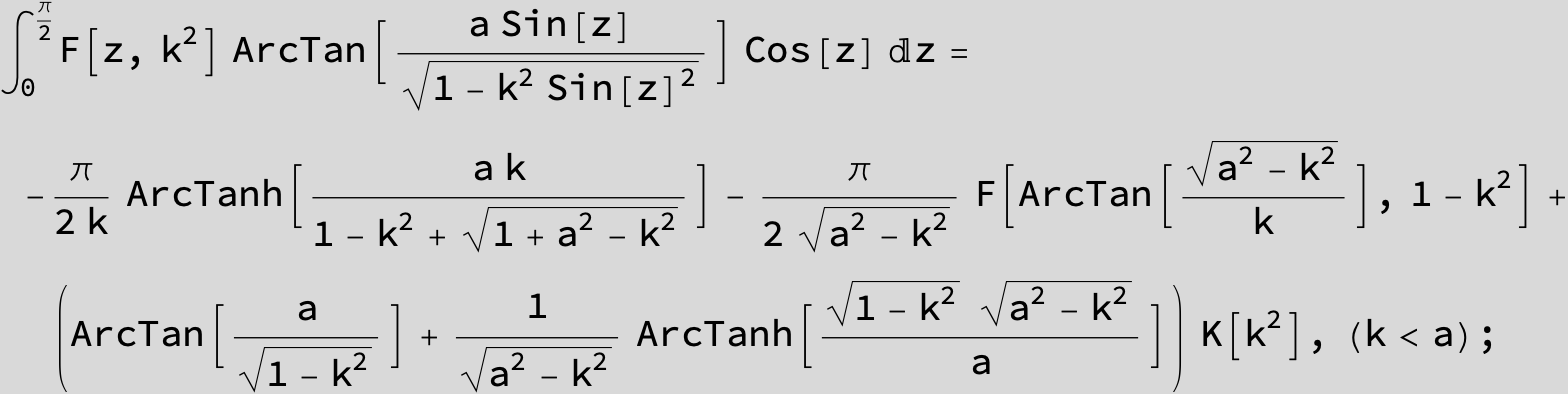




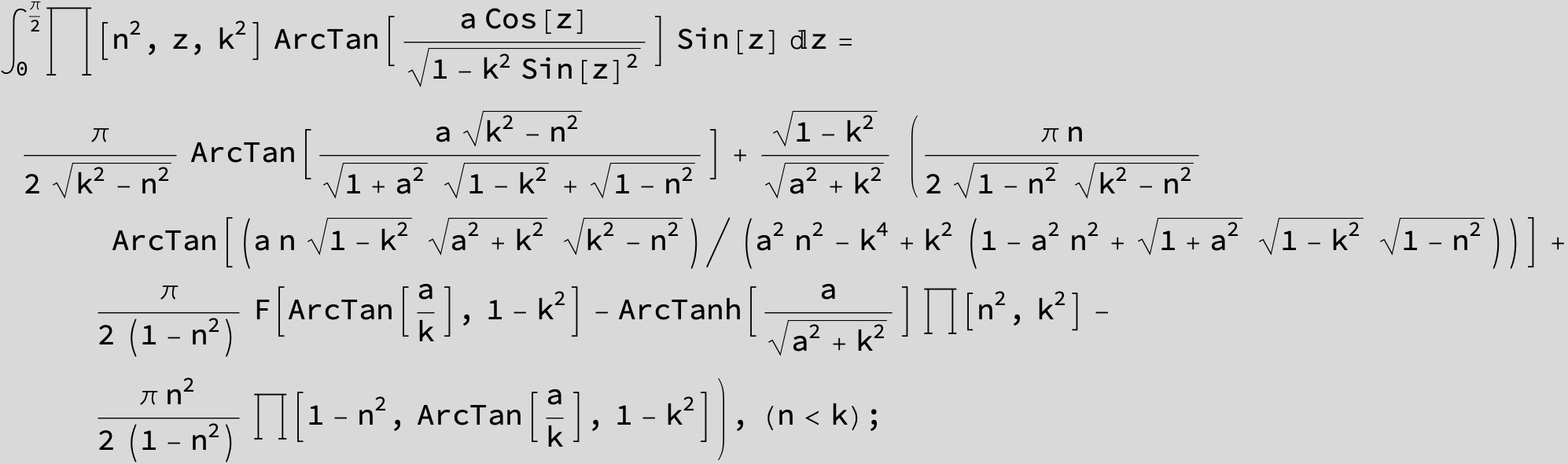
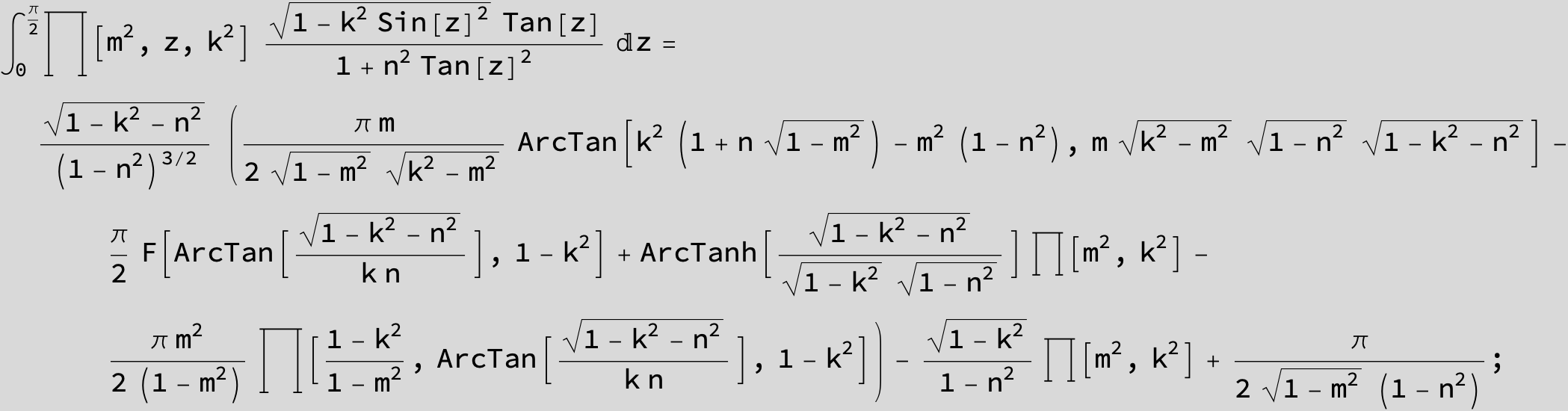
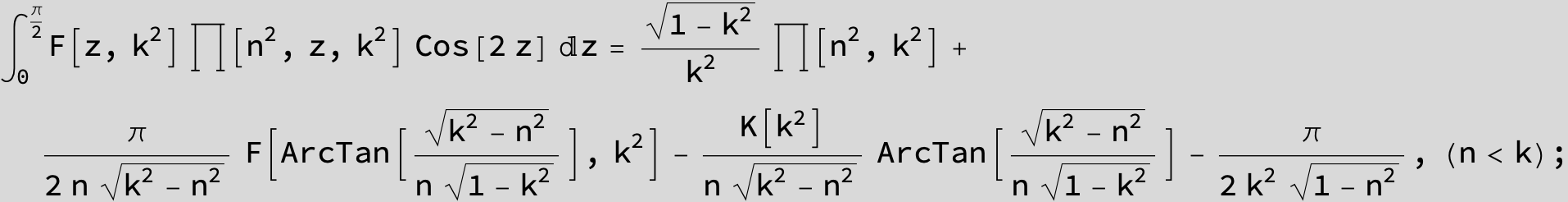
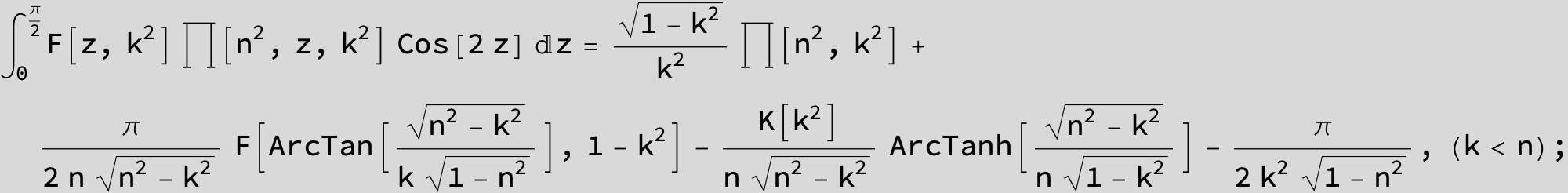
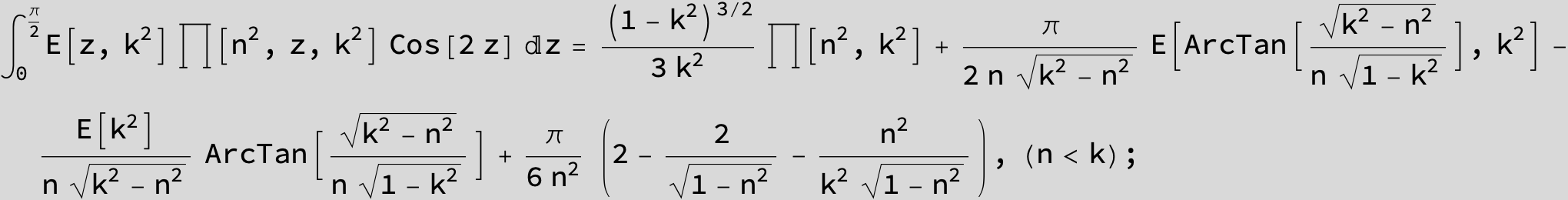
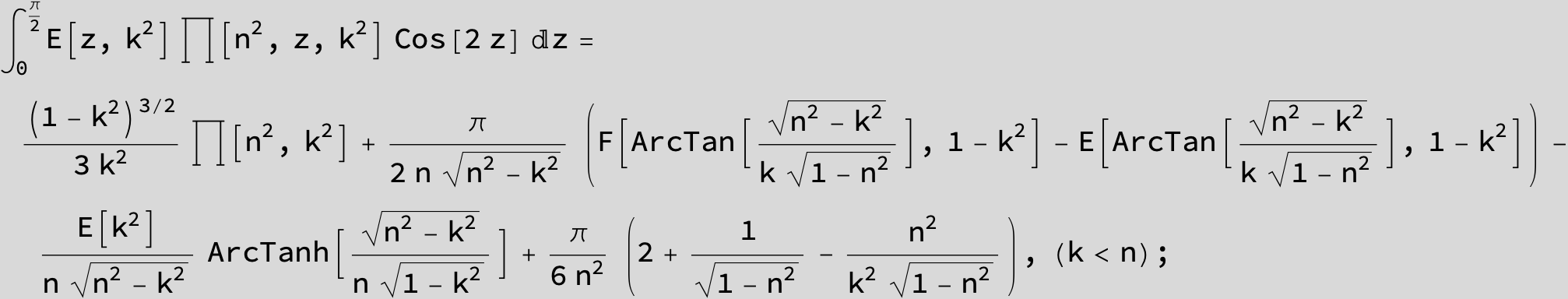
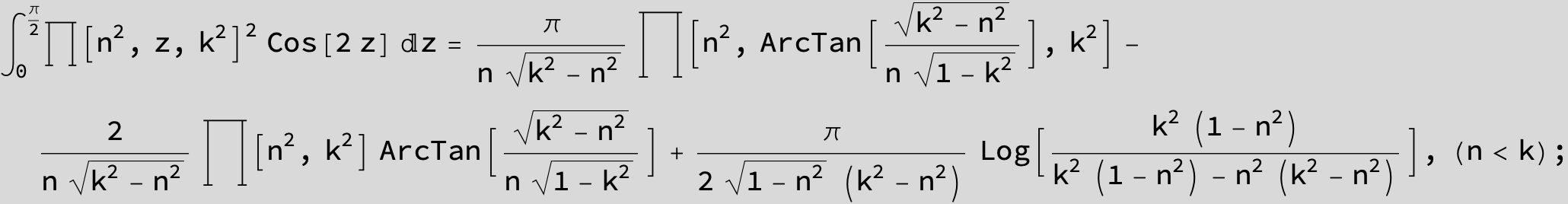
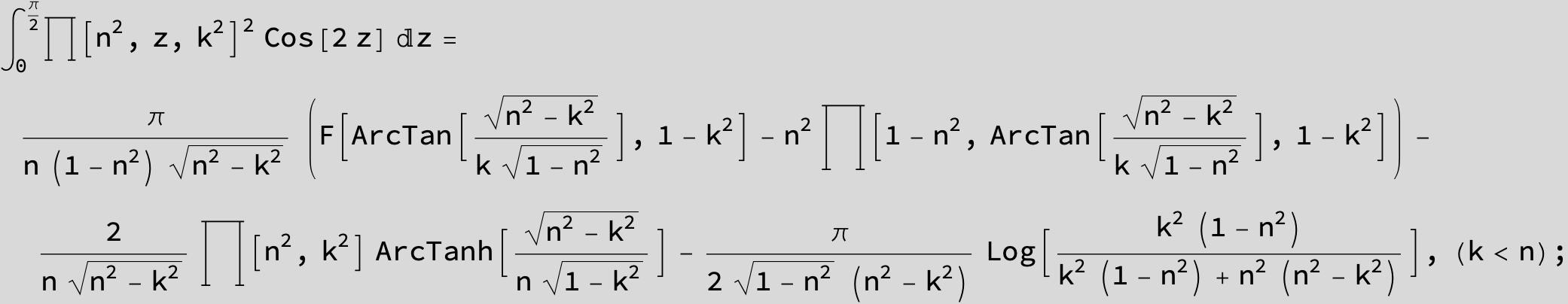
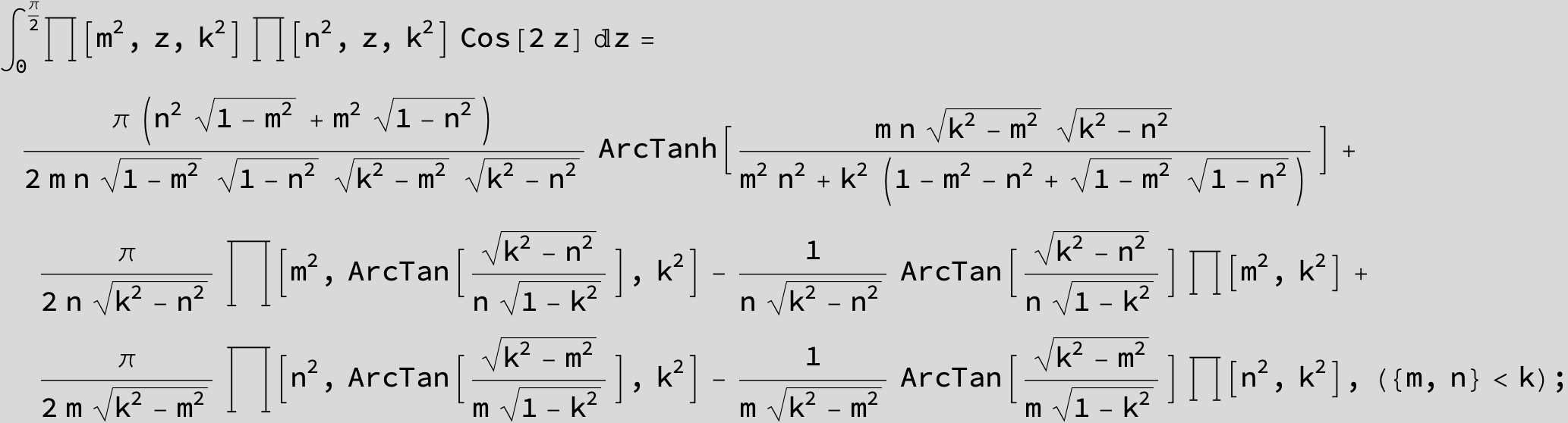
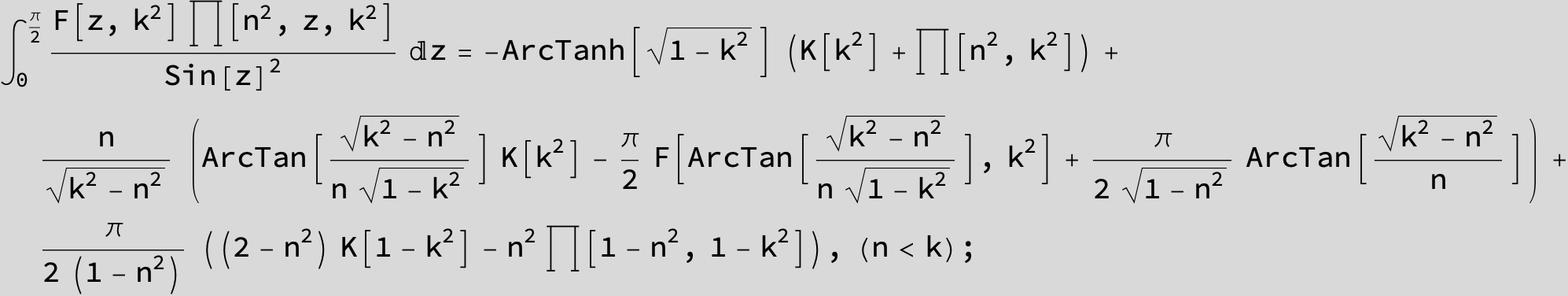
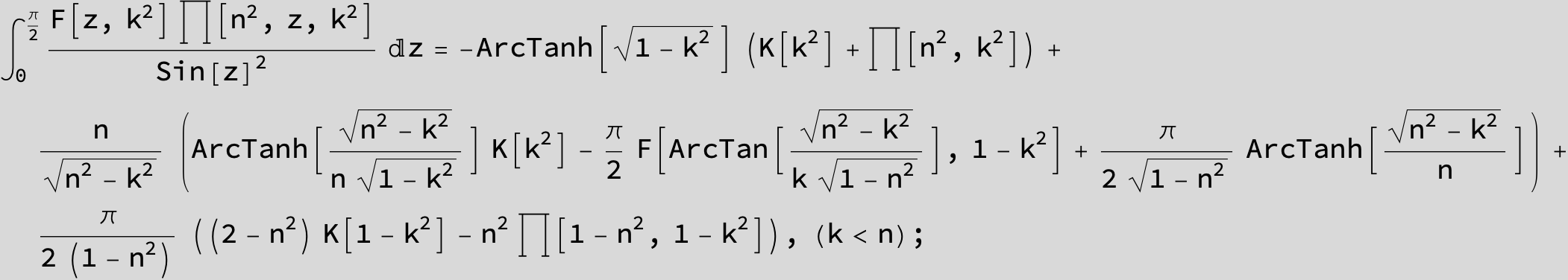
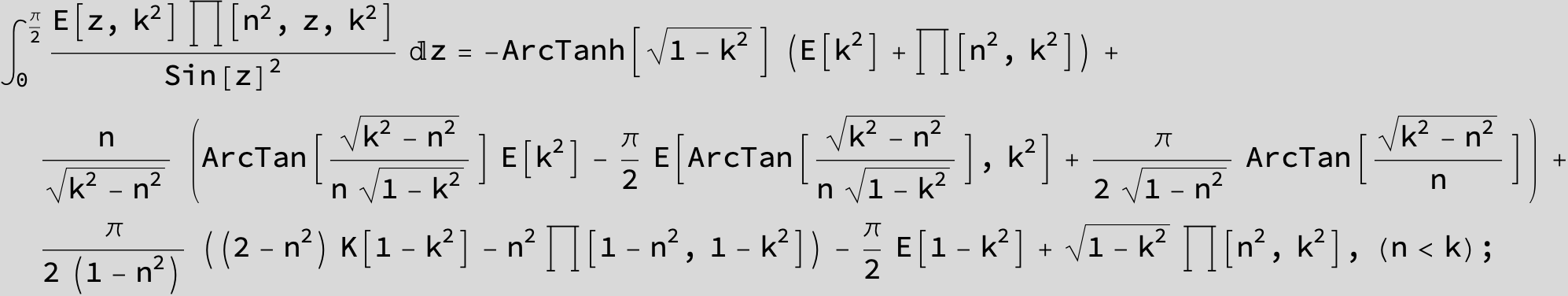
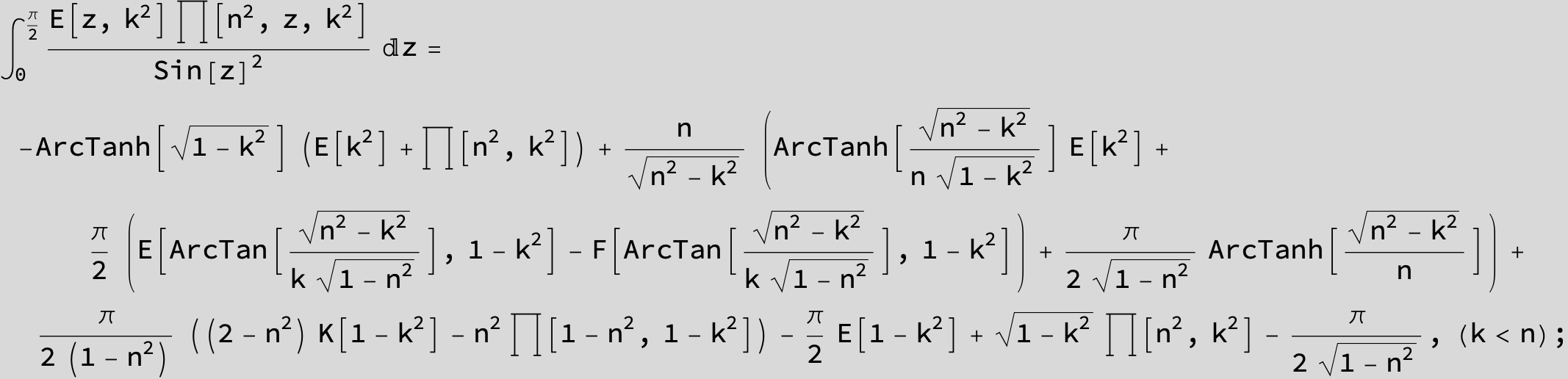
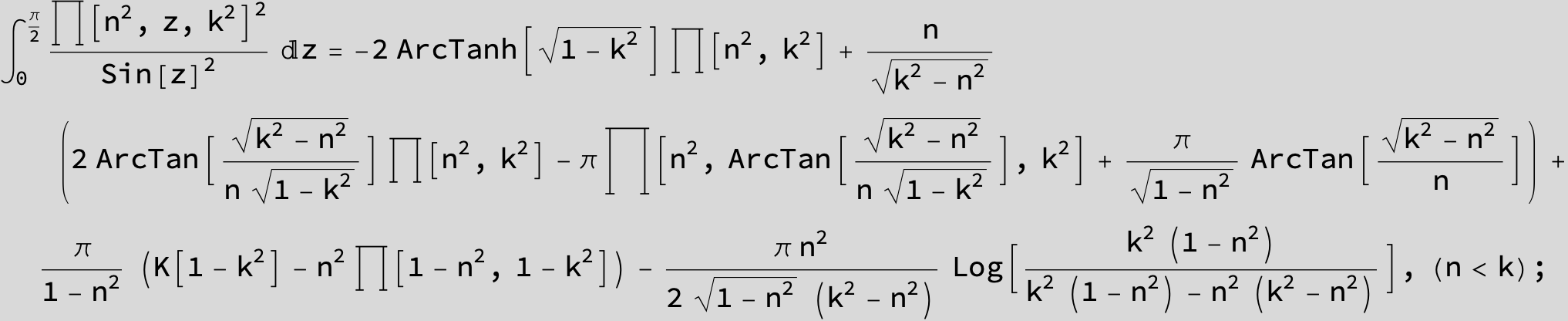
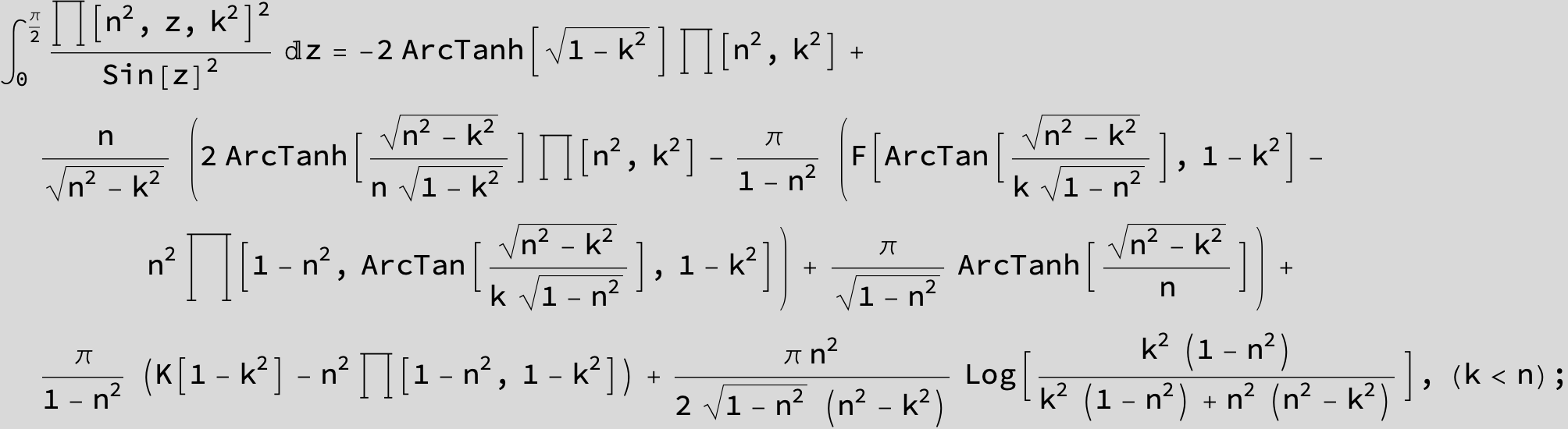
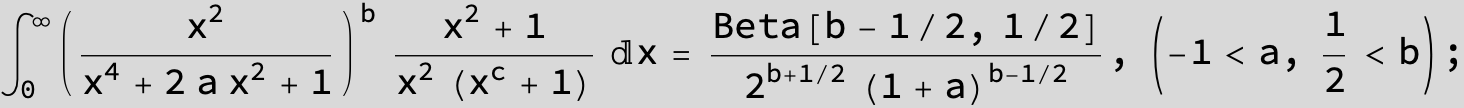
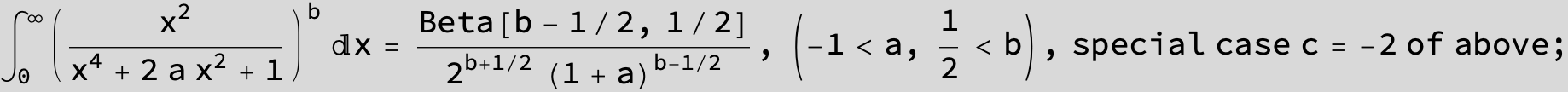


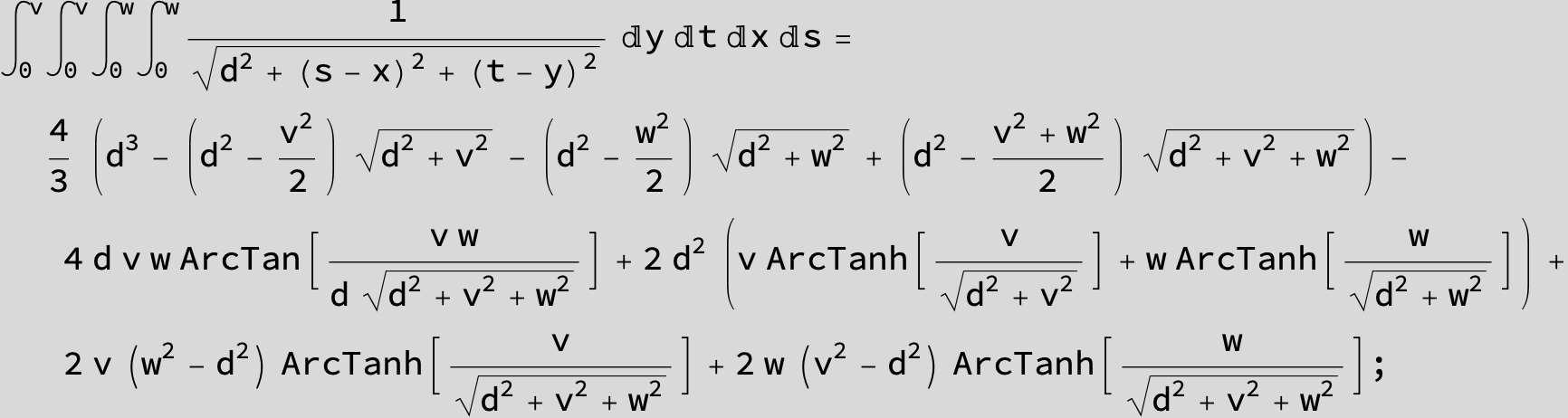
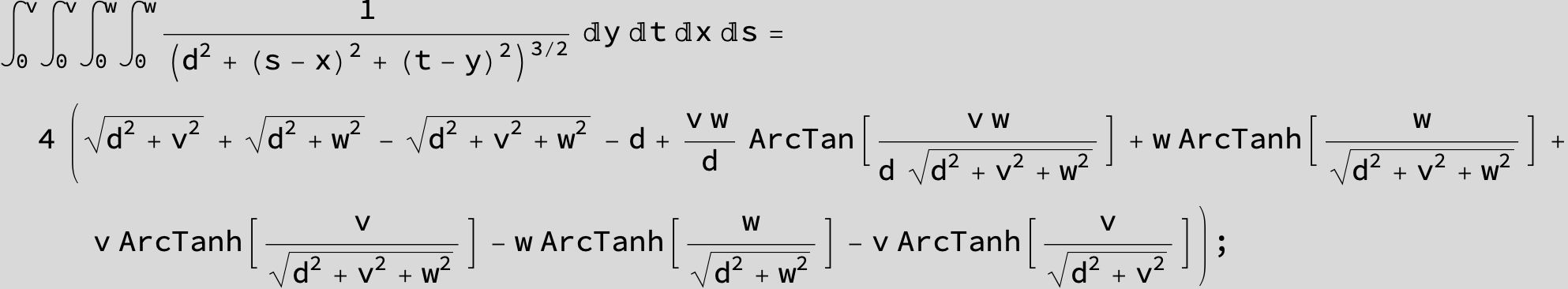

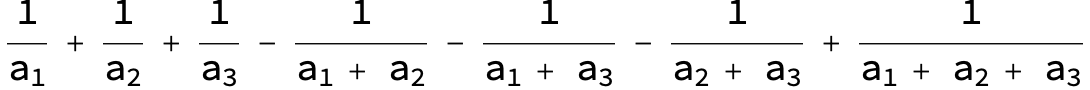

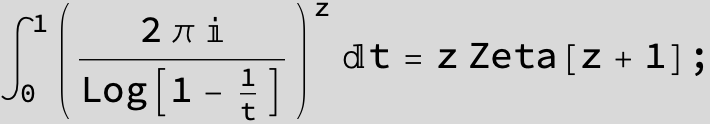
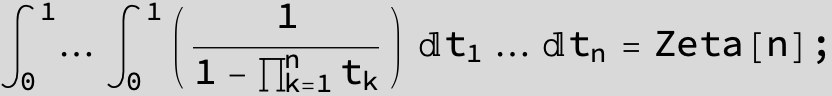




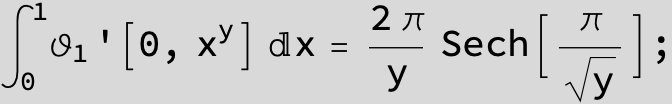
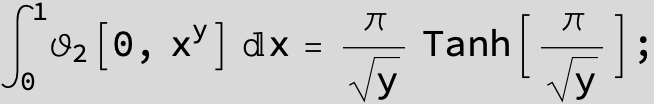
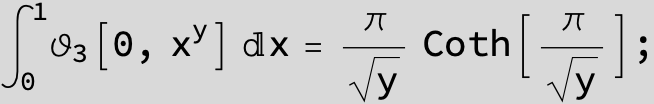
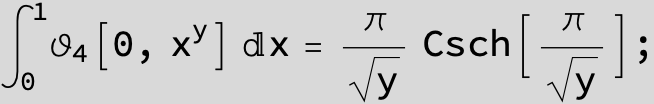


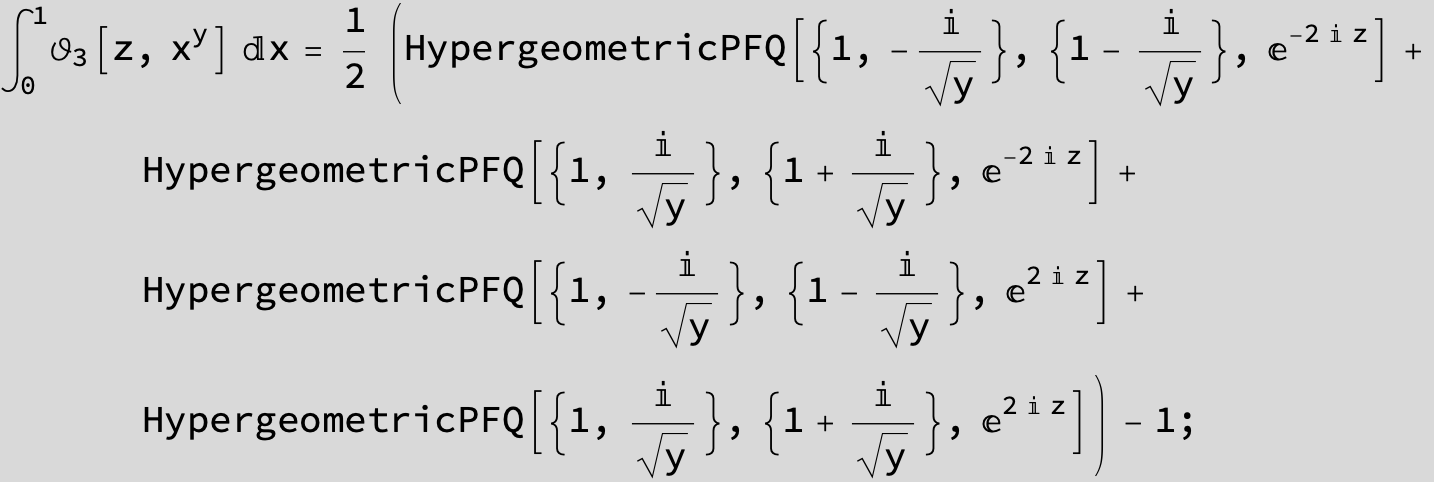

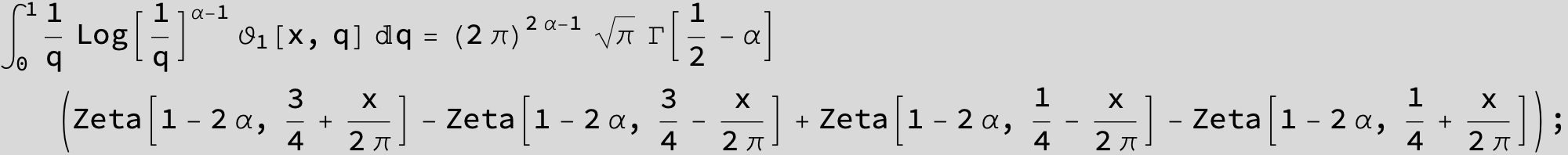
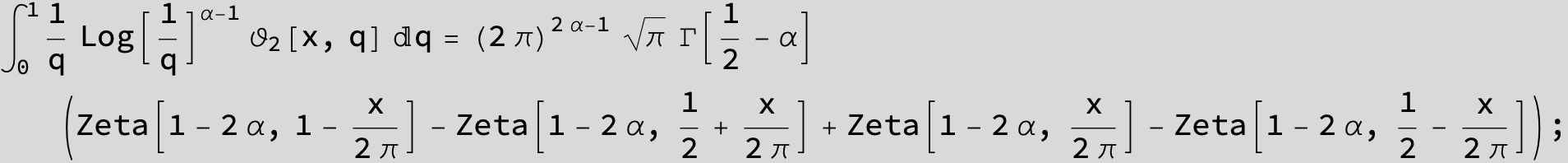
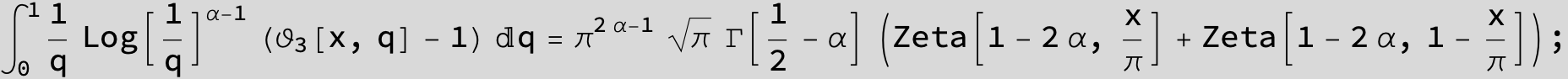
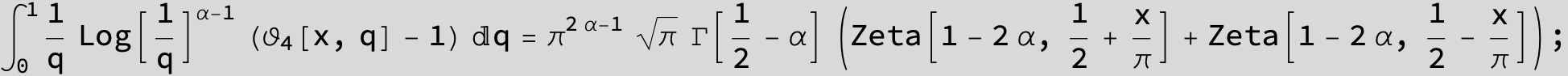
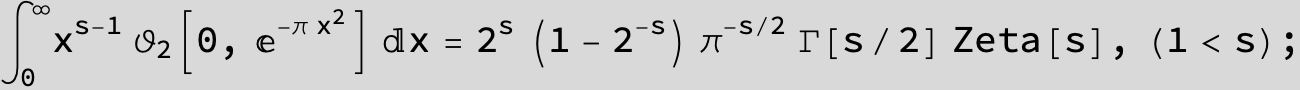
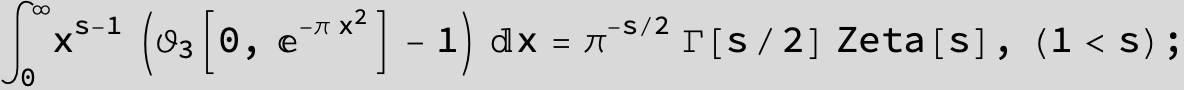
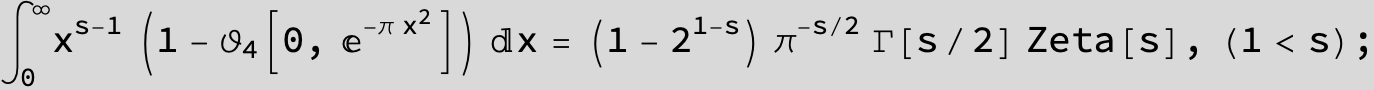
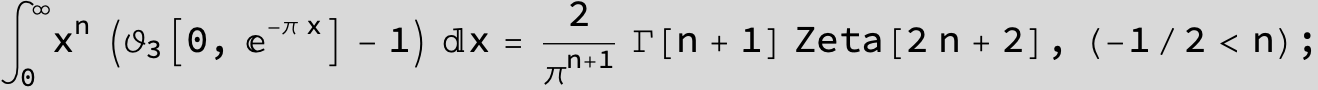

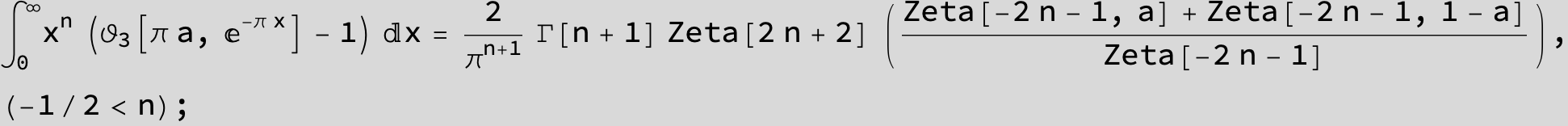

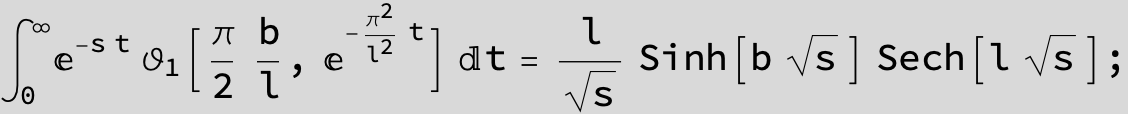
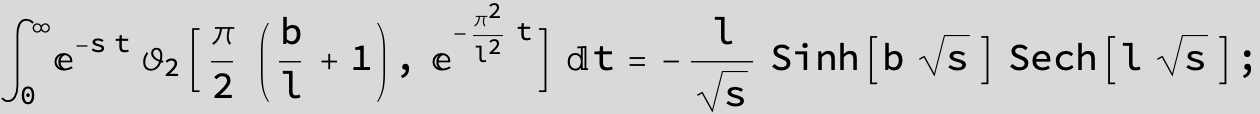
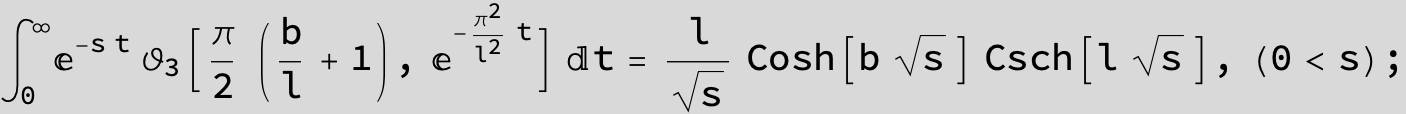
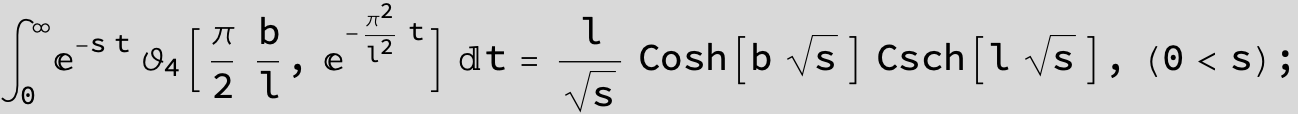
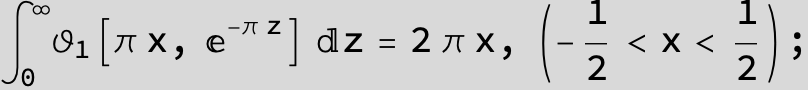
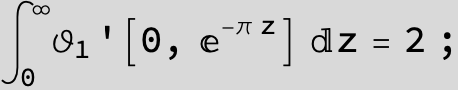
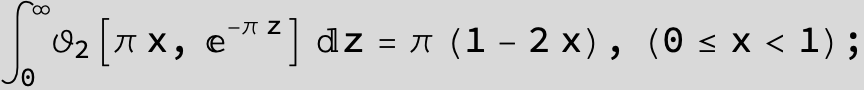
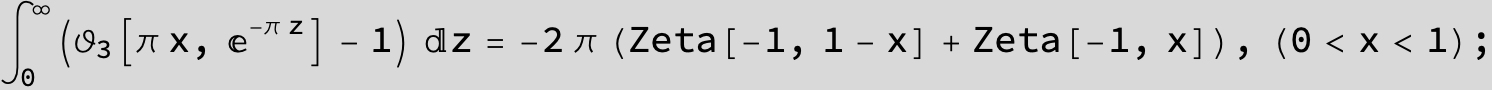
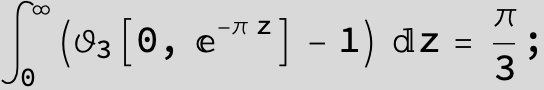
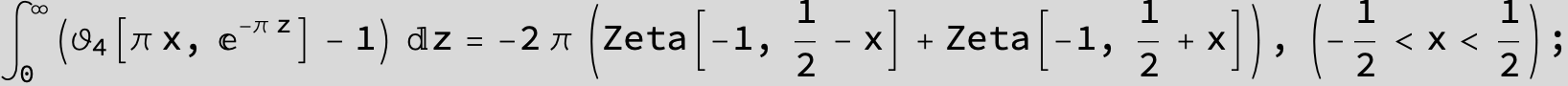
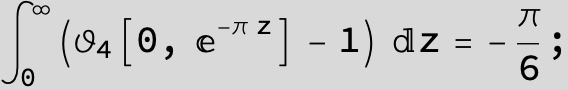
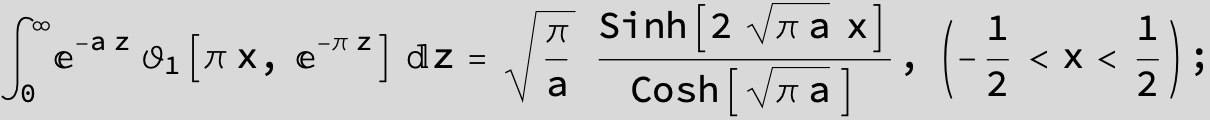


Master formula of Boros and Moll:

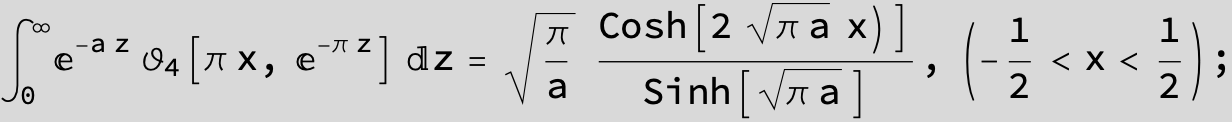
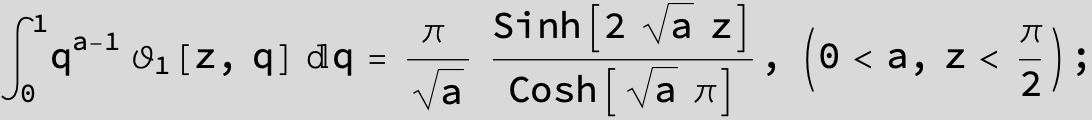

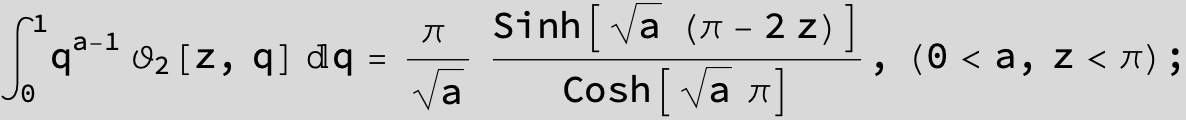
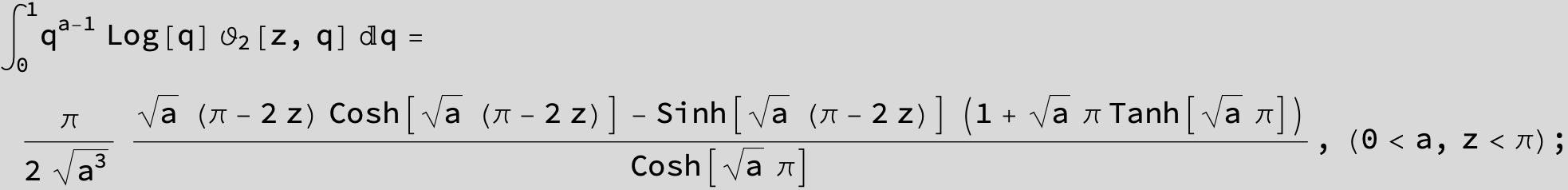
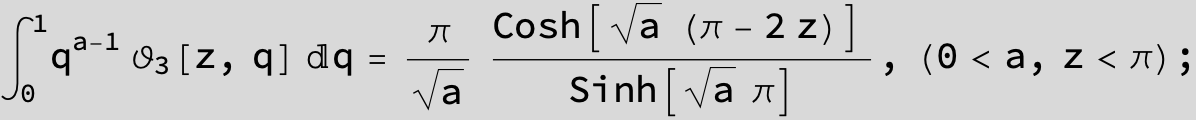
Here the result is a threefold sum shown in Mathematica syntax:
KSubsets[aList, k] is in Package DiscreteMath`Combinatorica` and gives a list of all subsets with k elements of aList .
For n=3 the sum is ![]() .
.
<<DiscreteMath`Combinatorica`
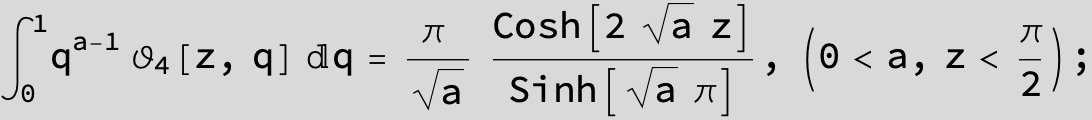

![]()

![]()
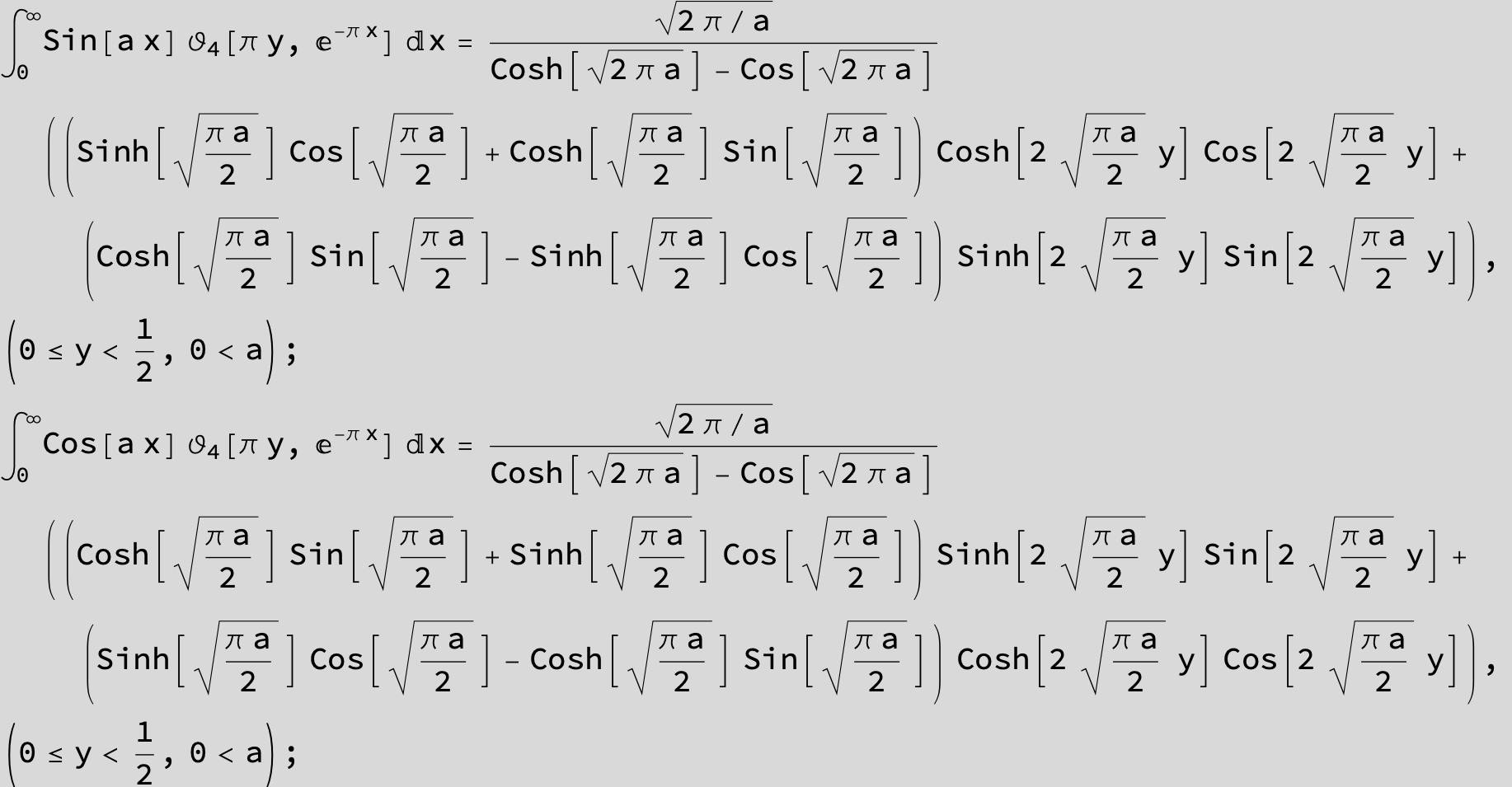

![]()
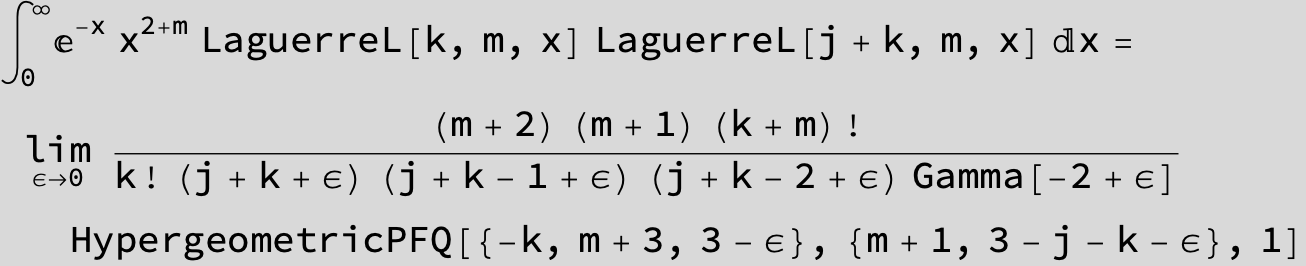



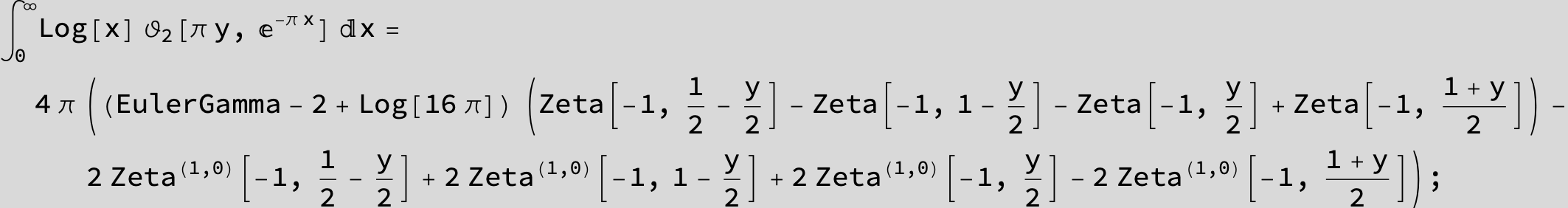


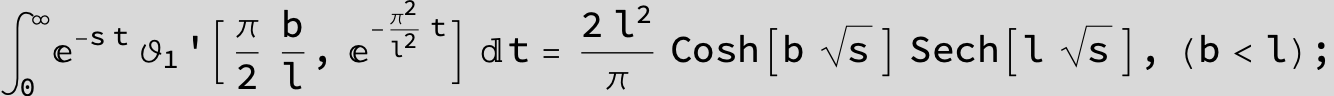
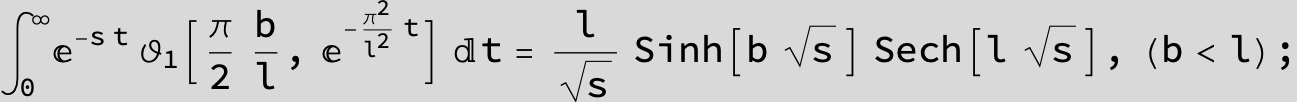
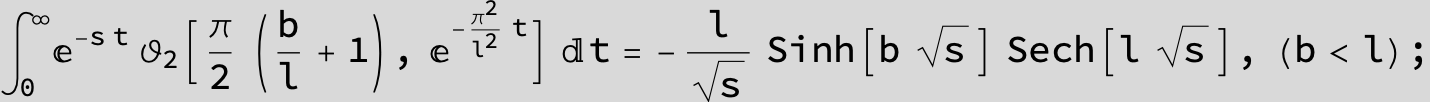

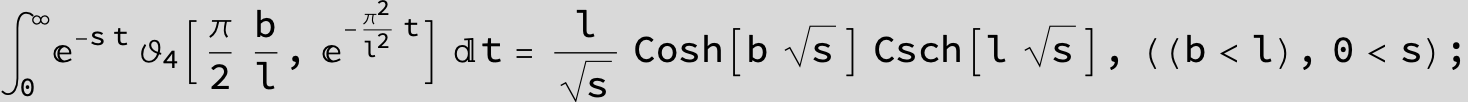
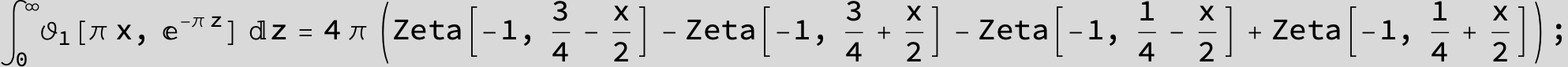
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
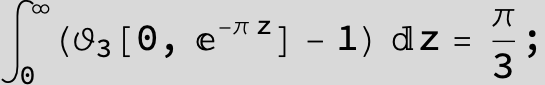
![]()
![]()
![]()
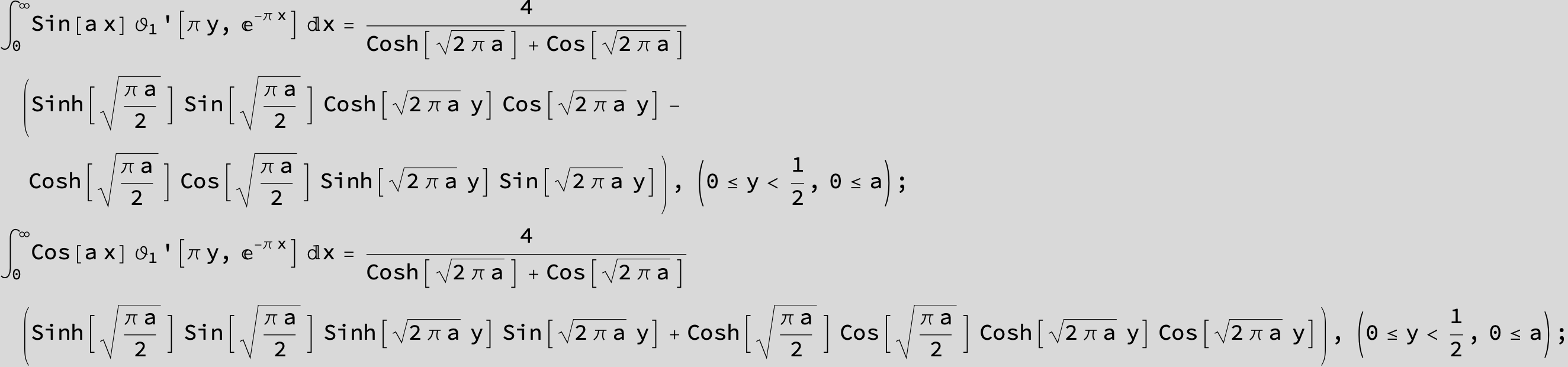
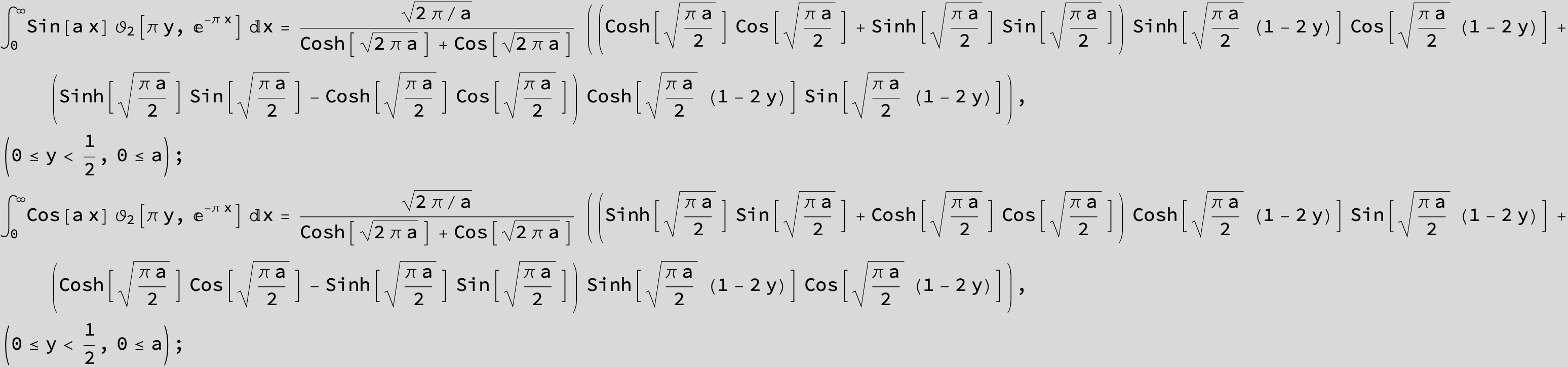
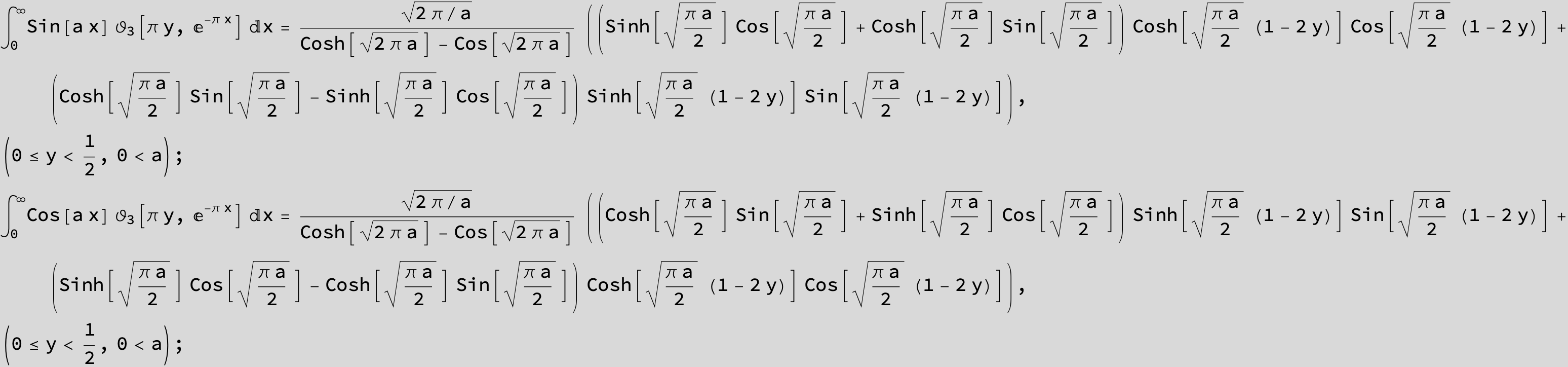

![]()
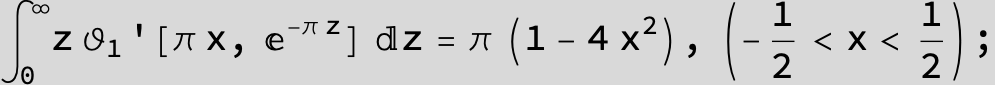
![]()
![]()

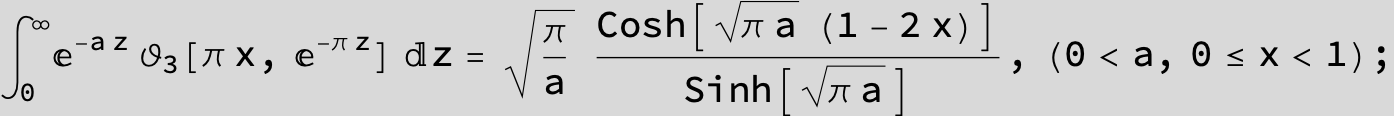

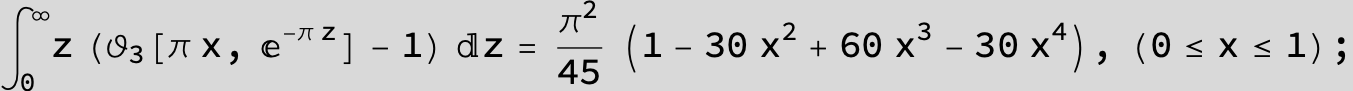
![]()
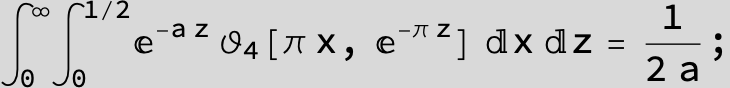
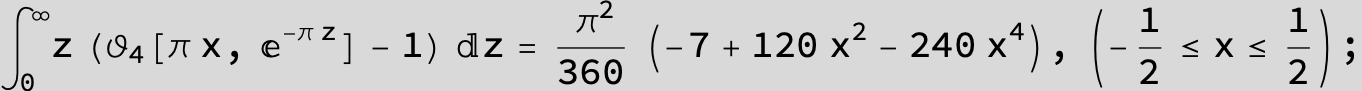
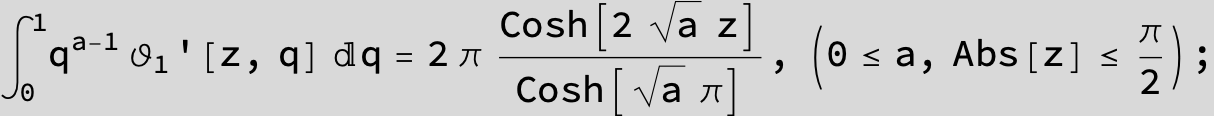
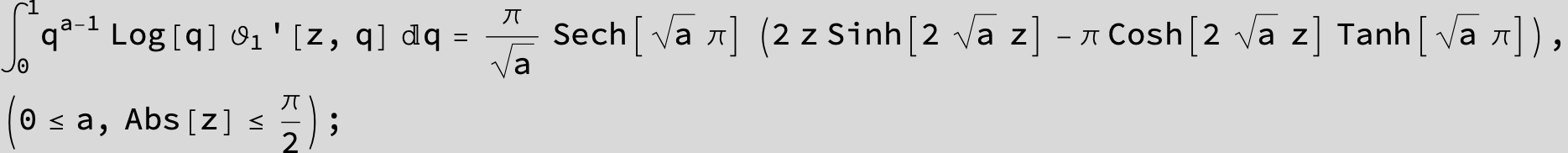
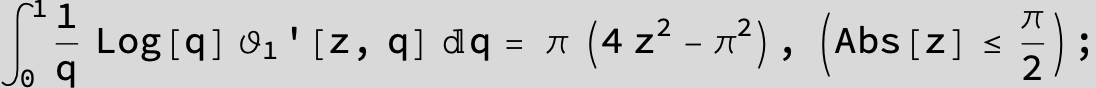
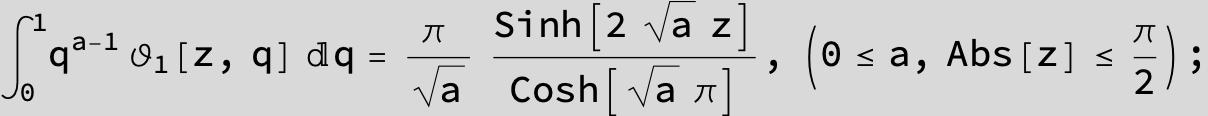
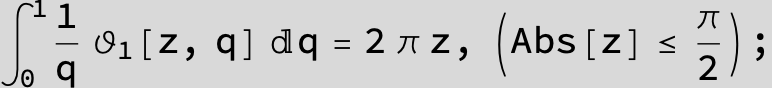
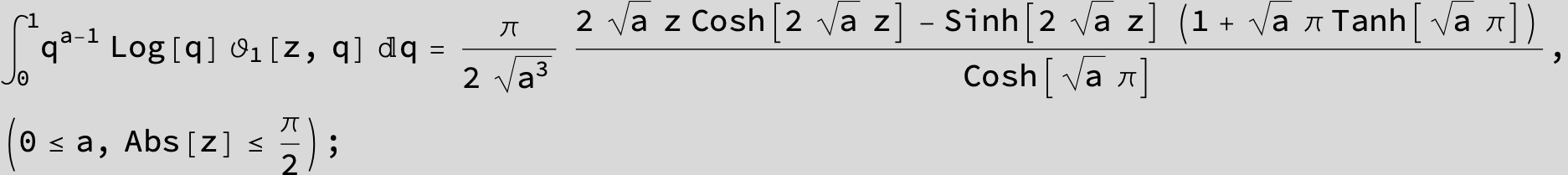
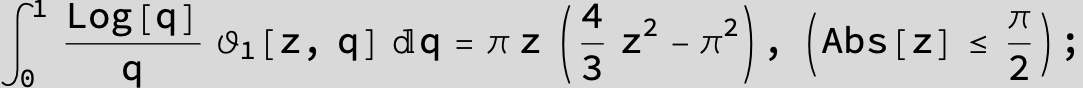
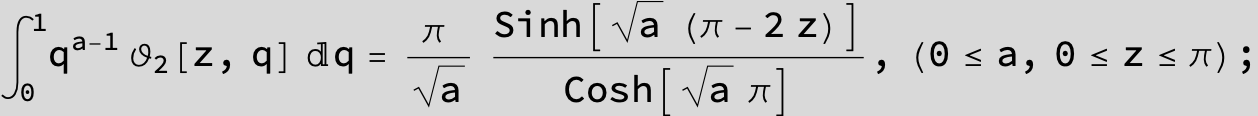
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
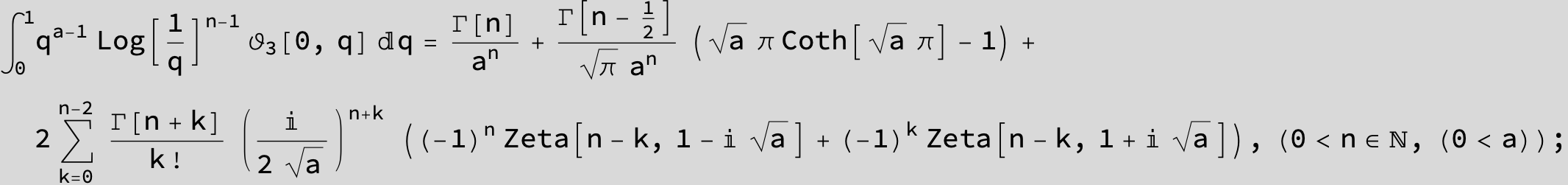
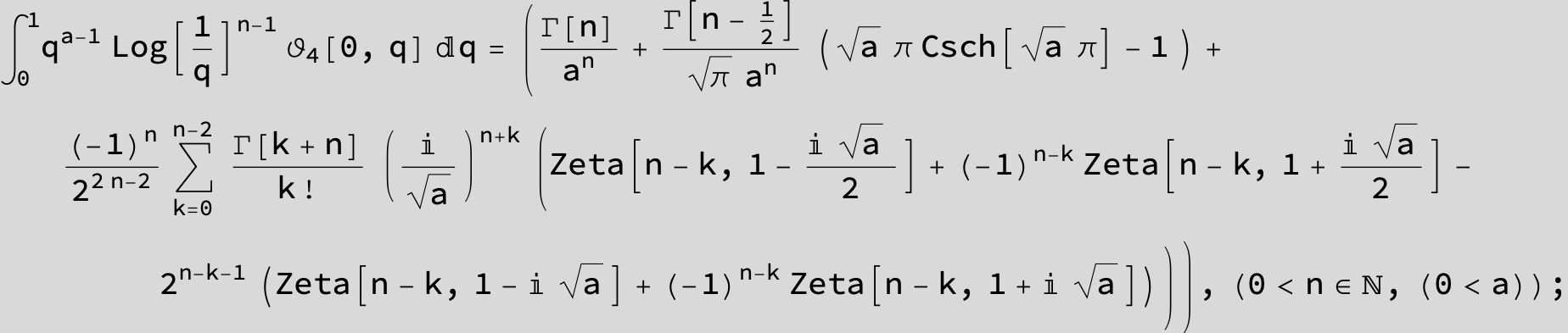
![]()
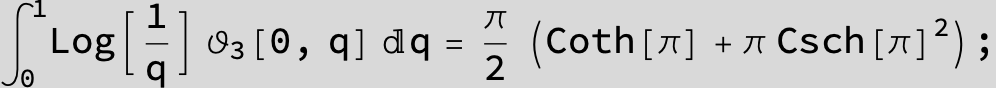
![]()
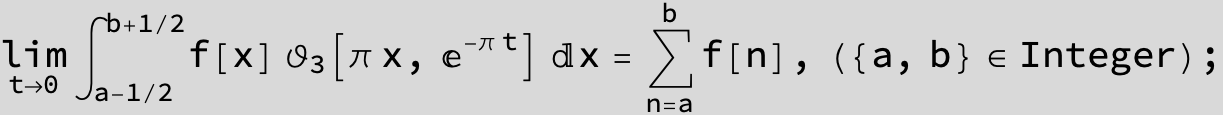
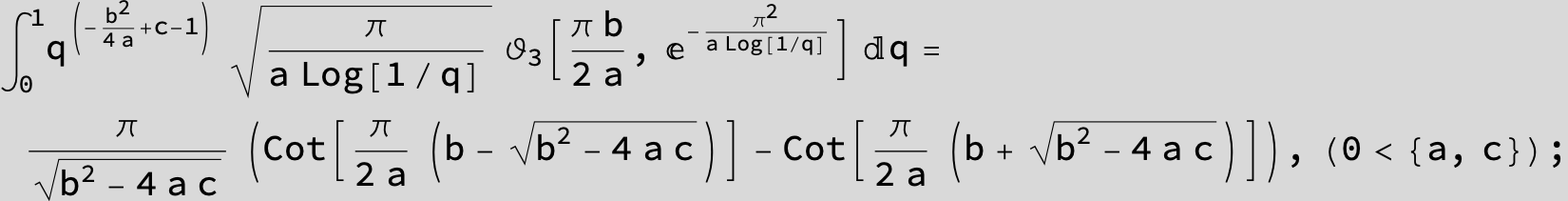
![]()
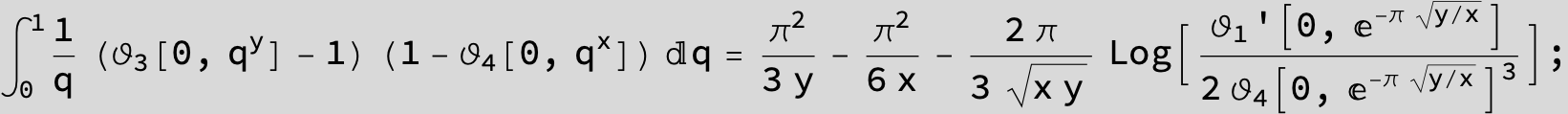
![]()
![]()
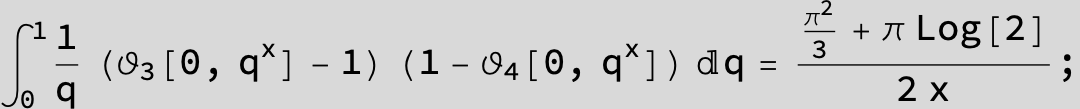
![]()
![]()
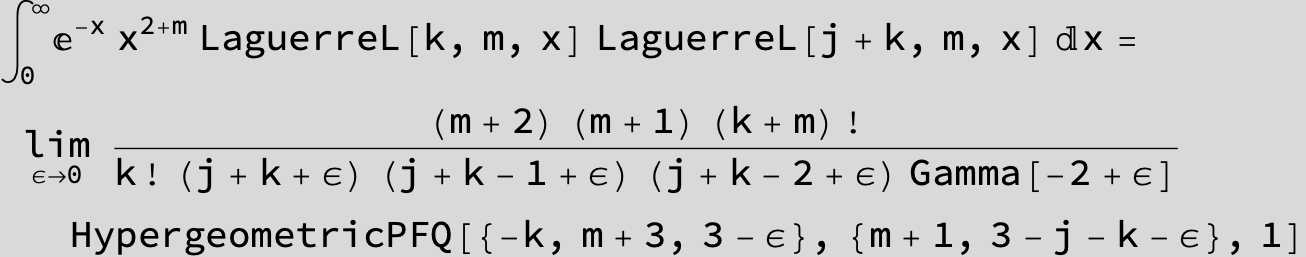

![]()
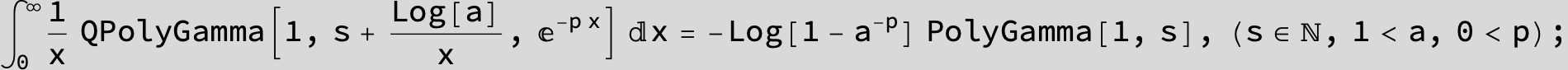
![]()

![]()

![]()

![]()


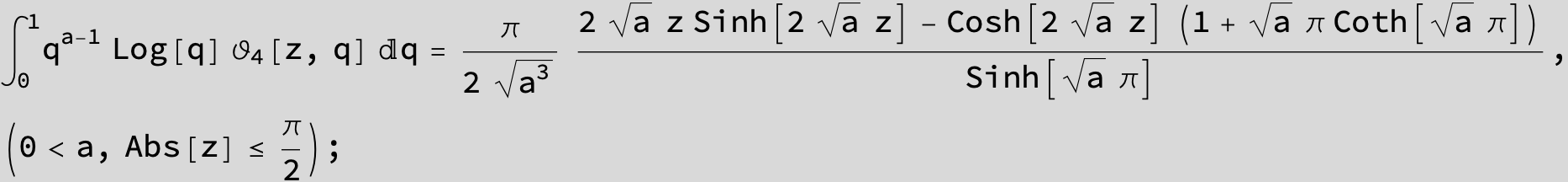

![]()



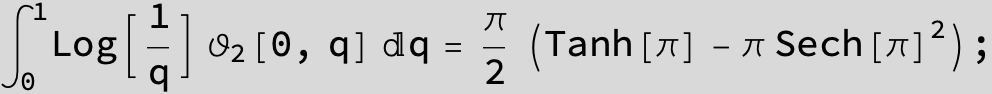
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
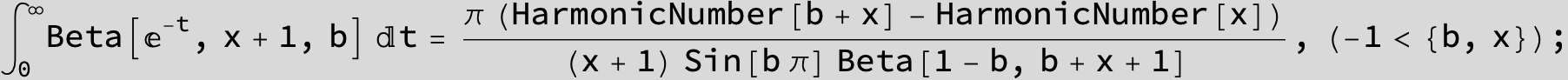

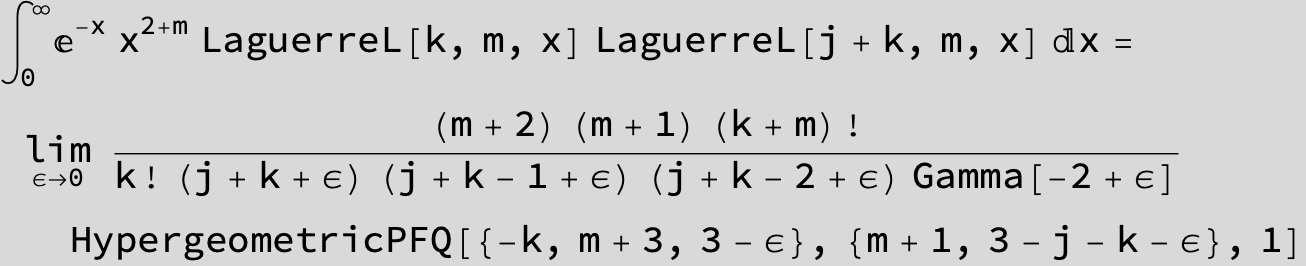


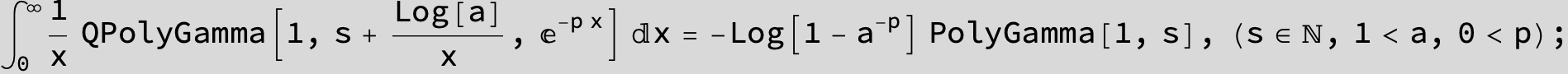
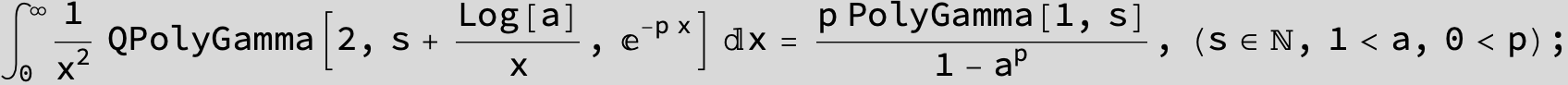
![]()

use Γ[1 - t] Γ[t] = π Csc[π t]

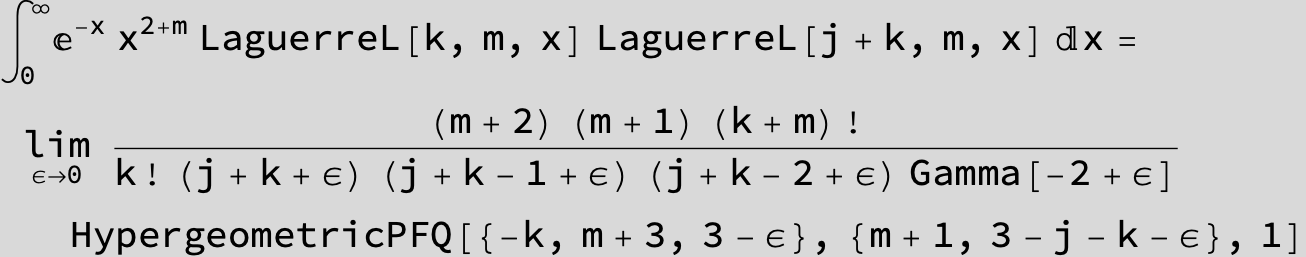
![]()
![]()
![]()